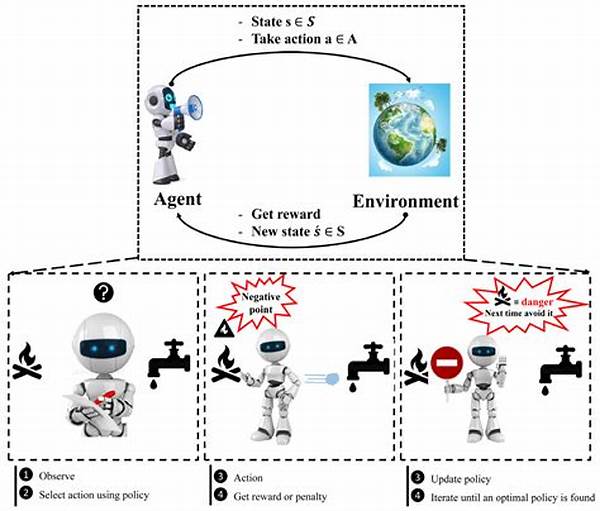
The Role of Machine Learning in Addressing Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is an escalating global challenge, posing significant threats to both human populations and ecological systems. With increasing demands and limitations in resources, developing innovative solutions has become imperative. Here, machine learning in water scarcity management emerges as a transformative approach. Machine learning systems introduce advanced algorithms capable of analyzing complex datasets to optimize water resource allocation and predict future scarcity scenarios. The robust capabilities of machine learning empower stakeholders, including governments and NGOs, to make informed decisions, enhance water use efficiency, and mitigate the adverse impacts of water shortages. By leveraging historical data and real-time analytics, machine learning in water scarcity management provides pivotal insights into usage patterns, weather forecasts, and aquifer levels, facilitating proactive and sustainable management strategies.
Read Now : Renewable Energy Adoption For Emission Cuts
Machine learning in water scarcity management has revolutionized traditional methods by introducing predictive analytics, thus enabling early identification of potential scarcity periods. This foresight prevents crises and ensures the effective delivery of water to both urban and agricultural sectors. Through data-driven decision-making, stakeholders can devise policies optimized for environmental sustainability and economic viability. Consequently, regions grappling with recurrent droughts have found a path towards resilience, aided by machine learning’s capability to integrate diverse data sources and derive actionable intelligence. The continuous refinement and adaptation of these systems promise a future where machine learning in water scarcity management not only addresses present needs but also anticipates future challenges.
Moreover, the application of machine learning in water scarcity management encourages the refinement of water-saving technologies and infrastructure. By analyzing consumption patterns and the efficacy of existing systems, machine learning provides insights that drive innovation. Investment in these technologies is indispensable for cultivating sustainable water practices, further showcasing the integral role of machine learning in fostering a holistic approach to water management.
Applications of Machine Learning in Water Scarcity Management
1. Prediction of Water Demand: Machine learning in water scarcity management effectively forecasts water demand patterns, allowing more efficient resource distribution. By employing various algorithms that analyze historical consumption data, machine learning models can predict future usage trends.
2. Optimization of Water Resource Allocation: By analyzing diverse data sets, machine learning in water scarcity management optimizes the allocation of water resources. This ensures the maximization of resource use while minimizing wastage, thus promoting sustainable water management.
3. Water Quality Monitoring: Machine learning in water scarcity management facilitates real-time monitoring of water quality, detecting pollutants and anomalies swiftly. Such systems enable timely interventions and maintain the integrity of water resources.
4. Infrastructure Management: Machine learning in water scarcity management can assess infrastructure condition, predict failures, and suggest maintenance activities. This increases the longevity of water distribution systems and ensures their efficient operation.
5. Climate Change Adaptation: By evaluating climatic data, machine learning in water scarcity management identifies patterns of change and equips decision-makers with strategies to adapt to shifting environmental conditions.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Machine Learning for Water Scarcity
The integration of machine learning in water scarcity management presents several challenges, particularly concerning data availability and quality. The success of these systems heavily relies on accurate, comprehensive datasets. Many regions, especially those facing severe water scarcity, lack the necessary data infrastructure to support advanced machine learning applications. Consequently, there is an urgent need for investment in data collection and management frameworks to enable effective use of machine learning technologies.
Additionally, the complexity of ecosystems and the variability of climatic conditions pose significant hurdles in the application of machine learning in water scarcity management. Algorithms need to be adaptive and capable of assimilating vast and varied data sets to generate reliable predictions. This necessitates ongoing refinement of models and collaboration among data scientists, hydrologists, and policymakers to tailor solutions suited to local contexts. With the right investments and technological advancements, these obstacles can be overcome, paving the way for transformative changes in water management practices.
Beyond data challenges, integrating machine learning into water management systems requires substantial financial and human resources. Training personnel to work with these advanced technologies is crucial for their successful implementation and operation. Governments and organizations must work together to build capacity, ensuring that the benefits of machine learning in water scarcity management are equitably distributed. Sustainable water practices, empowered by technology, are attainable with collaboration and comprehensive planning.
The Impact of Machine Learning on Water Scarcity Strategies
Machine learning in water scarcity management significantly enhances conventional strategies through innovative approaches to prediction and optimization. By processing extensive datasets, machine learning tools provide decision-makers with precise, data-driven insights. These insights guide strategic planning and contribute to the development of robust water scarcity mitigation frameworks. The impact of machine learning extends beyond predictions; it informs infrastructure development, aids in risk assessment, and supports effective resource allocation.
Machine learning algorithms evaluate a multitude of factors affecting water scarcity. They analyze variables such as weather patterns, population growth, and agricultural demands to project future water availability. This analysis allows for the anticipation of potential shortages and the formulation of contingency plans. Additionally, real-time data processing can inform immediate actions during crisis situations, ensuring that water resources are allocated efficiently and equitably. The integration of machine learning in water scarcity management enables a proactive approach, which significantly mitigates the impacts of water shortages.
Read Now : Implementing Real-time Data Solutions
Machine learning-backed systems promote accountability and transparency in water management by providing clear evidence of resource utilization. These systems enable the tracking of water consumption patterns and the identification of inefficiencies. By empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions, machine learning fosters collaboration across institutions, helping to ensure sustainable water use. As technology continues to evolve, its application in water scarcity management will likely expand, further enhancing the effectiveness of global water management strategies.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Implementing machine learning in water scarcity management necessitates careful consideration of ethical and social implications. The potential of these technologies to address water scarcity raises questions about data privacy, equity, and access. Decisions based on machine learning must ensure that they do not disproportionately disadvantage vulnerable populations. It is essential that data collection and analysis practices adhere to ethical standards and respect individual privacy rights.
Equitable access to machine learning technologies should be a priority to prevent the exacerbation of existing disparities. Efforts must be made to ensure that regions already experiencing water scarcity benefit from technological advances. This requires collaboration between governments, international organizations, and private sectors to distribute resources and expertise fairly. Furthermore, transparency in algorithmic processes is necessary to build trust among stakeholders and demonstrate that machine learning systems function in the public interest.
Machine learning in water scarcity management also highlights the need for inclusive decision-making processes. Engaging with local communities and incorporating their knowledge and perspectives can enhance the effectiveness and acceptability of technological solutions. By promoting a participatory approach, machine learning applications can complement traditional knowledge and contribute to sustainable water management practices that reflect diverse needs and values.
Innovation and Future Directions
The future of machine learning in water scarcity management lies in continued innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration. As algorithms become more sophisticated and data collection techniques improve, these systems will offer even greater precision and versatility in managing water resources. The integration of machine learning with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and remote sensing, will likely amplify its impact.
Collaboration across fields, including data science, environmental science, and public policy, is essential to advance the capabilities of machine learning applications. By fostering partnerships, stakeholders can leverage a broad range of expertise to refine algorithms and develop comprehensive water management solutions. As research and development in machine learning progress, there will be an increasing opportunity to address global water challenges more effectively.
Public awareness and education will play a critical role in the successful implementation of machine learning in water scarcity management. Efforts to inform communities about the benefits and limitations of technology can promote acceptance and cooperation. Policymakers, educators, and technologists must work together to develop outreach programs that emphasize the importance of sustainable water practices and the transformative power of technology.
Conclusion
The application of machine learning in water scarcity management represents a significant advancement in addressing one of the most pressing global challenges. Its ability to analyze complex datasets and generate actionable insights offers valuable support for sustainable water management strategies. By overcoming data challenges and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, machine learning holds the promise of securing water resources for future generations.
As efforts continue to refine these technologies and expand their reach, it is crucial to address ethical and social considerations to ensure equitable access and respect for individual rights. The transformative potential of machine learning in water scarcity management can only be fully realized with the commitment to inclusive, transparent, and fair implementation practices. Through innovation, collaboration, and public engagement, machine learning can contribute to a future of resilient and sustainable water use.
By remaining committed to advancing machine learning technologies, society can move closer to achieving global water security. The integration of data-driven decision-making into water management practices will enhance the ability to anticipate and respond to scarcity challenges, ultimately fostering a sustainable relationship with natural resources. The continued dedication to ethical, equitable, and effective application of machine learning will be a cornerstone in the successful management of water scarcity.