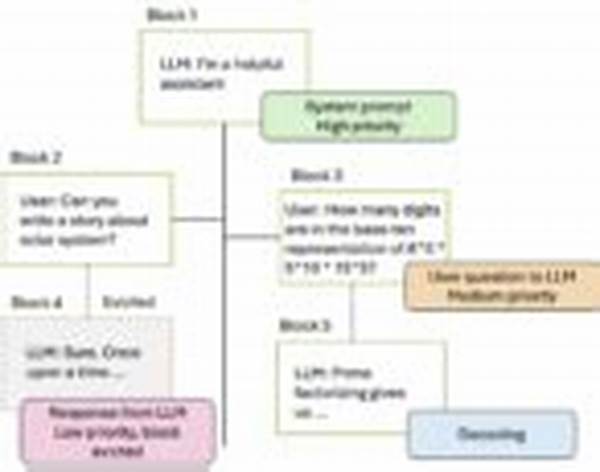
In the ever-evolving realm of computing, where data management is of paramount significance, cache eviction emerges as a crucial process. Cache eviction refers to the method of removing old or unnecessary data from cache storage to make room for new data. As data proliferates, traditional eviction strategies such as least recently used (LRU) or first-in, first-out (FIFO) often fall short in optimizing resources. Herein lies the significance of priority-based cache eviction logic. This advanced approach not only considers the recency or frequency of data access but also assigns a priority level to each piece of data, thus ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation. By utilizing prioritization, data retrieval becomes more efficient, and the system’s overall performance is significantly enhanced.
Read Now : Api Capacity Planning Techniques
Understanding Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
Priority-based cache eviction logic uniquely positions itself in data management by emphasizing the importance of assigning varying priority levels to different data entries. Contrary to conventional methods that treat all data uniformly, this logic enables systems to retain more critical information longer, thus mitigating performance bottlenecks. As a result, systems employing priority-based cache eviction logic experience reduced latency and improved response time, catering effectively to high-demand environments. Furthermore, priority-based cache eviction logic empowers applications to adapt to workload variations dynamically, making the system more resilient to changing data patterns and access frequencies. This adaptive feature is vital, given today’s rapidly shifting computational requirements.
Key Aspects of Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
1. The implementation of priority-based cache eviction logic addresses the limitations of traditional eviction methods.
2. By assigning priority levels, critical data can be retained longer in cache storage.
3. Priority-based cache eviction logic improves system response times and reduces latency.
4. Dynamic adaptation to workload variations is a significant advantage of priority-based cache eviction logic.
5. This logic offers resilience to changing computational demands, enhancing overall system efficiency.
The Mechanisms Behind Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
Priority-based cache eviction logic operates on several principles. Initially, data is analyzed and assigned a priority level based on predefined criteria, such as frequency of access, data value, and relevance to system operations. These criteria ensure that essential data remains readily accessible. Following this assessment, the system evaluates the cache’s current storage capacity to determine if eviction is necessary. In scenarios necessitating eviction, lower priority data is discarded first, preserving high-priority entries. Furthermore, this logic facilitates proactive cache management by predicting potential data access trends, thereby preemptively adjusting cache contents. Consequently, priority-based cache eviction logic not only optimizes data retrieval but also enhances system reliability.
Read Now : Enhancing Api Throughput Capacity
Advanced Features of Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
Prioritization is an integral component of this logic, allowing for differentiated data treatment. This ensures that critical data is not prematurely evicted. Additionally, priority-based cache eviction logic incorporates predictive analytics to anticipate future data needs, providing a foresight advantage over traditional methods. Moreover, this logic supports scalability, making it suitable for both small-scale applications and expansive systems. By accommodating various data types and determining their importance, priority-based cache eviction logic ensures robust resource allocation. Crucially, the adaptability offered by this logic promotes seamless integration within diverse technological ecosystems, aligning with evolving computational landscapes. These attributes collectively enshrine priority-based cache eviction logic as a cornerstone of modern data management practices.
Applications and Efficacy of Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
The diverse applications of priority-based cache eviction logic span multiple sectors, including telecommunications, financial services, and healthcare, where rapid access to critical data is essential. By employing this logic, these sectors reduce response times, enhance user experience, and effectively manage high data loads. The efficacy of priority-based cache eviction logic lies in its strategic allocation of cache resources, which mitigates undue strain on system operations. By adapting to varied data demands, this logic provides businesses a competitive edge, ensuring data integrity and availability. Moreover, the robust performance of systems utilizing priority-based cache eviction logic underscores its indispensability in navigating complex data landscapes. As data requirements continue to evolve, the logic’s prominence in optimizing cache utilization and maintenance remains undisputed.
Insights and Recommendations for Implementing Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
Implementing priority-based cache eviction logic requires a detailed understanding of system architecture and data flow. An in-depth analysis of data priorities ensures that resources are allocated effectively. Collaboration with IT professionals allows for customization, addressing specific operational needs. Regular monitoring is essential to assess the logic’s impact on system performance and to make necessary adjustments. Additionally, organizations should invest in training teams on the nuances of priority-based cache eviction logic to maximize its benefits. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, enterprises can effectively leverage this logic to enhance their data management capabilities, driving operational excellence.
Concluding Thoughts on Priority-Based Cache Eviction Logic
Priority-based cache eviction logic represents a paradigm shift in data management, addressing the inefficiencies of outdated methods through a sophisticated, priority-centred approach. By differentiating between data based on importance, it streamlines processes, reduces latencies, and augments system performance. Its predictive and adaptive capabilities ensure a resilient response to dynamic data environments. As organizations navigate increasingly complex data landscapes, the integration of priority-based cache eviction logic is not merely beneficial but essential. Embracing this advanced logic paves the way for optimized resource allocation and sustained competitive advantage in data-centric industries.