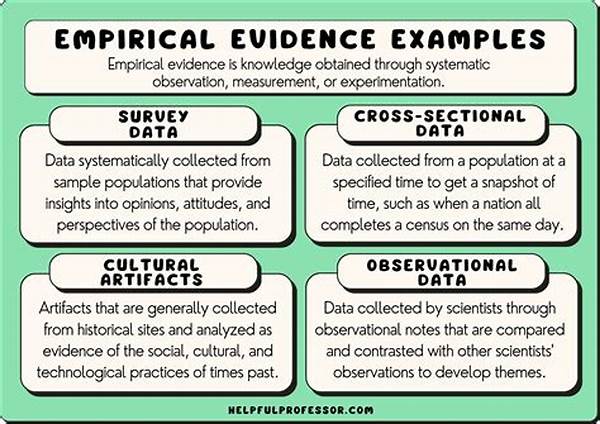
Statistical inference in empirical research plays a pivotal role in the validation and generalization of findings across a myriad of scientific disciplines. Through the application of statistical methods, researchers are equipped to draw conclusions that extend beyond the immediate data at hand. The essence of statistical inference in empirical research lies in its ability to make probabilistic judgments about populations based on sample data. This process not only aids in the characterization of unknown parameters but also facilitates hypothesis testing. By leveraging tools such as confidence intervals and significance tests, researchers can evaluate the strength and reliability of their findings. This structured approach ensures that conclusions are not merely anecdotal but are backed by rigorously tested evidence. Ultimately, statistical inference in empirical research serves as the foundation upon which scientific truths are built and verified, thus fostering advancements and innovations across fields.
Read Now : **predictive Analytics In Climate Adaptation**
Importance of Statistical Inference in Empirical Research
The role of statistical inference in empirical research cannot be overstated as it provides the backbone for making informed decisions from data. By utilizing various statistical techniques, researchers can interpret complex data sets and derive conclusions that otherwise remain elusive. The primary objective of statistical inference in empirical research is to make predictions about a population based on a sample’s data, enhancing the precision and reliability of these predictions. This discipline allows researchers to understand patterns, test hypotheses, and infer relationships within data. Statistical inference in empirical research thus becomes indispensable in the validation and advancement of knowledge, contributing to the continuous growth and development of scientific understanding. In essence, it aids in translating raw data into meaningful insights, forming the crux of empirical research endeavors.
Methods in Statistical Inference for Empirical Research
1. Hypothesis Testing: Hypothesis testing forms a core element of statistical inference in empirical research, allowing scientists to assess the validity of their propositions through structured testing mechanisms.
2. Confidence Intervals: Utilized within statistical inference in empirical research, confidence intervals offer a range of values which estimate the true parameter, thus providing a measure of certainty around data conclusions.
3. Regression Analysis: This method in statistical inference enables empirical research to explore relationships between variables, often providing insights into causational links.
4. Sample Size Determination: An essential aspect of statistical inference in empirical research, determining the appropriate sample size ensures the reliability and validity of the study findings.
5. Significance Tests: Central to statistical inference in empirical research, these tests determine if the results observed in a sample can be generalized to the larger population.
Challenges in Applying Statistical Inference in Empirical Research
Implementing statistical inference in empirical research is fraught with several challenges that necessitate a nuanced approach. One core issue relates to the quality and integrity of data, which fundamentally impacts the inference process. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to false conclusions, emphasizing the importance of rigorous data collection methods. Additionally, the assumptions underpinning statistical methods often do not hold true in real-world data, posing further complications in the analysis. Researchers must therefore exercise caution and discretion when selecting appropriate techniques for statistical inference in empirical research. Moreover, issues like overfitting and underfitting in modeling can yield unreliable predictions or conclusions, thereby compromising the study’s generalizability. Ultimately, overcoming these challenges demands both methodological expertise and a critical understanding of the inherently probabilistic nature of statistical inference in empirical research.
Methodologies to Enhance Statistical Inference in Empirical Research
1. Advanced Sampling Techniques: Employing robust sampling techniques enhances statistical inference in empirical research by increasing the representativeness of the data.
2. Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Vital to the reliability of statistical inference in empirical research, these processes ensure the removal of noise and inconsistencies in data sets.
3. Robust Statistical Models: Adopting flexible and robust statistical models can mitigate some inherent limitations in traditional approaches of statistical inference in empirical research.
4. Cross-Validation: This technique assures the reliability and validity of statistical inference in empirical research findings by testing models on different data segments.
Read Now : “systematic Literature Review Methodologies”
5. Use of Bayesian Methods: Incorporating Bayesian methods into statistical inference in empirical research can offer a probabilistic framework that provides deeper insights and more nuanced conclusions.
6. Software Utilization: Leveraging advanced statistical software facilitates accurate and efficient statistical inference in empirical research by simplifying complex computations and analyses.
7. Collaborative Approaches: Collaborations with experts in statistics can help refine statistical inference in empirical research, ensuring rigorous methodological application.
8. Sensitivity Analysis: Conducting sensitivity analysis helps assess the impact of varying assumptions or parameters in statistical inference in empirical research.
9. Ethical Considerations: Ethical integrity is crucial, as biases or conflicts of interest can undermine the credibility of statistical inference in empirical research.
10. Continuous Education: Engaging in continuous learning ensures that researchers remain proficient in the latest methods and technologies in statistical inference in empirical research.
Future Directions in Statistical Inference in Empirical Research
The future of statistical inference in empirical research will likely witness significant transformations driven by technological advancements and evolving scientific paradigms. Machine learning algorithms, with their capacity to handle large and complex data sets, present new opportunities to enhance statistical inference by offering more accurate and nuanced insights. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence can aid in identifying patterns and relationships that were previously elusive, thereby enriching the inference process. The rise of big data further facilitates this shift, providing researchers with a wealth of information upon which more rigorous and comprehensive analyses can be conducted. Moreover, as interdisciplinary collaboration becomes increasingly prevalent, statistical inference in empirical research is poised to benefit from the exchange of methodologies and insights across fields, thus broadening its application and impact. Emphasizing open science and reproducibility will also remain crucial to ensure that the fruits of empirical research are both credible and accessible. As these developments unfold, the role of statistical inference in empirical research will continue to expand and evolve, underscoring its indispensable contribution to scientific advancement.
Conclusion on Statistical Inference in Empirical Research
In conclusion, statistical inference in empirical research remains a cornerstone of scientific inquiry, providing the tools necessary to navigate the complexities of data interpretation and analysis. Its application allows for the validation and generalization of findings, thereby advancing knowledge across various disciplines. The methodologies employed in statistical inference in empirical research offer researchers systematic approaches for hypothesis testing, parameter estimation, and data modeling, ensuring that conclusions drawn are robust and credible. The challenges encountered in this domain underscore the need for meticulousness, adaptability, and continuous learning to refine approaches and improve outcomes. As technologies progress and interdisciplinary collaborations flourish, the future of statistical inference in empirical research looks promising, with enhanced potential to drive innovation and discovery. Ultimately, the integrity and efficacy of scientific research hinge upon the adept application of statistical inference, emphasizing its pivotal role in fostering a deeper understanding of the natural and social world.