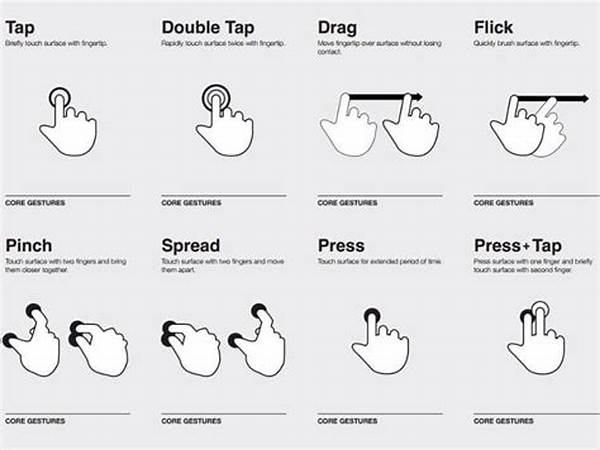
In the rapidly evolving landscape of user interface design, gesture-based control systems have emerged as a pivotal element. As technology continues to advance, developers and designers are tasked with the challenge of creating intuitive and efficient interfaces that cater to user expectations and usability standards. This article delves into various aspects of gesture-based UI design considerations, providing insights that are essential for crafting seamless user interactions.
Read Now : **optimizing Api Data Handling Techniques**
Understanding Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
The field of gesture-based UI design considerations entails a comprehensive understanding of how users interact with digital devices via movements rather than traditional input methods, such as a mouse or keyboard. This design approach requires an intricate balance between innovation and usability, ensuring that the gestures are both intuitive and efficient for users. Implementing these considerations involves assessing the complexity of movements, the naturalness of gestures, and their responsiveness. It is crucial to provide clear visual feedback to users as they perform gestures, ensuring an intuitive and responsive interface. Gesture-based UI design considerations necessitate a focus on accessibility, offering alternative input methods for users with disabilities, thereby fostering an inclusive user experience. Designers must stay attuned to evolving user behaviors and technological advancements, continuously refining gesture-based interactions to enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
Moreover, the implementation of gesture-based UI design considerations involves tackling challenges such as gesture recognition accuracy and minimizing latency. High recognition accuracy is strictly necessary to ensure users do not experience frustration while interacting with the interface. Furthermore, latency must be reduced to provide real-time feedback, which is imperative for maintaining user trust in the interface’s reliability. Finally, conducting usability testing is vital for understanding how well users navigate the gesture-based UI, allowing for data-driven improvements and iterative design processes.
Key Aspects of Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
1. Gesture-based UI design considerations require a balance between intuitive design and usability, ensuring gestures are straightforward and easily grasped by users.
2. Providing visual feedback, such as animations or highlights, is essential for users to understand completed gestures, an important aspect of any good gesture-based UI design.
3. Accessibility remains a pressing consideration, requiring alternative interaction methods for those unable to perform specific gestures, strengthening the inclusivity of gesture-based UI design.
4. Regular usability testing is paramount to evaluate the effectiveness of gesture-based interface designs and make necessary adjustments based on user input.
5. Continual assessment of technological advancements is vital, as it informs designers on modern practices and tools that can enhance gesture-based UI design considerations.
Challenges in Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
The development of gesture-based UI design considerations is not without its challenges and complexities. A primary obstacle is achieving high accuracy in gesture recognition. In an environment where precision is essential, errors can lead to frustration and diminished user satisfaction. Thus, building sophisticated algorithms that correctly interpret user intent while distinguishing between intentional gestures and accidental movements is paramount. Developers also face the challenge of ensuring low latency in gesture recognition, as delays in response can impair the natural feel intended to be achieved by a gesture-based interface.
Furthermore, gesture-based UI design considerations necessitate a deep understanding of cultural implications, as certain gestures may have different meanings across varying contexts or regions. Designers must patiently research and tailor interfaces accordingly, preventing inadvertent misunderstandings. Security, too, must remain at the forefront of consideration; gesture-based interfaces can unknowingly open opportunities for unauthorized access if maintained improperly. Through comprehensive threat evaluation, security vulnerabilities within gesture-based UI systems can be mitigated.
To truly grasp gesture-based UI design considerations, conducting thorough and iterative usability testing is indispensable. Feedback from real users aids in refining and evolving the interface, ensuring gestures align with user expectations and behaviors. A continuous process of user-centric evaluation contributes to crafting interfaces that not only meet initial design goals but also adapt fluidly to user needs over time.
Exploring Advanced Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
Comprehending advanced gesture-based UI design considerations involves integrating complex interactions with simple, user-friendly designs. Advanced sensors, which can detect the slightest nuances in user gestures, are pivotal in creating a sophisticated user experience. Evaluating the users’ cognitive load when interacting with gesture-based interfaces is crucial, as an overload can impede functionality and user satisfaction. Ensuring fluid and natural interactions remains a cornerstone of design consideration, allowing users to leverage gestures effortlessly to navigate robust systems.
1. Differentiating between similar gestures while minimizing errors is significant for high-functioning interfaces.
2. Designing gestures that mimic natural hand movements ensures high user adaptability to gesture-based interfaces.
3. Integrating haptic feedback can enhance user immersion, providing tactile responses to successful gestures.
4. Evaluating gesture execution context aids in delivering appropriate responses contingent on varying user environments.
5. Testing gesture recognition in diverse ambient conditions guarantees robust performance under various circumstances.
Read Now : Techniques For Scalable Data Integration
6. Inclusivity remains pivotal; accommodating different user abilities maintains equal accessibility of interfaces.
7. A focus on minimalistic gesture design reduces user fatigue associated with complex interactions.
8. Prioritizing gestural learning curves enables users to learn and master gestures with less effort and greater satisfaction.
9. Visual cues accompanying gestures reinforce user understanding, minimizing potential confusion during interactions.
10. Cross-device consistency in gesture-based interactions ensures a seamless transition across different platforms and devices.
Future Directions in Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
In exploring future directions from a gesture-based UI design considerations perspective, it becomes increasingly evident that innovation will continue to drive transformation in this domain. As artificial intelligence and machine learning augment gesture recognition systems, we anticipate even more nuanced and intelligent interpretations of user gestures. These advancements require meticulous consideration of privacy concerns, as more sophisticated data processing algorithms demand increased access to user interaction data.
Another area of rapid expansion lies in virtual and augmented reality, where gesture-based UI design considerations will serve as the backbone of immersive user experiences. By enabling users to interact with digital environments through natural gestures, these technologies could see unprecedented levels of user engagement, with applications from entertainment to educational settings. However, this evolution commands a rigorous understanding of how users perceive three-dimensional interfaces and the gestures that operate within this framework.
Moreover, gestures will evolve beyond traditional hand movements to incorporate full-body gestures and even biometric signals such as eye movements. The intersection of gestures with biometric data will require designers to rethink security from a holistic standpoint while upholding high standards of user privacy. Overall, the pursuit of progressive gesture-based UI design considerations will focus on unifying the user experience with ongoing technological advancements, promising to unlock potential that could redefine digital interactions.
Evaluating Usability in Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
The evaluation of usability within gesture-based UI design considerations is an essential aspect, as it deeply influences user satisfaction and interface effectiveness. Usability testing methodologies, including task completion rates and error frequency analysis, provide insightful metrics that guide designers toward optimally functioning interfaces. Interaction patterns are vitally scrutinized to determine the intuitiveness and clarity of proposed gestures, ascertaining that users grasp them without extensive trial and error.
Another significant aspect is the sustained engagement resulting from evaluating gesture-based UI design considerations. When an interface aligns with user expectations and efficiently addresses their unique requirements, prolonged interaction and investment are inevitably cultivated. Usability evaluations should always emphasize accessibility, ensuring that alternative methods are available for those who cannot perform specific gestures. Achieving this inclusivity not only widens the user base but also reflects a commitment to accommodating diverse user capabilities.
Ultimately, the endeavor of evaluating usability in gesture-based UI design considerations is rooted in agile practices that embody continuous improvement. By systematically incorporating user feedback into iterative interface enhancements, designers succeed in evolving gestures that celebrate simplicity, naturalness, and user preference. This attention to comprehensive usability ensures the lasting relevance and appeal of gesture-based interfaces, fostering meaningful digital experiences across differing user contexts and demographics.
Final Thoughts on Gesture-Based UI Design Considerations
To encapsulate the essence of gesture-based UI design considerations, it is imperative to recognize the profound potential that gestures hold in reshaping user interfaces. As the landscape of technology evolves, designers and developers are presented with opportunities to advance gesture-based systems beyond traditional paradigms. In this context, creativity and strategic thinking become paramount, envisioning interfaces that are simultaneously innovative and accessible.
Gesture-based UI design considerations remain a dialogue between functionality and human-centered design. By ensuring that gestural interactions are intuitive and minimize user effort, designers enrich the user experience holistically. The success of these interventions, however, relies on meticulous usability testing and user feedback consolidation, which are integral to refining and enhancing gesture-based systems.
Looking ahead, gesture-based UI design considerations will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in future technological advancements. To maximize potential, ongoing education and scholarly exploration into human interaction patterns will be necessary, guiding designers in delivering relevant solutions aligned with user preferences and behaviors. Thus, as we advance into a future of infinite digital possibilities, gesture-based UI design considerations will continue to spark innovative transformations, leading the charge in defining next-generation user experiences.