Agroforestry, the integration of trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, offers a sustainable approach to habitat restoration. This practice is gaining recognition as an effective strategy to restore ecosystems, combat climate change, and enhance biodiversity. The following sections explore various dimensions of agroforestry practices for habitat restoration, its significance, and practical applications.
Read Now : **peer Review Quality Control**
Understanding Agroforestry Practices for Habitat Restoration
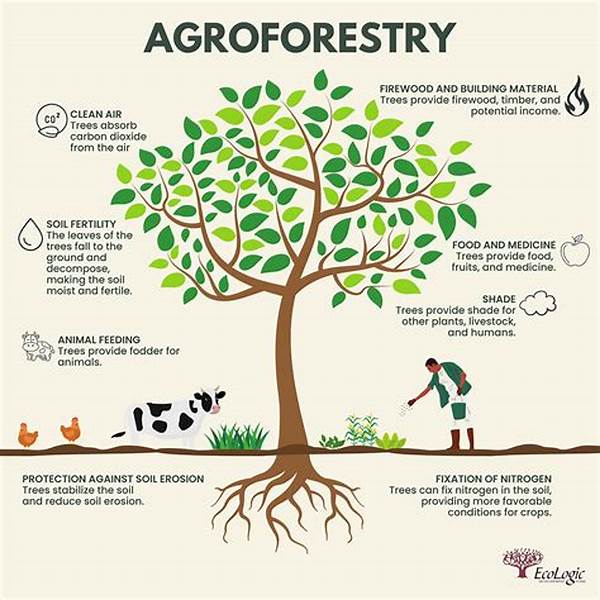
Agroforestry practices for habitat restoration involve the deliberate inclusion of woody perennials into agricultural systems. This strategic integration aims to restore and conserve native habitats while providing economic and environmental benefits to agricultural lands. Agroforestry establishes a symbiotic relationship between agricultural activities and natural ecosystems, fostering biodiversity, improving soil health, and reducing deforestation rates. These practices are particularly effective in regions experiencing severe land degradation due to unsustainable farming techniques. By creating a multi-functional landscape, agroforestry enhances habitat connectivity and provides shelter and food for diverse wildlife species.
A key advantage of agroforestry practices for habitat restoration is their ability to improve soil fertility and structure. Tree roots help in stabilizing the soil, reducing erosion, and facilitating water infiltration, which is crucial for vegetation regeneration. Moreover, agroforestry systems can sequester significant amounts of carbon, thus contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. As trees capture atmospheric carbon dioxide, they help in restoring the carbon balance, making these practices invaluable in addressing global warming challenges. Consequently, agroforestry not only supports ecological restoration but also fortifies agricultural productivity by maintaining a healthy environment.
Key Benefits of Agroforestry Practices for Habitat Restoration
1. Biodiversity Enhancement: Agroforestry practices for habitat restoration create diverse ecosystems that support various flora and fauna, leading to increased biodiversity.
2. Soil Erosion Control: The presence of trees and shrubs helps prevent soil erosion, thus maintaining the quality and fertility of the land.
3. Water Conservation: Agroforestry systems improve water retention and groundwater recharge, essential for sustaining both agriculture and natural habitats.
4. Climate Change Mitigation: By capturing carbon dioxide, agroforestry practices for habitat restoration play a significant role in carbon sequestration.
5. Economic Viability: These practices can increase agricultural productivity and provide additional income sources through timber and non-timber forest products.
Implementing Agroforestry Practices for Habitat Restoration
Successful implementation of agroforestry practices for habitat restoration requires comprehensive planning and collaboration among stakeholders. Landowners, farmers, environmentalists, and government agencies must work together to design agroforestry systems suited to specific ecological and socioeconomic contexts. Identifying native species that thrive in local conditions is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of these practices. Moreover, ongoing management and monitoring are essential to adapting practices to changing environmental conditions, securing long-term ecological gains.
Agroforestry practices for habitat restoration can be tailored to different landscapes, from temperate to tropical regions, each with its unique ecological requirements. For example, in regions affected by desertification, introducing drought-resistant tree species can aid in restoring arid landscapes. Communities can benefit from educational programs that raise awareness about the benefits and techniques of agroforestry, facilitating widespread adoption. By integrating these systems, agricultural areas can transition into models of sustainability, balancing human needs with ecological restoration objectives.
Challenges in Agroforestry Practices for Habitat Restoration
Implementing agroforestry practices for habitat restoration is not without challenges. Several obstacles can hinder the successful adoption and execution of these practices:
1. Lack of Awareness: A significant barrier is the lack of awareness about the benefits and methods of agroforestry among farmers and landowners.
2. Initial Costs: The initial investment required for establishing agroforestry systems can be prohibitive for small-scale farmers.
3. Technical Expertise: Proper implementation often requires technical knowledge and expertise that may not be readily available in certain regions.
Read Now : Advanced Api Management Platforms
4. Policy and Regulation: Inadequate policies and regulatory frameworks can limit the expansion of agroforestry practices for habitat restoration.
5. Market Access: Limited access to markets for agroforestry products can hinder farmers from reaping the economic benefits of these practices.
6. Competing Land Use: There can be competition for land between agricultural needs and conservation goals, complicating land-use planning.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously assessing the effectiveness of agroforestry systems is essential but can be complex and resource-intensive.
8. Climate Variability: Unpredictable climate conditions pose challenges in selecting appropriate species and management practices.
9. Cultural Acceptance: Local cultural practices and traditional farming approaches can impact the acceptance and integration of agroforestry.
10. Infrastructural Limitations: Lack of infrastructure such as roads and transportation can limit the implementation and scaling up of these practices.
Promoting Agroforestry Practices for Habitat Restoration
To maximize the benefits of agroforestry practices for habitat restoration, it is imperative to create supportive environments that encourage their development. Government incentives and subsidies can motivate farmers to adopt these practices by offsetting initial costs and providing financial support. Building partnerships with NGOs and educational institutions can facilitate knowledge transfer and capacity building, equipping communities with the necessary skills and resources.
Furthermore, integrating agroforestry practices into national land management and conservation strategies can amplify their impact. Including agroforestry programs in educational curricula can raise awareness among younger generations, fostering a culture of sustainable land management. Research and development initiatives aimed at improving agroforestry techniques and demonstrating their long-term benefits can aid in overcoming technical and cultural barriers. By promoting an inclusive framework for agroforestry, both ecological restoration and economic development objectives can be achieved in harmony.
The Role of Agroforestry Practices in Biodiversity Conservation
Agroforestry practices for habitat restoration play a pivotal role in biodiversity conservation by establishing corridors that connect fragmented habitats. These practices allow species to move freely, decreasing vulnerability to extinction. The diversified structures within agroforestry landscapes create niches for various organisms, supporting pollinators, pest predators, and other beneficial wildlife. Engaging communities in conservation efforts through agroforestry initiatives can also enhance social-ecological resilience, as local stewardship ensures sustained management of restored habitats.
Conclusion
In summary, agroforestry practices for habitat restoration provide a multifaceted approach to addressing ecological and socio-economic challenges. By enhancing biodiversity, improving soil and water resources, and mitigating climate change effects, agroforestry practices pave the way for sustainable habitat restoration. Through collective efforts and informed policies, the adoption of agroforestry can transform landscapes, contributing to a balanced coexistence of agricultural productivity and natural ecosystem health. As the global community strives toward environmental sustainability, agroforestry stands out as a viable and promising solution.