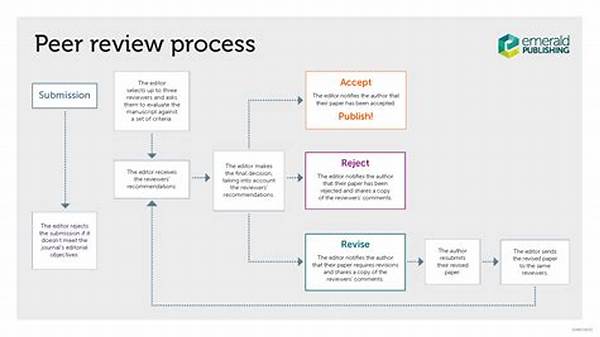
In recent years, the academic community has experienced a substantial transformation in the mechanisms underpinning the peer review process. As research output grows exponentially, the peer review system has faced increasing pressure to adapt and evolve. The aim of this article is to explore modern trends influencing peer review system modernization, highlighting innovative practices that are shaping the future of academic publishing.
Read Now : **impact Of Legislative Reforms**
Technological Integration in Peer Review
Technological advancements have been paramount in driving peer review system modernization trends. The traditional, manuscript-centric approach is being replaced by more technologically advanced systems, leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies streamline the review process by automating routine tasks, thereby reducing the burden on reviewers and accelerating publication timelines. Moreover, the incorporation of digital platforms facilitates enhanced communication and transparency among authors, reviewers, and editors. As a result, technological integration is not only enhancing efficiency but also improving the quality and rigor of the peer review process.
Another critical aspect of modernization involves the adoption of open peer review models. Unlike the traditional single- or double-blind formats, open peer review fosters greater transparency by revealing reviewer identities and making reviews publicly accessible. This approach encourages accountability and constructive feedback, aligning with the contemporary emphasis on openness in scientific discourse. The trend towards open peer review is gaining traction, as it promotes a collaborative environment that benefits authors, reviewers, and the broader scientific community alike.
Furthermore, the rise of preprint servers has impacted peer review system modernization trends significantly. Preprints allow researchers to disseminate findings rapidly prior to formal peer review, thus accelerating the exchange of knowledge. This practice not only enhances the visibility of research but also facilitates early-stage feedback from the community. Consequently, preprints serve as a catalyst for innovation within the peer review landscape, necessitating a shift in the traditional paradigms and encouraging a more dynamic dissemination of scientific knowledge.
Benefits of Peer Review System Modernization
1. Enhanced Efficiency: Peer review system modernization trends aim to streamline the review process through automation and technology, reducing time lags in publication.
2. Greater Transparency: Open peer review models contribute to increased transparency, providing insights into reviewer identities and feedback to foster accountability.
3. Improved Quality: The adoption of advanced technologies enables more thorough and rigorous evaluations, resulting in higher quality research outputs.
4. Accelerated Knowledge Dissemination: Preprint servers exemplify peer review system modernization trends by allowing for rapid sharing and feedback of research prior to formal review.
5. Increased Collaboration: Modern trends promote collaborative interactions among researchers, reviewers, and editors, fostering a more cohesive scientific community.
Challenges in Implementing Modernization
Despite the benefits, peer review system modernization trends present certain challenges. Resistance to change is a significant obstacle, as stakeholders accustomed to traditional models may be hesitant to embrace new practices. Equally important is the concern surrounding the quality and reliability of automated systems. Ensuring that technologies accurately assess research without compromising critical evaluation is crucial for maintaining scientific standards. Furthermore, open peer review models necessitate cultural changes in how feedback is given and received, which may require significant adaptation and acceptance within the research community.
Financial constraints also pose a challenge to adopting modernization efforts. Implementing advanced technologies and platforms requires substantial investment, which may not be feasible for all publishers or institutions. Additionally, while preprint servers offer benefits, they introduce complexities in intellectual property management and ethical considerations, as content shared prematurely may face issues with plagiarism or misrepresentation. Hence, balancing innovation with these challenges is essential for the sustainable advancement of peer review practices.
In response to these challenges, continuous engagement with researchers, editors, and institutions is necessary. Open dialogue can address concerns, educate stakeholders, and foster an environment conducive to embracing modernization efforts. Collaborative initiatives aimed at refining technologies and establishing standardized protocols will be key to overcoming these barriers, ultimately paving the way for a more robust and efficient peer review system.
Collaborative Approaches in Modernization
Collaboration plays a vital role in advancing peer review system modernization trends. Collective efforts between stakeholders can facilitate the exchange of best practices and development of unified standards. Collaborative platforms promote cross-disciplinary interactions, breaking down silos and fostering a holistic approach to scientific evaluation. Moreover, partnerships with technology providers enable tailored solutions, ensuring the integration of systems aligns with the needs of diverse academic fields. By fostering a culture of collaboration, the scientific community can collectively address challenges and promote a vibrant future for peer review modernization.
1. Cross-Discipline Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration across various fields can lead to the development of universal standards benefiting diverse research domains, exemplifying peer review system modernization trends.
2. Engagement with Technology Providers: Partnerships with technology companies ensure that automated systems are customized to the specific needs of academic publishing, enhancing the modernization efforts.
3. Stakeholder Involvement: Continuous dialogue with researchers and editors can foster acceptance and adaptation of new peer review models, facilitating smoother transitions.
Read Now : Intellectual Property Rights Education
4. Education and Training: Providing resources and training to familiarize stakeholders with new technologies and practices ensures seamless integration and maximized benefits of modernization trends.
5. Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing robust feedback systems for continuous assessment of modernization efforts can refine processes and ensure alignment with community needs.
6. Policy Development: Collaborative efforts must include the development of policies that address ethical considerations, data privacy, and intellectual property in the context of modernization.
7. Innovation Incentives: Encouraging innovation through grants and incentives can accelerate the adoption of new practices and technologies within the peer review process.
8. Recognition of Efforts: Acknowledging contributions of reviewers and editors towards modernization efforts can promote engagement and motivation to embrace new methodologies.
9. Global Outreach: Extending modernization trends to underserved regions can ensure equitable access and participation in the peer review process, democratizing scientific evaluation.
10. Sustainability Focus: Integrating sustainability considerations into modernization efforts can ensure long-term viability and positive environmental impacts.
The Future of Peer Review Modernization
The future of peer review system modernization trends promises to be transformative, driven by technological advancements and cultural shifts within the academic community. As stakeholders grow more accepting of open review processes, transparency is likely to become a cornerstone of scientific evaluation. This shift is expected to enhance the integrity and credibility of published research, fostering trust and confidence in the scientific enterprise.
Moreover, the continued evolution of AI and machine learning holds the potential for unprecedented levels of efficiency and accuracy in research assessments. Innovations in data analytics and natural language processing could enable more nuanced evaluations, identifying nuances and patterns that are otherwise overlooked. Crucially, this progress is anticipated to alleviate the burden on human reviewers, allowing them to focus on providing comprehensive feedback and mentoring emerging researchers.
In Charting the course for future advancements, ongoing dialogue and collaboration between stakeholders will be essential. This collaboration can ensure that modernization efforts are informed by the needs and expectations of the scientific community, while fostering an atmosphere of adaptation and acceptance. Ultimately, the future of peer review system modernization trends will rely on a shared commitment to embracing change, ensuring that the process remains robust, fair, and aligned with the evolving landscape of academic research.
Conclusion on Peer Review Modernization
In conclusion, peer review system modernization trends offer numerous opportunities to revolutionize scientific publishing. The integration of technological advancements, coupled with a shift towards open and transparent processes, signifies a new era in academic evaluation. By embracing these trends, the academic community can mitigate existing challenges and develop a more efficient, collaborative, and equitable peer review process.
However, overcoming resistance and navigating the complexities associated with modernization requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders. Through engagement, education, and continuous improvement initiatives, the potential benefits of modernization can be fully realized. Ultimately, the pursuit of innovation in peer review processes will bolster the credibility and impact of scientific research, ensuring its relevance and reliability in a rapidly changing world.