In recent years, long-term weather forecasting models have garnered significant attention due to their profound impact on various sectors, ranging from agriculture to emergency management. These models represent a culmination of extensive research and technological advancements in meteorology, aiming to predict weather patterns over extended periods. The ability to foresee atmospheric conditions months in advance provides a strategic advantage in planning and decision-making processes across multiple domains. As such, this article endeavors to elucidate the complex nature and pivotal importance of long-term weather forecasting models. The following sections will delve into the intricacies of these models, their methodologies, and the implications of their predictions.
Read Now : Reducing Latency In Api Data Handling
The Science Behind Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models
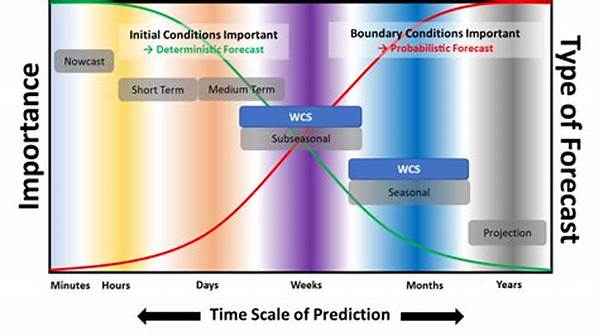
Long-term weather forecasting models are sophisticated systems designed to simulate and predict weather patterns over an extended timeframe, often ranging from weeks to several months. These models rely on an intricate blend of data from various sources, including satellite observations, ocean temperatures, and atmospheric pressures. By assimilating this data through complex algorithms, the models can project future climatic conditions. Typically, they employ statistical, dynamical, or hybrid approaches, each with its strengths and limitations. Statistical models utilize historical weather data to establish patterns and trends, while dynamical models incorporate physics-based equations to simulate atmospheric processes. Hybrid models often combine these methodologies to enhance predictive accuracy. The ultimate goal of long-term weather forecasting models is to provide reliable forecasts that can be used for strategic planning, helping mitigate the impacts of adverse weather phenomena.
Key Components of Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models
1. Data Collection and Analysis: Long-term weather forecasting models rely on comprehensive data collection, including satellite imagery, surface observations, and oceanic readings.
2. Algorithm Integration: These models integrate advanced algorithms to process vast datasets, ensuring the generation of accurate long-term predictions.
3. Model Calibration: Continuous calibration of the models is essential to account for new data and enhance the reliability of forecasts.
4. Predictive Dynamics: Meteorologists use the models to simulate complex atmospheric dynamics, crucial for predicting future weather patterns.
5. Risk Assessment: Long-term weather forecasting models play a critical role in assessing potential climate-related risks and formulating mitigation strategies.
Advantages and Limitations of Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models
Despite their advanced capabilities, long-term weather forecasting models are not without limitations. Their predictive power is contingent upon the quality and quantity of input data, which can sometimes be limited by technological constraints or data gaps. Furthermore, while these models can identify overarching weather trends, they may struggle to predict specific events, such as localized storms or sudden climatic shifts. Nevertheless, the advantages of long-term forecasting models are substantial. They enable governments and organizations to prepare for seasonal weather changes, optimize resource allocation, and develop comprehensive disaster management plans. By providing a broader understanding of future weather trends, these models contribute significantly to economic planning and environmental conservation efforts. Long-term weather forecasting models are indispensable tools in the modern world, balancing statistical and dynamical approaches to offer insights into future climatic conditions.
Read Now : Improved Experimental Design Principles
Enhancing Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models with Technology
Advancements in technology have greatly contributed to refining long-term weather forecasting models. Sophisticated satellite arrays and ground-based sensors have amplified data collection capabilities, providing high-resolution inputs essential for accurate long-term forecasts. Machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies further augment these models by identifying subtle patterns within complex datasets. These innovations have introduced a new era of predictive accuracy and reliability. Many experts assert that the continued integration of cutting-edge technologies will bolster the efficacy of long-term weather forecasting models, ensuring better preparedness for climate fluctuations and extreme weather events.
Implications and Applications of Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models
Long-term weather forecasting models have far-reaching implications for various sectors. In agriculture, these models help farmers anticipate weather conditions, thereby optimizing planting and harvesting schedules. Energy companies leverage forecasts to manage resources effectively, especially concerning renewable energy sources dependent on weather conditions. In public health, predictions aid in anticipating and mitigating weather-related health risks. Moreover, tourism industries utilize long-term forecasts for operational planning and guest management. These models also play a pivotal role in climate research, assisting scientists in understanding broader climatological shifts and trends. Ultimately, long-term weather forecasting models are vital instruments for sustainable development and disaster risk reduction, consistently providing critical insights that inform policy and strategic direction across multiple industries.
Future Directions for Long-Term Weather Forecasting Models
As the quest for better predictive capabilities continues, research and development in the field of long-term weather forecasting models show promising directions. Future innovations are expected to focus on enhancing data assimilation techniques and developing more robust computational algorithms. Collaborative efforts between national and international meteorological institutions will aim to refine models continuously and promote information sharing globally. One key area of interest is the improved prediction of extreme weather events, which remain challenging to forecast accurately. Additionally, incorporating socio-economic factors into models may offer more holistic forecasts, addressing not only climatic but also societal impacts. Continued investment in long-term weather forecasting models is crucial for addressing the ever-evolving challenges posed by climate change, ensuring a resilient future for communities worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, long-term weather forecasting models are vital tools for understanding and predicting future weather conditions. They facilitate informed decision-making in various sectors, from agriculture to public health. Advancements in technology and global collaboration continue to enhance these models’ precision and reliability. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, long-term weather forecasting models provide a framework for anticipating weather trends, thereby reducing vulnerabilities and optimizing resource use. The commitment to advancing these models will remain pivotal in adapting to a dynamic climate, safeguarding both human and environmental well-being. Through continued research and innovation, long-term weather forecasting models hold the potential to transform the way societies interact with the natural world, promoting resilience and sustainability in an ever-changing global landscape.