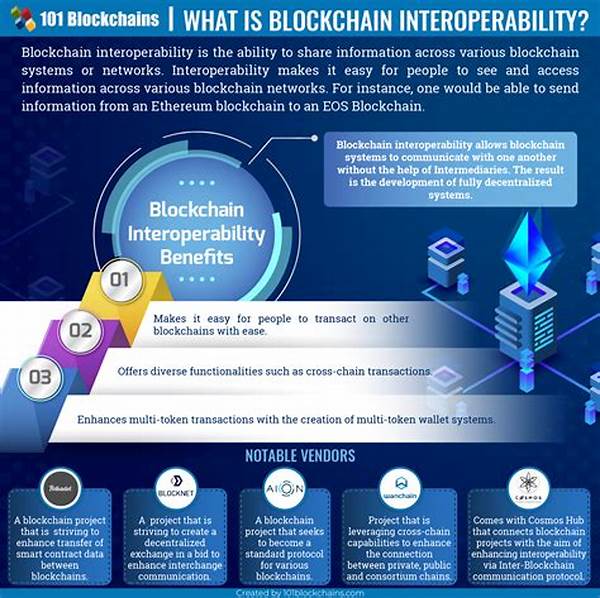
Introduction to Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
In the current digital landscape, the notion of interoperability and decentralization plays a pivotal role in the evolution of data frameworks. Interoperable decentralized data frameworks are designed to allow different systems and organizations to access, share, and utilize data in a seamless manner, without compromising control or ownership. These frameworks leverage decentralized technologies, such as blockchain, to ensure that data remains secure, transparent, and immutable while being accessible across various platforms.
Read Now : Standards For Diverse Learning Assessment
The advent of interoperable decentralized data frameworks marks a significant shift from traditional data management practices that often struggle with issues related to data silos and lack of compatibility. By embracing decentralization, organizations can foster an environment where data flows more freely, enhancing collaboration and innovation. These frameworks offer a solution to the challenges posed by proprietary systems that limit the effectiveness of data-sharing activities.
Furthermore, interoperable decentralized data frameworks ensure that data privacy and security are prioritized, mitigating risks associated with centralized data storage. With data being a critical asset, these frameworks offer a future-proof approach to managing and harnessing information effectively. Adopting such systems can be transformative, empowering organizations to leverage data in new and advanced ways, ultimately contributing to a more connected and efficient global digital ecosystem.
Key Features of Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
1. Enhanced Data Accessibility: Interoperable decentralized data frameworks allow seamless data sharing across various platforms, enhancing accessibility while maintaining data integrity.
2. Robust Security Protocols: By design, interoperable decentralized data frameworks employ advanced cryptographic methods to ensure data security, providing a robust defense against unauthorized access.
3. Scalability: These frameworks offer scalable solutions, accommodating growing data requirements without performance degradation, thus ensuring consistent data availability.
4. Efficient Data Governance: Interoperable decentralized data frameworks facilitate effective data governance, empowering organizations to enforce policies and standards while maintaining data control.
5. Cost-Efficiency: Implementing interoperable decentralized data frameworks can reduce operational costs by eliminating intermediaries and inefficiencies inherent in traditional data systems.
Technological Innovations in Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
Recent advancements in technology have been instrumental in accelerating the development of interoperable decentralized data frameworks. The integration of distributed ledger technologies, such as blockchain, has provided a new dimension to these frameworks, ensuring that data remains immutable and transparent. This innovation allows for the creation of trustless environments where data can be verified without relying on a central authority.
Moreover, the rise of smart contracts has further enhanced the capabilities of interoperable decentralized data frameworks. By automating predefined conditions and transactions, smart contracts facilitate efficient and error-free data exchanges between entities. Such technological advancements are pivotal in overcoming challenges related to traditional data management systems, which often suffer from lack of transparency and efficiency.
The integration of machine learning algorithms within interoperable decentralized data frameworks also presents new opportunities for data analysis and knowledge discovery. By harnessing the power of decentralized data, machine learning can uncover patterns and insights that were previously inaccessible. This convergence of technologies represents a significant leap forward, transforming the way organizations interact with and derive value from their data assets.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
1. Interoperability Challenges: Ensuring compatibility among diverse systems is a significant hurdle for interoperable decentralized data frameworks, requiring standardized protocols and formats.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex regulatory landscapes can be challenging, necessitating adherence to data privacy laws and standards in interoperable decentralized data frameworks.
3. Technical Complexity: The sophisticated nature of interoperable decentralized data frameworks may require advanced technical expertise, which can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
4. Adoption and Integration Costs: Initial expenses associated with deploying interoperable decentralized data frameworks can be high, but long-term benefits often justify the investment.
5. Scalability Concerns: Scaling interoperable decentralized data frameworks to accommodate larger datasets and user bases demands robust infrastructure and resources.
6. Data Quality Issues: Maintaining high data quality and consistency is crucial, requiring effective data validation and cleansing processes within interoperable decentralized data frameworks.
Read Now : **data Security In Api Usage**
7. User Engagement: Encouraging user participation and engagement remains a challenge; user-friendly interfaces and proper training can facilitate smoother adoption.
8. Cybersecurity Threats: Protecting against evolving cybersecurity threats is vital, necessitating continuous monitoring and updates to interoperable decentralized data frameworks.
9. Trust Issues: Building trust among stakeholders is essential for successful deployment, achieved through transparent operations and effective communication strategies.
10. Organizational Resistance: Overcoming resistance to change requires strong leadership, clear vision, and effective change management strategies to integrate interoperable decentralized data frameworks.
Benefits and Opportunities of Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
Interoperable decentralized data frameworks offer numerous advantages that can significantly alter the existing data landscape. One of the primary benefits is enhanced data accessibility, enabling organizations to seamlessly access and share data across various platforms and networks. This accessibility is fundamental for promoting collaboration and innovation, paving the way for new opportunities in various sectors.
These frameworks also provide robust security measures that protect data from unauthorized access and potential breaches. By utilizing cutting-edge cryptographic techniques and decentralized mechanisms, organizations can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their data, boosting trust among stakeholders. This security feature is vital in industries where data protection is paramount, such as finance and healthcare.
Furthermore, interoperable decentralized data frameworks exhibit a high degree of scalability, accommodating growing data volumes and expanding user bases without compromising performance. The ability to efficiently scale operations is crucial in a digital age where data is exponentially increasing. This scalability, combined with reduced operational costs and improved efficiency, makes these frameworks a viable solution for future data management needs.
Future Prospects of Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
The future of interoperable decentralized data frameworks appears promising with ongoing advancements in technology and infrastructure. As more organizations recognize the value of these frameworks, adoption rates are expected to rise, leading to broader industry-wide transformations. The convergence of technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), with interoperable decentralized data frameworks will unlock new potential for data-driven insights and decision-making.
Moreover, as data becomes more integral to competitive advantage, the demand for solutions that ensure seamless, secure, and efficient data management will grow. Interoperable decentralized data frameworks stand at the forefront of this evolution, poised to redefine how data is managed and utilized. Their potential to foster a more interconnected and data-rich ecosystem holds promise for significant progress in various domains, including smart cities, supply chain management, and beyond.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of interoperable decentralized data frameworks in providing effective solutions for complex data challenges will be ever more critical. The journey towards a fully interoperable and decentralized data-driven future is underway, presenting unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth.
Conclusion: The Impact of Interoperable Decentralized Data Frameworks
The emergence of interoperable decentralized data frameworks signifies a fundamental shift in the way data is perceived and utilized within organizations. By prioritizing interoperability and decentralization, these frameworks set a new standard for data management, characterized by enhanced security, accessibility, and efficiency. This transformation holds the potential to revolutionize how organizations operate, breaking down silos and fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
The implications of these frameworks extend far beyond the technology sector, influencing numerous industries that rely on data for strategic decision-making. As the adoption of interoperable decentralized data frameworks continues to expand, organizations will likely experience increased competitive advantage and improved operational effectiveness. This advancement marks a decisive step toward a future where data can be leveraged to drive innovation and growth in unprecedented ways.
To fully realize the potential of interoperable decentralized data frameworks, ongoing investment in research, development, and education is essential. By building a strong foundation for these frameworks, stakeholders can ensure they remain adaptable to future challenges and opportunities. The transformative power of these frameworks lies in their ability to empower organizations to harness the full potential of their data, opening doors to a more connected, efficient, and prosperous digital world.