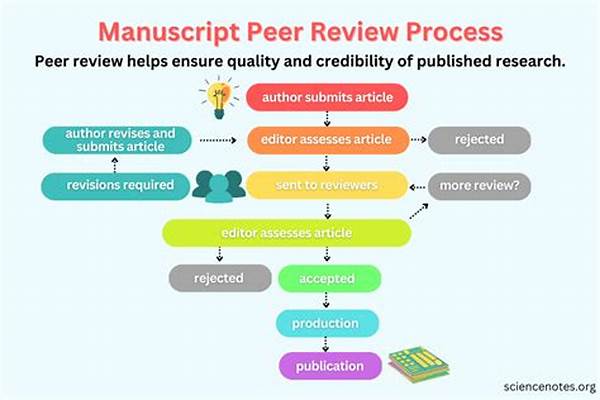
Peer review is a cornerstone of scholarly research and academic publication. As crucial as this process is, it is not without its flaws, and there is a recognized need for improving peer review processes to ensure their efficiency, fairness, and effectiveness. In recent times, with the increased volume of research submissions and the growing complexity of scientific inquiries, the traditional peer review framework faces several critiques. These include biases, lengthy review times, a lack of transparency, and inconsistent review quality across different journals and disciplines.
Read Now : Maintaining Integrity In Academic Evaluations
Enhancing the Framework of Peer Review
The ongoing challenge of improving peer review processes involves several facets. First, the mechanism must become more inclusive to mitigate biases and ensure diverse perspectives are considered in the evaluation of scholarly work. Secondly, enhancing transparency in the review process can bolster trust and accountability among researchers. Structured guidelines and training for reviewers should also be implemented to standardize evaluations and improve the consistency of review quality.
Moreover, leveraging technology can significantly aid in improving peer review processes by streamlining submissions, facilitating blind reviews, and employing software to detect potential conflicts of interest. Increasing the support and incentives for reviewers is another crucial aspect, as the meticulousness and dedication required for reviewing are often underappreciated and insufficiently rewarded. Lastly, an ongoing feedback system from authors, reviewers, and editors can identify persistent pain points and areas for continual improvement.
Strategies for Improvement
1. Inclusivity and Diversity: Encouraging a broad spectrum of reviewers reduces biases and enhances the quality of assessment, thereby improving peer review processes.
2. Transparency: Implementing open peer review mechanisms can increase accountability and trust, ultimately improving peer review processes.
3. Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced software tools ensures efficiency and accuracy, serving as an essential facet of improving peer review processes.
4. Training and Education: Providing resources for reviewers enhances their capabilities and increases the quality of evaluations, contributing significantly to improving peer review processes.
5. Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing regular feedback channels among stakeholders facilitates the identification and rectification of bottlenecks, thereby improving peer review processes.
Technological Advancements in Peer Review
The integration of technology is increasingly becoming indispensable in improving peer review processes. Digital platforms now allow for smoother submission and tracking of manuscripts, ensuring that the transition from submission to review is swift and efficient. Software algorithms can assist in identifying potential conflicts of interest through carefully curated databases and historical submissions, thereby enhancing the objectivity of the process.
Artificial intelligence (AI) also plays a promising role. By using AI for initial manuscript checks, journals can significantly reduce the burden on human reviewers. These AI systems can efficiently handle routine checks like plagiarism detection and formatting issues, allowing human reviewers to focus on the content and scientific merit of submissions. This symbiosis of technological and human insights results in an improved experience for both authors and reviewers, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of the peer review process.
Criticisms and Challenges
1. Bias Management: Despite technological advances, inherent biases still exist in the review process, emphasizing the need for improving peer review processes.
2. Consistency: There is often a lack of consistency across different journals, underscoring the importance of improving peer review processes.
3. Reviewer Fatigue: The increasing number of submissions leads to exhaustion, highlighting the necessity of improving peer review processes.
Read Now : Tools For Monitoring Api Performance Bottlenecks
4. Incentive Structures: Reviewers often receive inadequate recognition, which is a critical barrier to improving peer review processes.
5. Transparency Issues: Ensuring transparent practices remains a persistent challenge in improving peer review processes.
6. Confidentiality Concerns: Balancing transparency and confidentiality requires careful management when improving peer review processes.
7. Conflict of Interest: Identifying conflicts remains crucial for integrity, hence improving peer review processes must address this issue.
8. Feedback Loops: Limited feedback opportunities constrain growth and development, indicating the importance of improving peer review processes.
9. Accessibility of Software: Not all reviewers have access to advanced tools for improving peer review processes, necessitating changes.
10. Interdisciplinary Evaluation: As research becomes more interdisciplinary, establishing effective review processes becomes vital for improving peer review processes.
The Role of Training and Development
Enhancing reviewer training is critical to improving peer review processes. Comprehensive training ensures that reviewers have the necessary skills to evaluate submissions effectively. This training should encompass best practices for fair judgment, identifying potential biases, and adhering to journal guidelines. It is equally important to educate reviewers about the significance of constructive criticism. Constructive remarks not only aid authors in refining their work but also contribute positively to the scholarly community by upholding high publication standards.
Access to educational resources, such as workshops, webinars, and newsletters, can further keep reviewers updated with the latest advancements in peer review methodologies. As the research landscape continuously evolves, maintaining an informed cadre of reviewers is essential. Therefore, investing in training and development for current and potential reviewers is a pivotal step towards improving peer review processes, fostering a more robust scholarly communication ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, improving peer review processes involves a multifaceted approach that addresses existing challenges while embracing innovation. By integrating technology, bolstering training efforts, and fostering transparent mechanisms, the academic community can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of peer reviews. The effort to improve peer review processes requires collaboration among authors, reviewers, editors, and publishers to fulfill the ultimate goal of disseminating high-quality, credible research outputs.