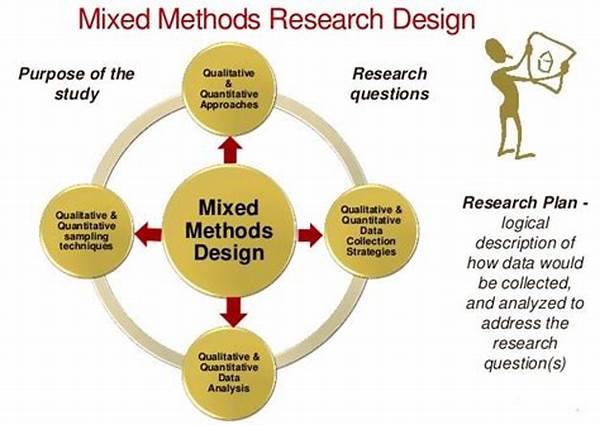
In the realm of scientific research, the application of mixed methods has become increasingly prominent. This approach, which integrates both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies, allows researchers to better understand complex phenomena by leveraging the strengths of each method. Mixed methods in scientific studies offer a comprehensive framework that facilitates a holistic analysis, as well as an opportunity to triangulate data, thus enhancing the validity and reliability of the findings. Through this integrative methodology, researchers gain a broader perspective, often leading to more robust conclusions.
Read Now : “wind Patterns In Crop Management”
The Importance of Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
Mixed methods in scientific studies provide a multifaceted approach to research that addresses both numerical and textual data. This approach is particularly beneficial when exploring complex research questions that cannot be addressed by a single method. For instance, quantitative data might reveal certain patterns that can be further explored through qualitative interviews, providing depth and context to the findings. By combining these methodologies, researchers can corroborate findings across different data sources, thereby enhancing the trustworthiness of the results.
Mixed methods in scientific studies also facilitate a dynamic interaction between the research data and its interpretation. Where numerical data provides a general overview, qualitative insights can delve into underlying mechanisms and participant perspectives. This synergy not only enriches the analysis but also addresses potential biases inherent in single-method research. Furthermore, this integrative approach promotes interdisciplinary collaboration, enabling researchers from varied fields to contribute their expertise, and thus fostering innovation and discovery.
Key Explanations of Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
1. Mixed methods in scientific studies allow researchers to draw upon both qualitative and quantitative insights, enhancing the depth and breadth of analysis.
2. The integration of different methodologies provides a richer understanding, particularly when examining multifaceted research questions.
3. Mixed methods in scientific studies enable the validation of findings through triangulation, increasing the credibility of the research outcome.
4. Researchers can address limitations inherent in singular methodological approaches by utilizing mixed methods in scientific studies.
5. Enhanced collaboration across disciplines is often a result of employing mixed methods in scientific studies, fostering a more comprehensive approach to research.
The Application of Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
Mixed methods in scientific studies have garnered recognition for their ability to capture the complexity of social phenomena. This methodological approach is advantageous in fields such as health sciences, education, and social sciences, where multifaceted issues often require a nuanced examination. By integrating quantitative surveys with qualitative case studies, researchers can uncover patterns and explain underlying reasons for observed outcomes. This comprehensive examination furthers the potential for actionable insights that single methods might overlook.
A key benefit of mixed methods in scientific studies is their adaptability to different research phases. During data collection, researchers can employ sequential or concurrent strategies, either collecting data in phases or simultaneously. This flexibility allows researchers to adapt to evolving research needs, ensuring that both quantitative trends and qualitative nuances are adequately captured. Such adaptability enhances the relevance and applicability of research findings, catering to both academic and practical demands.
Examples of Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
1. Mixed methods in scientific studies may begin with a quantitative survey, followed by qualitative interviews to explore survey results.
2. Researchers often employ mixed methods in scientific studies to combine statistical analysis with case studies for comprehensive insights.
3. In educational research, mixed methods in scientific studies can evaluate teaching methodologies through numeric scores and detailed observations.
4. Health research frequently uses mixed methods in scientific studies by contrasting medical records with patient interviews.
Read Now : Conducting Thorough Peer Evaluations
5. Social science researchers employ mixed methods in scientific studies to assess policy impacts quantitatively and through stakeholder analysis.
6. Mixed methods in scientific studies are beneficial in environmental research by correlating data trends with community narratives.
7. Understanding consumer behavior often involves mixed methods in scientific studies, merging focus groups with market analysis.
8. Mixed methods in scientific studies are utilized in psychological research to corroborate experimental results with participant feedback.
9. Evaluators of program effectiveness often rely on mixed methods in scientific studies for balanced assessments of outcomes and processes.
10. Mixed methods in scientific studies provide a robust foundation for exploring cultural phenomena through surveys and ethnographic studies.
Detailed Analysis of Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
The adoption of mixed methods in scientific studies is rooted in its capacity to address diverse research questions that necessitate multiple perspectives. This is particularly valuable in addressing complex questions where quantitative data alone fails to capture the intricacies that qualitative insights can provide. For example, while a quantitative survey might highlight a phenomenon’s prevalence, qualitative data can explain why it occurs. Through this integrative approach, mixed methods not only augment the richness of the research but also ensure that no critical aspect is overlooked.
Mixed methods in scientific studies are instrumental in exploring emerging areas where research demands are evolving. The flexibility offered by this approach permits researchers to pivot their methodologies as new data emerges. Hence, studies remain relevant and responsive to unforeseen findings, maintaining their academic rigor while embracing practicality. Importantly, this flexibility fosters an environment where traditionally siloed academic disciplines can intersect, thus driving innovative research solutions and cross-disciplinary exploration.
Methodological Considerations in Mixed Methods in Scientific Studies
When conducting mixed methods in scientific studies, researchers must carefully consider the integration process of different methodological paradigms. This involves not only selecting appropriate tools and techniques for data collection and analysis but also ensuring coherent integration across the research phases. Such planning is crucial to successfully merging diverse datasets and attaining synergistic insights.
Moreover, mixed methods in scientific studies necessitate a rigorous evaluation of ethical considerations. Researchers must navigate challenges associated with participant consent across different methodological approaches, ensuring ethical standards are upheld in both qualitative and quantitative phases. By addressing these challenges, researchers can confidently leverage the advantages of mixed methods to generate comprehensive and ethically sound research findings.