In the academic realm, the process of preparing for journal peer review is a crucial step in the dissemination of scholarly work. This phase ensures the quality and integrity of research before it reaches the wider academic community. Understanding the intricacies of this process can significantly enhance the chances of a successful publication. With a meticulous approach to manuscript preparation, authors can navigate the peer review system more effectively, potentially gaining valuable feedback and recommendations that can enrich their research outcomes.
Read Now : Security Challenges In Restful Apis
Understanding the Peer Review Process
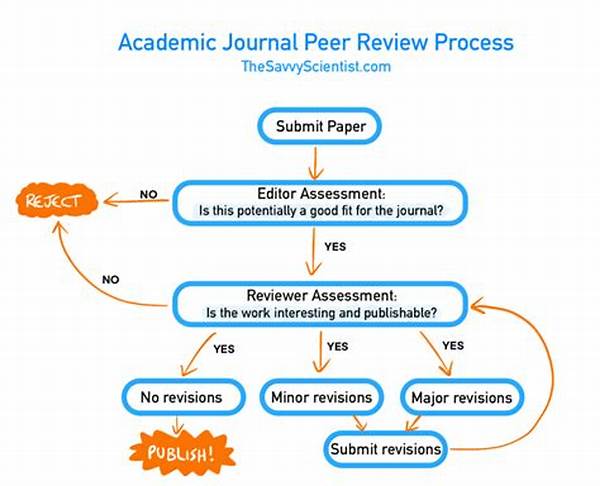
Preparing for journal peer review necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the peer review process itself. The procedure typically involves submitting your manuscript to a journal, where it undergoes initial screening by the editor. This initial assessment checks for adherence to the journal’s scope and guidelines. Once cleared, the manuscript is sent to external reviewers who are experts in the field. These reviewers critically evaluate the work for its originality, significance, methodological robustness, and clarity. Their feedback can range from suggestions for minor revisions to major overhauls. In some cases, they may recommend rejection if the research does not meet the necessary standards. Authors must be prepared for all possible outcomes and ready to revise their work accordingly, always with the aim of improving the quality and impact of their scholarship. Hence, preparing for journal peer review is not merely a procedural requirement but a vital step in ensuring the credibility and contribution of one’s research.
Essential Steps for Manuscript Preparation
1. Thorough Literature Review: Preparing for journal peer review begins with an exhaustive literature review. Understanding existing research helps position your work within the academic dialogue and demonstrates the novelty and significance of your findings.
2. Clear Research Question: A well-defined research question is crucial. Preparing for journal peer review requires clarity in defining what your research aims to address, helping reviewers quickly grasp the intent and focus of your study.
3. Methodological Rigor: Detail and justify your research methods. Meticulously outlining methodological approaches enhances the credibility of your work during the journal peer review process.
4. Adherence to Journal Guidelines: Each journal has specific formatting and submission requirements. Preparing for journal peer review involves aligning your manuscript with these criteria to avoid unnecessary delays in the review process.
5. Pre-submission Editing: Prior to submission, ensure your manuscript is free from grammatical errors and inconsistencies. A polished document reflects professionalism and attention to detail, crucial during the peer review process.
Responding to Reviewer Feedback
Once the peer review process is complete, authors receive feedback that often includes recommendations for revision. Preparing for journal peer review thus extends beyond submission to actively engaging with reviewer comments. Constructive criticism can significantly enhance the quality of the research. Authors should approach feedback with an open mind and a willingness to refine their arguments or rework sections of their manuscript as needed. When responding to reviewer feedback, it is essential to address each comment thoroughly, providing clear explanations for any changes made or justifying why certain suggestions may not be feasible. This dialogue between authors and reviewers is a cornerstone of scholarly communication. It not only strengthens the final publication but also fosters a culture of academic rigor and collaboration. Preparing for journal peer review, therefore, involves an iterative process of refinement, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
Common Challenges in Journal Peer Review
Navigating the challenges associated with preparing for journal peer review requires an understanding of common pitfalls and strategies to overcome them. Key challenges include:
1. Time Constraints: Balancing research with other academic responsibilities can make the preparation for journal peer review demanding.
2. Varying Reviewer Expectations: Different reviewers might have diverse expectations, making it challenging to satisfy all critiques.
Read Now : Real-time Data Sync Services
3. Rejection Risks: Rejection is a harsh possibility. Preparing for journal peer review involves accepting feedback constructively to prepare for resubmission.
4. Complex Feedback: Addressing detailed and sometimes conflicting feedback can be daunting.
5. Maintaining Objectivity: Authors must detach personally from their work to address critiques objectively.
Despite these challenges, preparing for journal peer review is a rewarding endeavor that enhances the quality and academic merit of the research.
Strategies for Effective Peer Review Preparation
Developing effective strategies during research preparation is imperative when preparing for journal peer review. These strategies not only increase the likelihood of a positive outcome but also contribute to the researcher’s professional development. Firstly, collaborating with co-authors and seeking their insights can provide diverse perspectives and strengthen the manuscript’s argumentation. Secondly, pre-submission peer review by colleagues can serve as a preparatory step, offering preliminary feedback and identifying potential weaknesses. Thirdly, participating in peer review as a reviewer for others’ work offers a reciprocal understanding of the process. This experience can refine one’s analytical skills and understanding of what constitutes a successful review cycle. Fourthly, continuously updating oneself with the latest research trends and peer review criteria keeps researchers informed and adaptive. Lastly, engaging with academic writing workshops or seeking mentorship from experienced scholars provides additional layers of support and guidance.
The Importance of Transparency and Ethical Considerations
Maintaining transparency and adhering to ethical standards is paramount when preparing for journal peer review. Ethical considerations encompass proper citation practices, ensuring originality, and avoiding conflicts of interest. Authors must transparently report their research findings and methodologies, enabling reviewers and readers to critically assess the validity of the study. Furthermore, disclosing any potential conflicts of interest is vital to uphold the integrity of the research, fostering trust within the academic community. Transparency extends to authorship practices as well, ensuring that all contributors are properly acknowledged for their roles in the research. Ethical breaches can have significant repercussions, including retraction of published work and damage to professional reputations. Therefore, preparing for journal peer review involves a steadfast commitment to ethical conduct, ensuring that the research contributes positively and reliably to the wider body of academic knowledge.
Summary of Preparing for Journal Peer Review
In summary, preparing for journal peer review is an integral component of the scholarly publication process. It begins with meticulously crafting a manuscript that adheres to journal guidelines and demonstrates methodological rigor and clarity. Engaging with the peer review process requires authors to be open to constructive feedback and willing to engage in iterative revision cycles. Strategies such as seeking pre-submission feedback, collaborating with peers, and participating in peer review activities of others enhance one’s preparation. Furthermore, understanding the importance of maintaining ethical standards and transparency is crucial to uphold the integrity of the research. Preparing for journal peer review thus ensures that scholarly work meets the highest academic standards, contributing significantly to the advancement of knowledge across disciplines. As researchers engage with this process, they not only elevate the quality of their individual work but also fortify the collective academic community’s commitment to excellence and ethical scholarship.