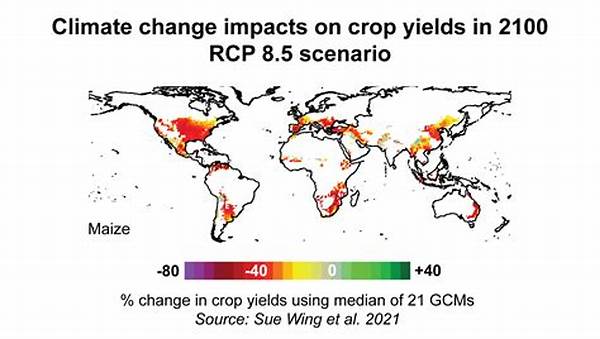
The interplay between weather and agricultural yield is a subject of considerable importance. Farmers across the world face a multitude of challenges stemming from unpredictable weather patterns, which can significantly influence the success of harvests. Understanding the relationship between weather impacts on harvests is crucial for developing adaptive strategies and maintaining food security. This article delves into various aspects of how weather impacts harvests and elaborates on potential measures to mitigate these effects.
Read Now : Cloud-based Encryption Key Management
The Influence of Weather Patterns on Crop Yield
Weather patterns play an integral role in determining the yield and quality of agricultural produce. Variations in temperature, precipitation, and extreme weather events such as droughts or floods can have profound effects on crop production. For instance, insufficient rainfall may lead to drought conditions, adversely affecting crop growth and leading to reduced yields or crop failure. Conversely, excessive rainfall can lead to flooding, waterlogging, and increased susceptibility to diseases among crops. Consequently, understanding weather impacts on harvests allows farmers and agricultural stakeholders to devise strategies to minimize risks and ensure sustainable crop production. By implementing measures such as irrigation management, selection of resilient crop varieties, and improved forecasting methods, the negative impacts of unfavorable weather can be mitigated to some extent.
Moreover, climate change exacerbates the uncertainties associated with weather impacts on harvests. Changes in global climate patterns are leading to increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, thereby posing additional challenges to agriculture. As a result, understanding the implications of climate change and integrating adaptive practices into current agricultural systems is imperative for enhancing resilience against weather-induced disturbances. Research and investments in technological advancements and sustainable farming practices are essential to building adaptive capacity and ensuring the stability of food supplies in the face of evolving climate conditions.
Key Factors of Weather Impacts on Harvests
1. Temperature Fluctuations: Sudden temperature changes can stress crops, interfering with growth and reducing yields.
2. Precipitation Variability: Unpredictable rainfall patterns affect soil moisture levels, crucial for crop development.
3. Extreme Weather Events: Droughts and floods can devastate harvests, leading to significant agricultural losses.
4. Soil Erosion: Intense rainfall can lead to soil erosion, diminishing land quality and crop potential.
5. Pest and Disease Outbreaks: Weather changes can prompt pest and disease proliferation, impacting crop health.
Adapting Agricultural Practices to Mitigate Weather Impacts
Given the increasing challenges posed by weather impacts on harvests, adapting agricultural practices to mitigate these effects becomes indispensable. Farmers can adopt various strategies to enhance their resilience and ensure sustainable crop production. Crop diversification is one such strategy, where farmers grow a variety of crops to reduce reliance on a single harvest, thereby spreading the risk associated with adverse weather conditions. Additionally, implementing advanced irrigation techniques can help in managing water resources efficiently during periods of irregular precipitation.
Furthermore, breeding crop varieties with enhanced resistance to extreme weather conditions can contribute to minimizing yield losses. Research in biotechnology and genetic engineering is vital in developing crops that are more tolerant to drought, heat, and other climatic stresses. Investing in weather forecasting technologies and data-driven decision-making tools can also provide farmers with the necessary insights to adjust their farming practices in line with anticipated weather changes. Through these adaptive measures, the agricultural sector can better withstand weather impacts on harvests and sustain food production in the face of climatic uncertainties.
The Role of Technology in Managing Weather Impacts
The integration of technology holds significant promise in addressing the challenges posed by weather impacts on harvests. Advanced satellite imaging and geographic information systems (GIS) enable real-time monitoring of weather conditions and crop health. This technological intervention allows for timely and effective decision-making, reducing the vulnerability of harvests to adverse weather. Additionally, precision agriculture technologies, including soil moisture sensors and automated irrigation systems, can optimize resource usage and enhance crop resilience by delivering water and nutrients efficiently. These innovations contribute to building a more robust agricultural system that can adapt to changing weather patterns.
Read Now : “data Documentation And Metadata Standards”
Technological advancements also extend to the development of climate-resistant crop varieties through genetic modification and selective breeding. These innovations equip crops with traits that enhance their ability to withstand extreme weather conditions, thereby mitigating the negative impacts on yield and quality. Furthermore, data analytics and machine learning algorithms are being increasingly utilized to improve weather forecasts and predict potential impacts on harvests. By leveraging such technologies, farmers can make informed decisions that enhance their preparedness and adaptive capacity. Overall, the effective deployment of technology is vital to managing weather impacts on harvests and ensuring a stable agricultural future.
Impact of Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events have become increasingly frequent and intense due to climate change, posing significant threats to harvests worldwide. The weather impacts on harvests caused by events such as hurricanes, floods, and heatwaves can lead to catastrophic losses in agricultural productivity. Hurricanes and tropical storms bring heavy rainfall and wind damage, disrupting crops and infrastructure. Flooding saturates fields, causing root rot and other water-related damages. Heatwaves, on the other hand, stress crops beyond their tolerance levels, leading to reduced yields or even crop failure.
Addressing the impacts of extreme weather on agriculture requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes implementing effective disaster risk reduction strategies, such as establishing flood control measures and creating early warning systems for extreme weather events. Promoting sustainable land management practices, including reforestation and soil conservation, can also mitigate the adverse effects of these events. Moreover, building institutional and community capacity to respond swiftly to weather-related disasters is crucial for minimizing disruptions to agricultural activities. By implementing comprehensive strategies, it is possible to enhance the resilience of agricultural systems and reduce the adverse weather impacts on harvests.
Community-Based Approaches to Address Weather Impacts
Communities play a vital role in managing weather impacts on harvests through collective action and knowledge sharing. By fostering collaborations among farmers, researchers, and policymakers, communities can develop locally adapted strategies to cope with adverse weather conditions. Community-based approaches may include forming cooperatives to share resources, building shared infrastructure to withstand weather challenges, and engaging in participatory research to identify suitable adaptive measures.
Educational programs focused on sustainable agricultural practices and climate resilience can empower farmers with the knowledge and skills needed to adapt effectively. Implementing traditional and indigenous knowledge systems can also enhance adaptive capacities, as these systems often incorporate valuable insights into natural resource management and agricultural practices in harmony with the environment. Emphasizing community-driven initiatives ensures that solutions are context-specific, culturally relevant, and sustainable in the long term. Overall, community-based approaches are indispensable for fostering resilience against weather impacts on harvests.
Conclusion on Weather Impacts on Harvests
Weather impacts on harvests present significant challenges that require a collective and adaptive response. From technological innovations and strategic planning to community engagement and sustainable practices, there are numerous avenues to mitigate these impacts. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns globally, building resilience in agricultural systems becomes ever more critical. Effective management of weather impacts on harvests involves a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between climate, technology, policies, and community actions. By adopting integrated approaches, it is possible to ensure sustainable agricultural productivity and food security in the face of uncertain weather patterns.
Summary
In summary, the interplay between weather and agriculture is of paramount importance in understanding and addressing the challenges that arise from adverse weather impacts on harvests. The unpredictability of weather patterns, exacerbated by climate change, poses serious risks to agricultural productivity worldwide. As these impacts become more pronounced, there arises an urgent need for collaborative efforts to develop adaptive strategies that enhance the resilience of agricultural systems.
Efforts to mitigate weather impacts on harvests encompass a multifaceted approach. This includes the integration of cutting-edge technologies, such as precision agriculture and climate-resilient crop varieties, which are essential for enhancing adaptation capacity. Additionally, fostering community-based initiatives and leveraging traditional knowledge systems are key to promoting sustainable agricultural practices suited to local contexts. By adopting a comprehensive approach that combines technological advancements, community engagement, and sustainable land management, it is possible to secure the stability of food systems and ensure the continued viability of agriculture amid evolving weather conditions.