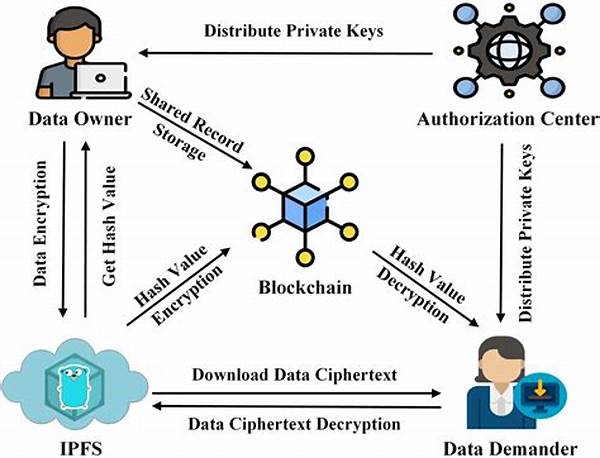
In an era where data integrity and transparency are paramount, blockchain technology offers revolutionary potential. Elusive and prone to manipulation, traditional data verification methods often undermine trust. By leveraging the immutability and decentralization of blockchain, transparent data verification emerges as a credible solution to contemporary challenges of data authenticity.
Read Now : Evaluating Outcomes Of Transformative Education
The Core Principles of Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
Transparent data verification via blockchain is grounded in principles of decentralization, immutability, and transparency. Blockchain stores data across a distributed network, ensuring no single point of failure or control. This decentralization empowers users, eliminating intermediaries and reducing vulnerability to data breaches. Immutability is another cornerstone, as once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered, ensuring a consistent and reliable audit trail. Transparency is inherent in the public nature of blockchain; stakeholders can verify records, facilitating accountability. Moreover, cryptographic principles underlie each transaction, enhancing security and trust. Embracing these principles, transparent data verification via blockchain provides an innovative framework addressing the intrinsic challenges associated with traditional verification methods, fostering enhanced trust and reliability in data-dependent industries.
Advantages of Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
1. Enhanced Security: Transparent data verification via blockchain provides robust security against unauthorized access and tampering, as blockchain’s cryptographic nature safeguards data integrity.
2. Decentralized Control: Unlike traditional systems, blockchain decentralizes control, eliminating potential single points of failure in transparent data verification processes.
3. Improved Trust: Stakeholders can independently verify data on the blockchain, thereby fostering a sense of trust and integrity due to its transparent nature.
4. Cost Efficiency: By removing intermediaries, transparent data verification via blockchain can reduce the costs associated with traditional verification methods.
5. Real-time Verification: Transactions are verified in real time with transparent data verification via blockchain, offering timely assurance of data authenticity and reliability.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
Despite its advantages, transparent data verification via blockchain faces several challenges. The technology’s nascent nature means that scalability issues persist, hindering its ability to handle high volumes of data swiftly. Moreover, integrating blockchain into existing systems may involve significant costs and complexities, necessitating comprehensive change management. Regulatory concerns also arise as legal frameworks struggle to keep pace with technological advancements. However, these challenges should not overshadow the immense potential blockchain holds in reshaping data verification. Concerted efforts by stakeholders can address these barriers, unlocking the vast benefits of transparent data verification via blockchain. Therefore, a judicious approach to implementation, informed by thorough understanding and adaptation, remains essential.
Key Features of Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
Transparent data verification via blockchain is characterized by distinct features:
1. Decentralized Ledger: Data entries are distributed across multiple nodes, ensuring no single point of control.
2. Immutable Records: Once recorded, data cannot be altered, providing a permanent historical record.
3. Cryptographic Security: Advanced cryptographic algorithms secure transactions, ensuring data integrity.
4. Transparency: Open-access nature allows stakeholders to verify and audit data independently.
Read Now : Impact Of Virtual Education Environments
5. Consensus Mechanism: Nodes validate transactions via agreed mechanisms, ensuring consistency.
6. Smart Contracts: Automate and enforce compliance, reducing manual intervention.
7. Interoperability: Easily integrates with diverse systems, enhancing functionality.
8. Auditability: Detailed logs enable effective auditing and compliance checks.
9. Real-time Verification: Immediate transaction validation ensures timely data authenticity.
10. Cost-efficiency: Reduces reliance on intermediaries, cutting associated costs.
Implications and Future Prospects of Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
The future of transparent data verification via blockchain is promising yet complex. Its potential to revolutionize industries, from finance to healthcare, is vast. The immutable and decentralized properties of blockchain enhance data integrity, opening avenues for more secure transactions and interactions. As industries continue to adopt blockchain, the need for standardized protocols becomes increasingly critical. Furthermore, the technology’s adaptability facilitates diverse applications, potentially more transformative than current usages. However, addressing existing technical limitations is imperative for wider adoption and effectiveness. The consortium approach, where multiple industries collaborate to standardize practices, is notable. This collective effort can propel blockchain from a nascent technology to a pervasive solution in transparent data verification. Awareness and education also play vital roles, equipping stakeholders with essential knowledge to harness blockchain’s benefits effectively.
Technological Advancements in Transparent Data Verification via Blockchain
The rapid advancement of blockchain technology holds significant implications for transparent data verification processes. Innovations in consensus algorithms promise to enhance scalability, addressing current limitations in processing speed and capacity. Additionally, pioneering research in quantum-resistant cryptography aims to future-proof blockchain against emerging security threats. As blockchain evolves, integration with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, is poised to expand its applicability. These integrations will enable more sophisticated, automated, transparent data verification systems capable of processing complex datasets in real-time. Moreover, advancements in interoperability protocols will facilitate seamless communication between disparate systems, reducing friction and enhancing efficiency. However, these technological advancements must be complemented by regulatory evolution to ensure ethical standards and compliance are maintained as blockchain technology transforms transparent data verification processes.
Conclusion
In summation, transparent data verification via blockchain represents a paradigm shift in how data integrity and credibility are ensured. By exploiting blockchain’s inherent properties of decentralization, immutability, and transparency, industries can overcome traditional verification challenges. However, the adoption of this innovative approach necessitates careful consideration of associated challenges. Regulatory adaptations, technological advancements, and stakeholder collaborations are crucial to unlocking the full potential of blockchain. Nonetheless, with strategic initiatives, transparent data verification via blockchain is poised to reshape not only data verification practices but also the broader landscape of data management across various sectors. As businesses and governments strive for more reliable data, blockchain emerges as an indispensable ally in this transformative journey towards transparency and trustworthiness in data verification.