In the contemporary digital landscape, safeguarding applications has become paramount for organizations seeking to protect sensitive data and maintain operation continuity. One of the critical components in ensuring robust security is the implementation of firewalls. Using firewalls for application protection offers a formidable defense mechanism against an array of cyber threats. This article delves into various facets of firewall deployment, elucidating its importance and articulating strategic considerations for optimal protection.
Read Now : Post Method In Rest Api
Importance of Firewalls in Application Security
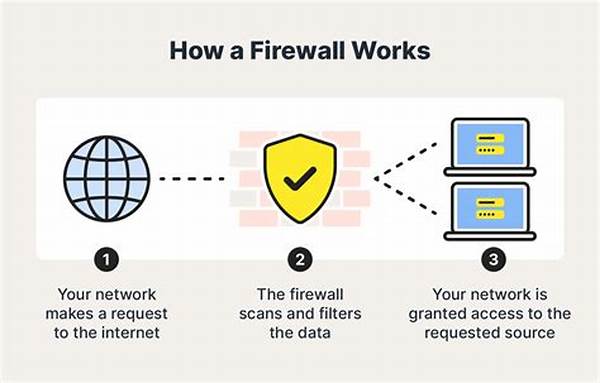
Firewalls serve as a barrier between internal networks and external sources, managing and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. When using firewalls for application protection, organizations can control access based on predefined security rules, minimizing unauthorized access and potential breaches. In contemporary IT environments, where threats are constantly evolving, utilizing firewalls effectively is crucial in safeguarding applications from sophisticated cyber-attacks. Given the diverse applications and sensitive data that traverse network interfaces, firewalls play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of information systems. By monitoring traffic and implementing controls, firewalls ensure that only legitimate users and systems interact with protected applications, thus forming an essential component of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Furthermore, the deployment of firewalls is not merely a reactive measure but a proactive stance, reinforcing security postures to preemptively deter and neutralize threats before they manifest into significant security incidents.
Key Considerations for Firewall Deployment
1. Comprehensive Coverage: Using firewalls for application protection entails ensuring that all potential entry points and applications are adequately safeguarded.
2. Consistent Policy Management: Consistent management of security policies across the firewall architecture is crucial in maintaining application security.
3. Intrusion Detection: Integrating intrusion detection systems with firewalls enhances the ability to identify and mitigate unauthorized access attempts.
4. Scalability: The capacity to scale with growing organizational needs is vital for effective firewall implementation and application protection.
5. Regular Updates: Regularly updating firewalls ensures they can combat new and emerging threats efficiently.
Advanced Strategies in Firewall Utilization
The role of firewalls has expanded beyond simple packet filtering to encompass advanced functionalities, which significantly contribute to enhanced security measures for applications. When using firewalls for application protection, adopting a multi-layered approach that integrates next-generation firewall technologies is highly advantageous. These firewalls incorporate features such as deep packet inspection, stateful inspection, and application-level gateways, providing an exhaustive examination and control of data traffic. Employing advanced models can effectively manage both known and unknown threats, which becomes particularly important as cyber threats become more sophisticated. Moreover, the employment of unified threat management systems, which converge firewall functionalities with other security tools such as anti-virus and intrusion prevention systems, offers a cohesive and robust defense strategy. Ultimately, these advanced strategies and technologies align with the imperatives of application security, supporting an unwavering commitment to operational resilience and data integrity.
Challenges and Solutions in Firewall Implementation
Implementing firewalls for application protection presents certain challenges, yet understanding these hurdles enables the development of effective solutions:
1. Complex Configurations: The intricate nature of firewall settings can lead to vulnerabilities if improperly configured.
2. Performance Trade-offs: Striking a balance between robust security and system performance is essential to maintain application usability.
3. User Training: Continuous education and training for IT staff and users are necessary to optimize firewall utilization.
Read Now : Restful Encrypted Data Flow
4. Policy Overhead: Managing complex firewall policies can be burdensome, necessitating automated tools for better efficiency.
5. Integration with Existing Systems: Ensuring seamless integration with current IT infrastructure is vital to avoid operational disruptions.
6. Security Myopia: Over-relying on firewalls may lead to neglect of other security measures; a comprehensive approach is necessary.
7. Adaptation to Emerging Threats: Firewalls must continuously adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
8. Budgetary Constraints: Allocating sufficient resources for firewall deployment and maintenance is imperative to ensure effective protection.
9. Vendor Reliability: Selecting reputable vendors ensures long-lasting and dependable firewall performance.
10. Compliance Requirements: Adhering to industry standards and regulations is crucial for legal and operational conformity.
Comprehensive Overview of Firewall Benefits
The benefits of using firewalls for application protection extend beyond mere threat mitigation. Firewalls effectively manage and regulate network traffic, ensuring that only authorized data packets are allowed passage, thereby maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information. Moreover, implementing firewalls is integral to fulfilling compliance requirements and industry standards, as they provide the necessary security controls and audit trails for regulatory adherence. Beyond technical advantages, adopting firewall solutions fosters user trust and organizational reputation by demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding digital ecosystems against breaches and data leaks. By providing a robust first line of defense, firewalls contribute to the operational continuity and risk management efforts of organizations, facilitating a security-conscious culture that is indispensable in today’s digital age.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using firewalls for application protection is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Firewalls serve as both the first line of defense and a crucial intermediary in controlling and securing access to applications. When effectively deployed and managed, they offer essential protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of applications. Therefore, prioritizing the continuous assessment and enhancement of firewall measures is imperative for organizations committed to robust security and resilience in an ever-evolving threat landscape.