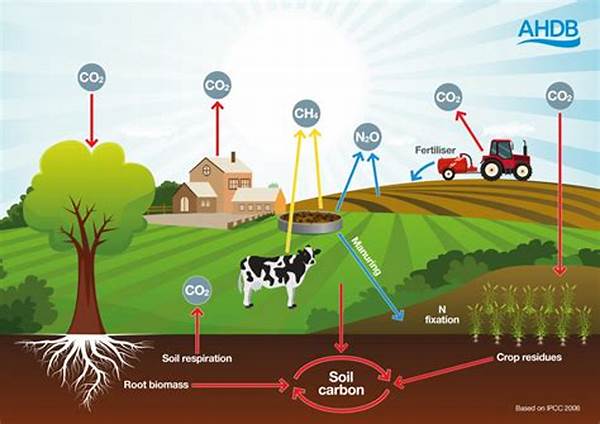
The critical intersection of sustainable farming and emissions reduction is of paramount importance in addressing contemporary environmental challenges. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food production is escalating, placing significant pressure on agricultural systems. Traditional farming methods, while productive, have contributed to considerable greenhouse gas emissions, prompting the urgent need for more sustainable practices. This article explores the integral relationship between sustainable farming methods and the reduction of emissions, focusing on innovative agricultural strategies that promise to mitigate climate change impacts while ensuring food security.
Read Now : Api-first Approach For Business Agility
The Importance of Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable farming is pivotal in mitigating the detrimental environmental effects associated with traditional agricultural practices. By incorporating eco-friendly techniques, farms can significantly minimize their carbon footprint, contributing to emissions reduction. Practices such as crop rotation, organic farming, and integrated pest management play a crucial role in enhancing soil health and biodiversity, while concurrently reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers and pesticides. These methods not only lower greenhouse gas emissions but also promote carbon sequestration, which is essential in combating climate change. Furthermore, the adoption of renewable energy sources and precision agriculture technology fosters resource efficiency, further supporting the goals of sustainable farming and emissions reduction. The transformation towards sustainable agriculture is not merely an environmental imperative but also an economic opportunity, offering a pathway to innovative market developments in eco-friendly products and renewable energy.
Key Strategies in Sustainable Farming and Emissions Reduction
1. Agroforestry and Carbon Sequestration: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes increases carbon storage and enhances biodiversity, contributing to emissions reduction.
2. Conservation Tillage: Reducing soil disturbance minimizes soil carbon loss, thereby supporting sustainable farming and decreasing emissions.
3. Renewable Energy Adoption: Utilizing solar and wind energy in farms reduces reliance on fossil fuels, aligning with sustainable farming and emissions reduction goals.
4. Precision Agriculture: Implementing data-driven farming techniques enhances resource efficiency, critical for sustainable farming and emissions reduction.
5. Organic Farming: Eliminating synthetic fertilizers and pesticides reduces emissions associated with their production and application.
Innovative Technologies in Sustainable Farming
Technological innovation is at the forefront of sustainable farming and emissions reduction. Recent advancements have paved the way for precision agriculture, where technologies like drones, GPS mapping, and sensor-based soil monitoring allow farmers to optimize inputs, reducing waste and emissions. Another significant advancement is the development of biochar, a charcoal-like substance that, when added to soil, enhances its carbon storage capacity. These technologies provide tangible paths toward lowering the carbon footprint of agricultural activities. Furthermore, the advent of vertical farming and hydroponics presents opportunities for urban agriculture to flourish, offering local food production with minimized land use and emissions. These novel methods exemplify the potential of integrating technology into sustainable farming strategies. By harnessing such innovations, the agricultural sector can effectively contribute to emissions reduction, ensuring a resilient food system that aligns with environmental sustainability goals.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Farming
1. Cost and Accessibility: Transitioning to sustainable farming requires substantial investment, often beyond the reach of small-scale farmers, posing a barrier to emissions reduction.
2. Knowledge and Training: Farmers require adequate knowledge and training to implement sustainable practices effectively.
3. Infrastructure and Technology Gaps: Limited access to modern technology and inadequate infrastructure can hinder sustainable farming efforts.
4. Policy and Regulation: Inconsistent or lack of supportive policies can impede the necessary transition towards sustainable practices.
Read Now : Biodiversity Conservation Management Practices
5. Market Incentives: Without market incentives, farmers may lack motivation to adopt emissions reduction practices.
6. Climate Variability: Unpredictable weather patterns challenge the adaptation of sustainable farming techniques designed for emissions reduction.
7. Soil Degradation: Severe soil degradation can limit the effectiveness of sustainable farming practices.
8. Water Scarcity: Sustainable farming often demands efficient water use, which may be challenging in arid regions.
9. Pest and Disease Management: Organic and low-impact pest controls are essential but may be less effective, complicating emissions reduction efforts.
10. Consumer Awareness and Demand: Increasing consumer demand for sustainably produced food needs to drive market changes.
Long-term Benefits of Sustainable Farming and Emissions Reduction
The long-term benefits of sustainable farming and emissions reduction extend far beyond immediate environmental impacts. Notably, sustainable farming practices rejuvenate soil health, thereby increasing agricultural productivity and resilience against climate change impacts. By halting land degradation and enhancing biodiversity, these practices ensure long-term land-use viability, critical for food production continuity. Furthermore, sustainable methods reduce farmers’ dependency on costly synthetic inputs, leading to improved economic stability. In terms of public health, minimizing chemical usage in farming decreases the prevalence of water and soil pollution, benefiting both ecosystems and human populations. As sustainable farming practices gain traction, they create a ripple effect encouraging industries to adopt more sustainable operations, ultimately contributing to comprehensive emissions reduction and fostering a low-carbon economy. These enduring benefits underline the necessity of global collaboration in promoting sustainable farming as a cornerstone of sustainable development goals.
Conclusion: Advancing Sustainable Farming for Future Generations
The progressive integration of sustainable farming and emissions reduction is imperative for cultivating a future where agriculture supports both human and planetary health. Policymakers, farmers, and consumers must collaboratively engage in this transition toward sustainability. By prioritizing education, investment, and policy support, we can propel the widespread adoption of sustainable farming practices, thus substantially curbing agricultural emissions. Empowering local communities and fostering international cooperation will be critical in standardizing sustainable approaches and sharing best practices globally. As sustainable farming becomes the norm rather than the exception, its positive impacts on emissions reduction, food security, and global health will set the foundation for a resilient agricultural system capable of sustaining the needs of future generations. In conclusion, the shift towards sustainable farming is not optional, but a necessary evolution in achieving a sustainable future.