The pressing issue of climate change necessitates the urgent adoption of sustainable practices across all sectors, including agriculture. Farming, by its very nature, significantly contributes to environmental degradation, primarily through greenhouse gas emissions. As global awareness of environmental issues increases, the focus on carbon footprint reduction in farming has become paramount. Adopting practices that minimize carbon emissions not only preserves the environment but also enhances the long-term viability of agricultural enterprises.
Read Now : Efficient Data Exchange Mechanisms
Innovative Technologies and Practices
The implementation of innovative technologies and practices plays a crucial role in carbon footprint reduction in farming. Techniques such as precision agriculture, which involves the use of GPS and remote sensing technologies, enable farmers to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently. This targeted approach not only optimizes resource use but also minimizes emissions associated with over-application. Furthermore, soil management practices such as conservation tillage and cover cropping help sequester carbon and reduce the need for synthetic inputs. In addition, renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can be integrated into farming operations to decrease reliance on fossil fuels, thereby contributing to carbon footprint reduction in farming. These advancements underscore the significant potential for technological integration in promoting sustainable farming practices.
Sustainable Livestock Management
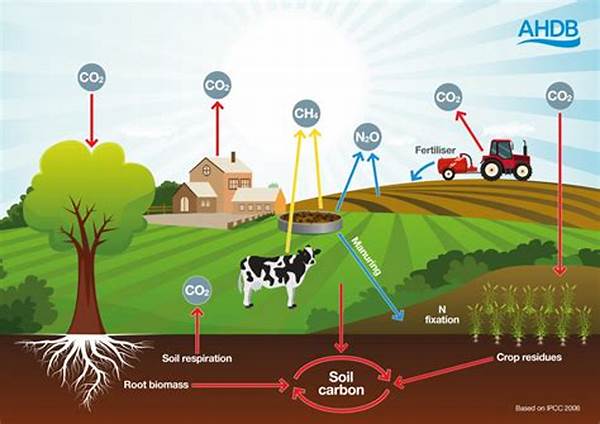
1. Implementing rotational grazing practices can significantly contribute to carbon footprint reduction in farming. By allowing pastures to regenerate, carbon sequestration is enhanced, thus reducing net emissions.
2. The adoption of feed additives that reduce methane emissions from ruminants is a promising strategy for carbon footprint reduction in farming. Such additives can enhance digestive efficiency while curbing greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Sustainable manure management practices, including anaerobic digestion, can also facilitate carbon footprint reduction in farming. These practices help capture methane emissions, converting them into usable energy forms.
4. Genetic selection for livestock that have lower methane emissions profiles presents another avenue for carbon footprint reduction in farming. Breeding low-emission animals is a long-term strategy that aligns with sustainability goals.
5. Promoting local sourcing of feed materials not only supports regional economies but also reduces transportation emissions, contributing to carbon footprint reduction in farming.
Enhancing Soil Carbon Sequestration
Carbon footprint reduction in farming is significantly supported by enhancing soil carbon sequestration. This involves adopting practices that increase the organic matter content in soil, thus capturing more carbon. Techniques such as agroforestry, which integrates trees into agricultural landscapes, contribute to increased carbon storage in both biomass and soil. Cover cropping and crop rotation also play vital roles in improving soil health and carbon retention. By maintaining continuous ground cover, soil erosion is minimized, and carbon loss is reduced. Additionally, integrating organic matter such as compost or biochar into soils can substantially elevate carbon sequestration rates. This approach highlights the multi-faceted benefits of soil management as a key strategy for carbon footprint reduction in farming.
Read Now : Performance Optimization For Microservices
Economic Implications of Carbon Footprint Reduction
Reducing the carbon footprint in farming can have considerable economic implications for agricultural producers. By adopting sustainable practices, farmers may experience cost reductions in inputs such as fertilizers and fuels. Additionally, carbon footprint reduction in farming can open new revenue streams through carbon credit markets and increased consumer demand for sustainably produced goods. These financial benefits can offset initial investment costs associated with adopting sustainable practices. Furthermore, promoting a low-carbon farming approach enhances the farm’s resilience to climate variability, safeguarding future yields. Thus, economic incentives are closely linked with the efforts towards carbon footprint reduction in farming.
Policy and Regulation in Promoting Carbon Reduction
Governments and international bodies have a pivotal role in addressing carbon footprint reduction in farming through policy and regulation. By establishing clear guidelines and providing financial incentives, policymakers can encourage farmers to adopt sustainable practices. Carbon taxes and subsidies for renewable energy adoption are examples of regulatory tools that drive behavioral change in the agricultural sector. Moreover, by facilitating access to technology and information, policy frameworks can empower farmers to implement carbon-saving practices effectively. Cooperation between governments, NGOs, and the private sector is essential to foster an environment conducive to widespread carbon footprint reduction in farming efforts.
Community Engagement and Education
Efforts towards carbon footprint reduction in farming are significantly bolstered by community engagement and education initiatives. Educating farmers and communities about the impacts of agriculture on climate change and the benefits of sustainable practices fosters a culture of environmental stewardship. Extension services and farmer-to-farmer knowledge exchange platforms are crucial in disseminating information on best practices. By involving local communities in decision-making processes, tailored strategies can be developed that recognize the unique challenges and opportunities within specific regions. Community involvement ensures that carbon footprint reduction in farming is not only a scientific and economic endeavor but also a socially inclusive process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey towards carbon footprint reduction in farming is multifaceted, necessitating the integration of technology, sustainable practices, and supportive policy frameworks. The agricultural sector must embrace innovation to address its environmental impact, particularly in the face of climate change. By striving for carbon footprint reduction in farming, producers not only contribute to global sustainability goals but also secure the economic viability of their operations. Collaborative efforts across the industry, academia, and government are critical in advancing sustainable farming practices. As these initiatives gain momentum, they will play a vital role in shaping a resilient agricultural landscape for future generations.