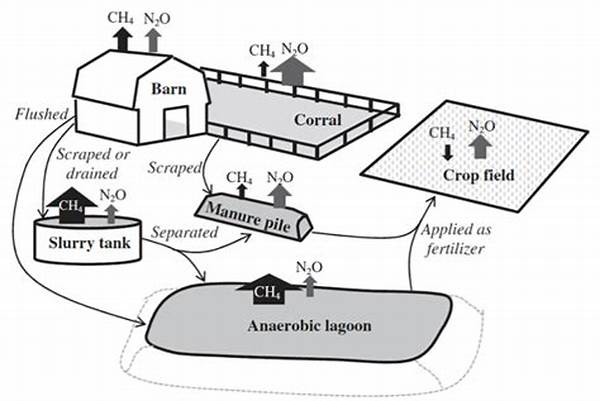
In the realm of modern agriculture, the importance of effective manure management practices cannot be overstated. The environmental impact of improper manure management is a pressing concern, as it can lead to significant emissions of greenhouse gases. These emissions, primarily methane and nitrous oxide, contribute to global climate change. As a result, there is an increasing emphasis on developing and implementing sustainable strategies for manure management. The objective is not only to minimize emissions but also to optimize the nutrient value of manure, thus enhancing agricultural productivity.
Read Now : Smart Contracts In Computing
The Importance of Sustainable Manure Management
Sustainable manure management and emissions reduction are critical components of modern agricultural practices. By adopting such approaches, farmers can significantly diminish the environmental impact of their operations. Implementing manure management practices that focus on emissions reduction involves understanding the biological processes that lead to gas production during manure decomposition. Techniques such as anaerobic digestion, composting, and proper storage can greatly mitigate emissions. Additionally, these practices can contribute to the sustainability of agricultural systems by recycling nutrients back into the soil. Effective manure management not only alleviates environmental concerns but also promotes resource efficiency and economic benefits for agricultural enterprises.
Strategies for Effective Manure Management and Emissions Reduction
1. Anaerobic Digestion: This process breaks down manure in the absence of oxygen, reducing methane emissions while generating biogas as an energy source.
2. Composting: Properly managed composting reduces emissions and enhances the nutrient value of manure by stabilizing it through aerobic decomposition.
3. Storage Covers: Utilizing covers on manure storage facilities can prevent methane and ammonia emissions by limiting exposure to air.
4. Nutrient Management Plans: These plans ensure that manure is applied to fields at the right time, rate, and method, optimizing nutrient uptake and minimizing emissions.
5. Frequent Removal: Regularly removing manure from animal housing reduces the time available for emissions to occur before proper treatment is applied.
Impact of Policy on Manure Management and Emissions
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping manure management and emissions practices. Regulations and standards set by agricultural and environmental agencies ensure that farmers adhere to best practices. These policies encourage the exploration of innovative technologies and provide incentives for adopting sustainable manure management techniques. Policy frameworks often mandate reporting and monitoring emissions, demanding transparency and accountability from agricultural operations. Furthermore, compliance with these regulations not only helps in controlling emissions but also aids in safeguarding public health by preventing water pollution from manure runoff. Hence, policy intervention is indispensable for harmonizing agricultural productivity with environmental conservation.
Read Now : Academic Journal Impact Factor Analysis
Technological Innovations in Manure Management
The advancement of technological innovations has pioneered new frontiers in manure management and emissions reduction. Innovative machinery and equipment facilitate the efficient handling, processing, and application of manure. Sensor technologies and data analytics enable real-time monitoring of emissions, allowing farmers to make informed decisions. Additionally, genetic advancements in livestock breeding aim to reduce the environmental footprint of manure naturally. The integration of precision agriculture techniques ensures that manure is applied efficiently, enhancing crop absorption and minimizing wastage. Ultimately, technology serves as a crucial ally in revolutionizing traditional practices by making them more sustainable and less damaging to the environment.
Challenges and Solutions
The multifaceted nature of manure management and emissions presents several challenges. Foremost among these is the financial burden associated with implementing advanced manure management technologies. However, various solutions are being explored. Subsidies and grants from governmental and non-governmental organizations can help alleviate some financial constraints faced by farmers. Furthermore, research and innovation can reduce costs by developing more affordable solutions. Education and training programs enhance farmers’ understanding of effective manure management techniques, ultimately leading to increased adoption. Collaborations between stakeholders—farmers, researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders—are imperative to develop comprehensive strategies that address both the environmental and economic aspects of manure management.
Future Prospects for Manure Management and Emissions
The future of manure management and emissions is promising, with ongoing research paving the way for breakthroughs. Continued exploration into microbial processes and genetic engineering holds potential for reducing emissions at the source. Integrating renewable energy systems with manure management can create closed-loop systems that produce energy from waste. Sustainable practices tailored to specific regional conditions can enhance their effectiveness and acceptance. Collaborative efforts at the international level can lead to the establishment of global standards, facilitating the sharing of knowledge, resources, and innovations. The interplay of these prospects will dictate the progress towards achieving low-emission, sustainable agricultural systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective manure management and emissions control are integral to sustainable agriculture, directly influencing environmental, economic, and social outcomes. As the agricultural sector faces increasing pressures to produce more while minimizing ecological impact, embracing innovative strategies is essential. The integration of advanced technologies, supported by robust policy frameworks, provides a path to achieving significant emission reductions. Moreover, collective action through education, collaboration, and research will strengthen efforts. By understanding the critical role of manure management and diligently mitigating emissions, the agricultural community can contribute positively to the global environmental agenda while securing future food resources.