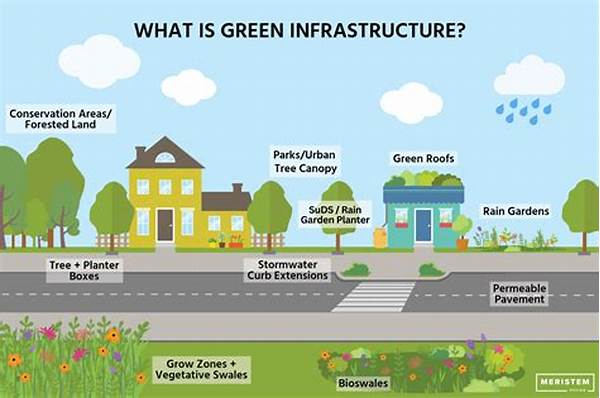
Understanding Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
In recent years, the concept of green infrastructure has gained significant traction as an innovative approach to urban planning and environmental sustainability. This concept encompasses a network of strategically planned natural and semi-natural areas with other environmental features designed to deliver a broad range of ecosystem services. The practice of implementing green infrastructure is crucial to mitigating the adverse impacts of urbanization, such as increased runoff, flooding, and urban heat islands, while simultaneously enhancing biodiversity and improving air and water quality.
Read Now : Workflow Automation In Data Management
Green infrastructure implementation practices involve integrating green and sustainable features into the built environment. This can include green roofs, permeable pavements, rain gardens, urban forests, and riparian buffers. These practices not only support sustainable urban development but also help municipalities address regulatory requirements related to water quality, stormwater management, and climate adaptation. Effective implementation requires a comprehensive understanding of site-specific conditions, regulatory frameworks, and stakeholder engagement to ensure sustained benefits and community support.
The integration of green infrastructure involves both technical and collaborative efforts. Professionals must employ cross-disciplinary knowledge and engage stakeholders, including residents, local authorities, developers, and environmentalists. Broader community awareness and participation are fundamental to the successful adoption and maintenance of green infrastructure implementation practices. This paradigm shift in urban development demands a careful balance between technological innovation, ecological preservation, and societal needs to create resilient and livable cities.
Key Aspects of Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
1. Design and Planning: Effective green infrastructure implementation practices begin with comprehensive design and planning, which require detailed site analysis, understanding local context, and setting realistic objectives to maximize environmental benefits.
2. Stakeholder Engagement: Collaboration between government agencies, private sectors, and communities is paramount in green infrastructure implementation practices to ensure shared objectives and sustained commitment to maintenance and support.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Aligning green infrastructure projects with existing policies and regulations, including stormwater and environmental standards, is vital to ensure the legal and practical feasibility of such initiatives.
4. Funding and Investment: Securing financial resources and investments through public-private partnerships or grants is essential for the successful rollout of green infrastructure implementation practices.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous monitoring and evaluation mechanisms should be integrated into green infrastructure implementation practices to assess the effectiveness and make adjustments as required over time.
Challenges and Opportunities in Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
Implementing green infrastructure in urban areas presents both challenges and opportunities for enhancing sustainability and resilience. One of the primary challenges is the high initial cost associated with installation and the technical expertise required for effective implementation. Additionally, public awareness and understanding of green infrastructure benefits are often limited, necessitating focused educational and outreach efforts to garner support and participation.
Despite these challenges, green infrastructure implementation practices offer substantial opportunities for cities to address environmental, social, and economic issues concurrently. By transforming built environments to accommodate natural elements, cities can improve public health, enhance aesthetic appeal, and increase property values. Furthermore, integrating green infrastructure fosters greater environmental stewardship, promoting sustainable practices that benefit both current and future generations. The transition towards green infrastructure can act as a catalyst for broader sustainable urban development, encouraging innovation and creating more resilient communities.
Factors Influencing Successful Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
Identifying Success Factors
1. Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in planning and decision-making processes is crucial for successful green infrastructure implementation practices, ensuring that projects align with community needs and values.
2. Government Support: Strong political will and policy support are essential for advancing green infrastructure initiatives, providing necessary resources and creating an enabling environment.
3. Technical Expertise: Access to skilled professionals in ecology, engineering, and urban planning is vital to navigate the complexities of green infrastructure implementation practices effectively.
4. Cross-Sector Collaboration: Partnerships across different sectors enhance resource pooling and knowledge exchange, increasing the success rate of green infrastructure implementation practices.
5. Adaptive Management: Flexibility in planning and execution allows for adjustments based on monitoring feedback, ensuring long-term sustainability of green infrastructure projects.
6. Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on the benefits and functions of green infrastructure enhances community acceptance and support for these practices.
Read Now : Steps For Academic Journal Publication
7. Economic Incentives: Offering financial benefits and incentives encourages private sector participation in green infrastructure initiatives.
8. Integrated Planning: Coordinated efforts between urban planning, transportation, and environmental management frameworks are necessary for coherent green infrastructure implementation.
9. Long-term Vision: Establishing a long-term strategic framework and objectives guides sustainable development and aligns with future urban growth and climate adaptation strategies.
10. Continuous Innovation: Embracing technological advancements allows for the evolution and improvement of green infrastructure implementation practices, responding effectively to emerging challenges.
The Future of Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
The outlook for green infrastructure implementation practices is promising, as urban areas increasingly recognize the need for sustainable solutions to address environmental and societal challenges. The integration of green infrastructure aligns with global agendas for climate action and sustainable development, presenting an opportunity for cities to lead by example in adopting environmentally-conscious growth models. As awareness and commitment to green infrastructure grow, so too will the range of innovations in design, materials, and technology, broadening the scope and impact of these practices.
Continued research and development are critical for enhancing the efficacy and efficiency of green infrastructure systems. Advancements in data analytics, remote sensing, and simulation models can offer valuable insights into optimizing green infrastructure design and performance. Collaborative research will also drive greater understanding of ecosystem services, supporting decision-makers in prioritizing investments and resources for maximum benefits.
The pathway to widespread green infrastructure implementation requires persistent effort from stakeholders at all levels. Mutual cooperation, combined with a shared dedication to achieving sustainable urban environments, will empower cities to counteract environmental degradation, enhance quality of life, and build resilience to unforeseen future challenges. The shift towards embracing green infrastructure is both a necessity and an opportunity for creating sustainable urban legacies.
Collaborative Approaches in Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
In advancing green infrastructure implementation practices, embracing collaborative approaches stands as a fundamental strategy. By fostering partnerships, cities can leverage diverse expertise, resources, and perspectives, thus enhancing the capacity and reach of green infrastructure projects. Collaborative efforts in this realm entail engaging a wide array of stakeholders, including government bodies, academia, private sectors, non-governmental organizations, and local communities.
Through effective collaboration, cities can transcend traditional administrative silos, paving the way for holistic and integrated planning approaches that align with broader sustainability goals. Sharing knowledge and best practices across networks cultivates an ecosystem of learning and innovation, essential for refining green infrastructure implementation practices. Moreover, collaborative frameworks ensure community voices are amplified, nurturing a sense of ownership and commitment that sustains projects in the long term.
To operationalize collaboration, establishing cross-disciplinary teams and platforms for dialogue is imperative. Institutional support and policies encouraging joint ventures and public-private partnerships can facilitate resources and expertise pooling, catalyzing green infrastructure project scalability. As cities strive for sustainable futures, the collective intelligence and collaborative spirit become vital engines driving the evolution and success of green infrastructure implementation practices.
Summary of Green Infrastructure Implementation Practices
The pursuit of sustainable urban development has brought green infrastructure implementation practices to the forefront as pivotal solutions for contemporary environmental and societal challenges. These practices embody an interdisciplinary approach, integrating ecological and infrastructural systems to address the adverse impacts of urbanization while promoting resilience and environmental stewardship. As cities worldwide contend with climate change, population growth, and increased urbanization, green infrastructure offers a flexible and adaptive framework to enhance livability and sustainability.
The implementation of green infrastructure requires concerted efforts across various dimensions, including planning, community engagement, regulatory compliance, and continuous evaluation. Emphasizing collaborative approaches fosters inclusivity and increases project ownership, ultimately ensuring long-term success and adaptability. While challenges related to costs, technical expertise, and public awareness persist, the opportunities presented by green infrastructure are vast and transformative, potentially reshaping urban landscapes and societal interactions with the environment. Embracing innovation, strengthening partnerships, and nurturing a shared commitment to sustainable futures are essential to the widespread adoption and success of green infrastructure implementation practices.