In the increasingly interconnected world of information systems, the imperative for seamless communication and integration among diverse applications and services cannot be overstated. As enterprises embrace digital transformation, the need for a robust infrastructure that can facilitate the integration of disparate elements becomes ever more critical. This is where scalable integration middleware architecture comes into play, serving as the backbone of modern IT strategies. This architecture provides a framework for connecting different systems and enabling interoperability in a scalable and efficient manner. The significance of such an architecture lies in its ability to adapt to the growing demands of an evolving technological landscape while maintaining performance and reliability.
Read Now : University Library Digital Collections
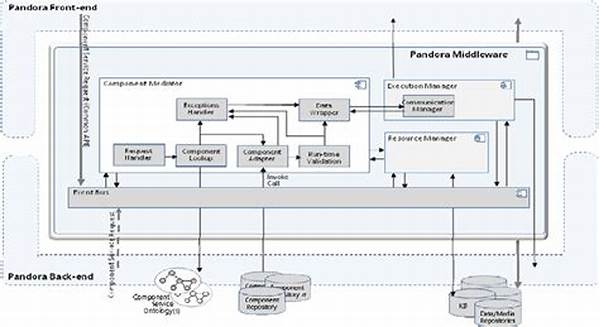
Understanding Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
Scalable integration middleware architecture is designed to manage complex interactions among multiple software applications and services, ensuring seamless data flow and functionality. In enterprise environments, where systems evolve and grow, scalability is paramount. This architecture supports the seamless integration of new applications without compromising existing functionality. By leveraging an adaptable framework, organizations can ensure that their middleware can handle increased loads and complexities. Such middleware solutions typically include various integration patterns and tools that allow for efficient communication between disparate systems, enabling businesses to optimize their operations and processes through enhanced connectivity.
The advantages of adopting scalable integration middleware architecture are manifold. Firstly, it facilitates improved interoperability among diverse systems, enabling organizations to harness the full potential of their technological investments. Secondly, scalability ensures that organizations can meet the increasing demands of data processing and integration without incurring significant additional costs. Finally, such architecture supports enhanced data management and governance, as it centralizes integration processes, thereby simplifying monitoring, maintenance, and compliance activities. In conclusion, scalable integration middleware architecture is a pivotal element in modern enterprise IT strategies, underpinning efforts to achieve operational efficiency and agility.
Components of Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
1. Adaptability: The scalable integration middleware architecture must be adaptable to changes in the technological ecosystem, supporting evolving business requirements seamlessly.
2. Interoperability: This architecture ensures comprehensive interoperability between disparate systems, enabling smooth data exchange and coordinated functionality.
3. Performance Optimization: It is critical for the architecture to maintain optimal performance as the number of integrated components increases, handling expanding workloads efficiently.
4. Security and Compliance: Scalable integration middleware architecture incorporates security protocols and compliance measures to safeguard data integrity across integrated systems.
5. Cost Efficiency: By facilitating scalable integration, the architecture minimizes additional costs associated with expanding IT infrastructures and integrating new applications.
Benefits of Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
One of the principal benefits of scalable integration middleware architecture is its versatility in accommodating a wide array of applications and services while ensuring coherence and interoperability. This architecture’s design inherently supports modularity, making it possible for enterprises to integrate new components smoothly as business needs evolve. This adaptability is critical in today’s fast-paced technological environment, where rapid changes demand flexible and responsive IT solutions.
Moreover, scalable integration middleware architecture plays a pivotal role in future-proofing organizational technology frameworks. By allowing for incremental scaling and integration, businesses can efficiently manage growth and technological advancements without the need for substantial overhauls or replacements. The ability to integrate new applications as technology evolves is essential for maintaining competitiveness and ensuring that organizations remain at the forefront of innovation.
Challenges of Implementing Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
Implementing scalable integration middleware architecture poses several challenges.
1. Complexity Management: The intricate nature of integrating numerous systems can lead to complex configurations, requiring meticulous planning.
2. Resource Allocation: Adequate resource allocation is vital to ensure the effective deployment and maintenance of the middleware architecture.
3. Change Management: As the architecture evolves, managing changes without disrupting existing operations can be a significant challenge.
Read Now : Real-time Event Data Handling
4. Vendor Coordination: Organizations often rely on multiple vendors, necessitating effective coordination to ensure seamless integration across platforms.
5. Performance Monitoring: Continuous performance monitoring is necessary to identify potential bottlenecks and maintain optimal system efficiency.
6. Data Governance: Ensuring robust data governance and compliance with security standards is paramount to safeguard sensitive information.
7. Customization Needs: Tailoring the middleware to meet specific enterprise requirements can demand significant customization efforts.
8. Legacy System Integration: Integrating legacy systems into a modern architecture requires innovative solutions to bridge technological gaps.
9. Scalability Assurance: Ensuring that the architecture can scale horizontally and vertically to accommodate growth is crucial for long-term viability.
10. Technical Support: Ongoing technical support is essential for addressing issues and ensuring the middleware operates seamlessly.
Strategic Importance of Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
In the contemporary business landscape, the strategic importance of scalable integration middleware architecture cannot be underestimated. This architecture not only supports current operational needs but also acts as a catalyst for innovation and competitive advantage. By facilitating seamless integration, organizations can enhance their agility, responding swiftly to market changes and customer demands.
Furthermore, scalable integration middleware architecture underpins digital transformation initiatives, providing a robust foundation for integrating cutting-edge technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain. These technologies hold the potential to revolutionize business processes, and having a scalable architecture is crucial for leveraging their full potential. Organizations equipped with a capable middleware architecture can innovate continuously, staying ahead of industry trends and outperforming competitors.
Future Directions for Scalable Integration Middleware Architecture
The future direction of scalable integration middleware architecture is characterized by a continued emphasis on advanced technologies and methodologies. The integration of AI and machine learning capabilities into middleware solutions promises to enhance the automation and intelligence of integration processes. Real-time data processing and analytics will become integral, offering deeper insights and faster decision-making capabilities.
Moreover, as cloud computing continues to gain traction, scalable integration middleware architecture will increasingly emphasize cloud-native designs, enabling organizations to leverage the cloud’s scalability and flexibility. Hybrid and multi-cloud environments will necessitate advanced integration capabilities, driving the evolution of middleware solutions in those directions. Ultimately, the future of scalable integration middleware architecture lies in its ability to adapt and innovate continuously, meeting the dynamic needs of modern enterprises while fostering growth and efficiency.