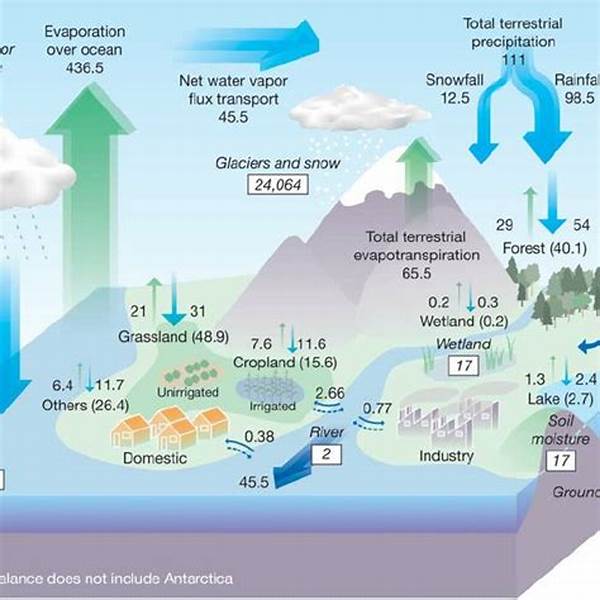
The Interconnection between Climate Change and Hydrological Cycles
Climate change is increasingly altering the dynamics of hydrological cycles, a fundamental component of Earth’s environmental system. The hydrological cycle, which involves the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth, is experiencing significant disruptions due to the changing climate. The primary drivetrain behind these changes is the increase in atmospheric temperatures, which intensifies evaporation rates and alters precipitation patterns. This, in turn, affects the availability and distribution of water resources across the globe. As climate change progresses, the hydrological cycles are expected to become increasingly unstable, leading to more frequent and intense weather events such as floods and droughts. These disruptions pose significant challenges for water management systems, which must adapt to the changing availability and reliability of water resources.
Read Now : Integrated Water Resource Management Policies
Moreover, climate change-induced shifts in hydrological cycles have profound implications for ecosystems and biodiversity. Altered precipitation patterns can disrupt habitats, affecting plant and animal species that rely on specific climatic conditions. Such changes can lead to shifts in biodiversity and even species extinction in affected regions. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of extreme weather events can exacerbate the vulnerability of ecosystems, further diminishing biodiversity. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive research and adaptive strategies that accommodate the evolving relationship between climate change and hydrological cycles. Collaborative efforts across scientific, political, and social spheres are necessary to mitigate the adverse impacts on natural and human-managed systems.
In conclusion, the impact of climate change on hydrological cycles is a critical environmental issue that demands global attention. The complexity of interlinked natural processes necessitates a comprehensive understanding of how climate change affects water cycles and the downstream implications for ecosystems and human societies. By embracing global cooperation and innovative approaches, humanity can work towards mitigating the impact of climate change on the hydrological cycle and preserving the planet’s essential water resources.
Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrological Cycles
1. Climate change influences the hydrological cycles by altering precipitation patterns globally, which can result in increased intensity and frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods. This affects water availability, leading to challenges in water resource management and planning.
2. The rise in global temperatures due to climate change impacts the evaporation rates within hydrological cycles. Higher temperatures lead to increased evaporation from land and water bodies, which ultimately influences precipitation and the overall distribution of water resources.
3. As polar ice caps and glaciers melt under the influence of climate change, the hydrological cycles experience alterations. The resulting increase in sea levels and changes in freshwater distribution impact coastal areas and freshwater availability, posing threats to communities and ecosystems.
4. Climate change has led to shifts in the timing and intensity of seasonal hydrological cycles, affecting agricultural practices and food security. Changes in water availability during critical growing periods can lead to reduced crop yields and increased vulnerability for farming communities worldwide.
5. The interrelation between climate change and hydrological cycles poses significant challenges for sustaining freshwater ecosystems. Altered water temperatures and flow patterns can impact aquatic habitats, leading to potential biodiversity loss and changes in species compositions within ecosystems.
Climate Change and Hydrological Cycle Disruptions
The intricate relationship between climate change and hydrological cycles presents significant environmental and socioeconomic challenges that demand urgent attention. Climate change not only affects the global temperature but also disrupts the delicate balance of Earth’s water systems. As global temperatures rise, evaporation rates increase, leading to alterations in precipitation patterns. This imbalance results in extended droughts in some regions while others may experience excessive rainfall and flooding. The direct impacts are far-reaching, affecting water supply, agriculture, energy production, and human settlement patterns.
Furthermore, climate change-induced disruptions to hydrological cycles exacerbate the challenges associated with water scarcity and overabundance. Regions that were once reliant on predictable seasonal rainfalls now face uncertainty and potential water shortages. This necessitates innovative water management strategies and infrastructure investments to ensure water availability and quality for future generations. Policymakers and environmental scientists must work collaboratively to devise adaptive strategies that consider both immediate responses and long-term resilience-building measures. By understanding the interconnectedness of climate change and hydrological cycles, societies can better prepare and adapt to these inevitable disruptions, ensuring ecological integrity and sustainable livelihoods for all.
Strategies for Managing Climate Change Impacts on Hydrological Cycles
1. Developing integrated water resource management systems can help mitigate the impacts of climate change on hydrological cycles by promoting sustainable water use and protection strategies.
2. Investing in advanced forecasting and modeling technologies aids in predicting climate-induced changes in hydrological cycles, enhancing preparedness and response capabilities.
3. Expanding efforts to restore and protect wetlands can buffer against extreme weather events, assisting in the management of climate change impacts on hydrological cycles.
4. Encouraging rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation practices supports climate adaptation by optimizing water use in agriculture and other sectors reliant on hydrological cycles.
5. Promoting conservation and reforestation efforts can improve watershed stability and resilience, mitigating the effects of climate change on the hydrological cycles’ sustainability.
6. Enhancing public awareness initiatives underscores the importance of conservation, reducing vulnerabilities emanating from climate change impacts on hydrological cycles.
Read Now : Voice-activated Communication Platforms
7. International cooperation and shared research can facilitate a collective response to the global changes occurring within climate systems and hydrological cycles.
8. Building infrastructure designed to withstand climate-induced hydrological variability ensures community resilience against extreme change impacts.
9. Implementing policies that regulate greenhouse gas emissions aids in mitigating the overarching influence of climate change on hydrological cycles.
10. Encouraging eco-friendly practices in urban development can minimize urban runoff, aiding in the preservation of natural hydrological cycles in urban environments.
Future Perspectives on Climate Change and Hydrological Cycles
As the effects of climate change continue to manifest with unprecedented intensity, the hydrological cycles stand at a crucial intersection of environmental science and policy development. Addressing this intricate relationship demands a multifaceted approach that positions resilience and sustainability at the forefront. Advancements in Earth system sciences provide critical insights into the impacts of climate change on hydrological cycles, offering valuable data that can shape effective policy interventions. Furthermore, the development of robust adaptation frameworks is imperative to manage the consequences of disrupted water cycles across diverse ecosystems and communities.
Future strategies should prioritize a cohesive integration of scientific research with socio-economic planning to enhance adaptive capacities. Policymakers are urged to pursue cross-disciplinary collaboration, leveraging technological innovations to improve prediction models and response mechanisms. Engaging both global and local communities in sustainable practices is essential to safeguard water resources while ensuring equitable access amidst a changing climate landscape. As the global community embraces these challenges, fostering a collective commitment towards reducing carbon footprints and investing in resilient infrastructure becomes vital.
Overall, the interplay between climate change and hydrological cycles underscores the necessity for immediate action and long-term vision. By implementing holistic measures that incorporate sustainable resource management, technological innovation, and environmental stewardship, humanity can forge a path towards safeguarding critical water systems. As societies advance together, addressing climate change’s impact on hydrological cycles exemplifies a global priority that resonates with both ecological preservation and human security.
Innovations in Hydrology to Combat Climate Change
Hydrology innovation initiatives are pivotal in addressing the extensive changes wrought by climate change on hydrological cycles. Progressive technologies, such as real-time water monitoring systems, offer invaluable data for predicting alterations in water availability due to climate shifts. These innovative approaches enable fast response strategies and proactive water management, contributing to regional resilience. Furthermore, adopting advanced modeling techniques aids scientists and policymakers in simulating future climate scenarios, offering insights into potential hydrological responses and uncertainties.
As the demand for accurate predictive tools increases, hydrology innovations empower communities to prepare for climatic extremes, thereby supporting sustainable adaptation strategies. Investment in hydrological research can foster the development of more efficient water use technologies, enhancing water conservation outcomes. Collaborative platforms uniting scientists, technologists, and policymakers are essential for translating research into actionable climate-responsive solutions.
Efforts to harness innovative hydrological strategies must align with global sustainability goals, prompting a coordinated response to the challenges posed by climate change on water systems. By embracing innovation in hydrology, international communities can galvanize pivotal changes, reinforcing collective resilience against the ongoing pressures of climate change.
Conclusion and Summary
The challenges presented by the intersection of climate change and hydrological cycles necessitate a global response characterized by cooperation and innovation. Hydrological cycles are profoundly affected by alterations in atmospheric conditions triggered by climate change, leading to numerous environmental and societal ramifications. The resultant disruptions underscore the importance of comprehensive research and adaptive management strategies that anticipate and mitigate adverse outcomes. Addressing these issues calls for an integrative approach, combining scientific research, policy frameworks, and community engagement to arrive at sustainable solutions.
Summarily, the impact of climate change on hydrological cycles echoes a significant ecological reality that commands global attention and concerted effort. As hydrological systems undergo transformation amid rising global temperatures and altered precipitation patterns, the importance of resilient water management policies becomes paramount. Comprehensive strategies that promote sustainable water use and enhance adaptive capacities will be essential in navigating these complex dynamics. The collective challenge for the future revolves around forging pathways to harmonize ecological preservation with the imperative of human and economic development in a climate-affected world.