The advancement of technology has significantly reshaped educational landscapes, making virtual learning environments (VLEs) an integral component of modern education. Institutions worldwide have increasingly adopted these digital platforms to facilitate a more interactive and flexible approach to learning. This review of virtual learning environments will elucidate their capabilities, challenges, and the future scope in educational domains.
Read Now : Key Metrics For Legal Process Improvement
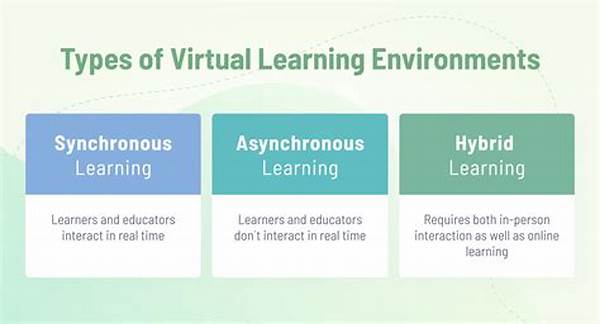
Understanding Virtual Learning Environments
Virtual learning environments are sophisticated platforms that offer students and educators a digital space to interact, collaborate, and manage learning processes efficiently. This review of virtual learning environments aims to highlight their multifunctional attributes, which include course management, content delivery, and communication tools that replicate the dynamics of a traditional classroom in a digital format.
In this digital age, VLEs have expanded beyond conventional online classes by incorporating multimedia integration, real-time feedback mechanisms, and customizable curricula tailored to individual learning styles. This review of virtual learning environments further explores how they enhance educational accessibility by breaking geographical barriers and providing learners with a plethora of resources at their fingertips.
Moreover, the review of virtual learning environments also sheds light on the challenges accompanying this digital transition. Teachers and students must adapt to these platforms, requiring adequate training and support. Additionally, concerns around data security, digital equity, and platform reliability persist, necessitating continuous improvement and innovation in these systems.
Key Aspects of Virtual Learning Environments
1. User-Friendly Interface: Ensures ease of navigation, enhancing the overall user experience in virtual learning environments.
2. Mobile Accessibility: Allows learners to access materials anytime and anywhere, providing flexibility in their educational journey.
3. Collaborative Tools: Facilitate seamless interaction among students and educators, nurturing a community of learners.
4. Personalized Learning Paths: Enable customization of learning experiences, accommodating diverse learning needs.
5. Assessment and Analytics Tools: Provide insights into learner performance, aiding in the effective monitoring and evaluation of educational outcomes.
Challenges in Virtual Learning Environments
While virtual learning environments offer numerous advantages, they are not without their challenges. One significant issue is the digital divide, as these platforms require internet access and a level of digital literacy that might not be available to all students. This review of virtual learning environments acknowledges the need for strategic implementations to ensure inclusivity across different socio-economic backgrounds.
Furthermore, maintaining engagement in a virtual setup poses another challenge. Educators must adopt innovative teaching strategies to keep learners motivated and involved. In this review of virtual learning environments, it becomes crucial to address issues of engagement by integrating interactive content and fostering active participation. Additionally, certain educational fields that require hands-on experience, such as laboratory-based sciences, face particular challenges in a virtual setting, necessitating creative solutions.
Innovative Features of Virtual Learning Environments
1. Integrated Multimedia: Enhances learning by incorporating videos, podcasts, and simulations.
2. Real-Time Communication: Supports instant messaging, video conferencing, and discussion forums.
3. Resource Availability: Offers extensive digital libraries and databases accessible to students worldwide.
4. Cloud-Based Operations: Support seamless data storage and retrieval, enabling access from multiple devices.
5. Security Protocols: Safeguard user data and ensure a secure learning environment.
Read Now : Contemporary Research Publication Trends
6. Feedback Systems: Allow immediate educator and peer feedback, promoting a constructive learning process.
7. Gamification Elements: Increase student engagement through interactive and rewarding learning experiences.
8. Support Services: Provide technical support and training to aid users.
9. Interoperability: Ensures integration with other software tools and platforms, enhancing functionality.
10. Scalability: Accommodates increasing numbers of users without compromising performance.
Future Prospects of Virtual Learning Environments
The future of virtual learning environments promises even more sophisticated features as artificial intelligence and machine learning become integral to their development. This review of virtual learning environments highlights the potential of AI-driven analytics in personalizing learning experiences and predicting educational trends. Advanced analytics can identify student performance patterns, tailor content delivery, and offer insights for improving teaching methods.
Moreover, virtual and augmented reality technologies are on the horizon to transform educational experiences in VLEs, providing learners with immersive simulations that enhance understanding and retention. This review of virtual learning environments underscores how these technological innovations can offer practical applications in fields like medicine, engineering, and arts, providing realistic practice settings that were previously impossible in digital formats.
However, the ethical implications of data usage, privacy concerns, and the impact of technology on human interaction in education will be topics of ongoing discussion. As this review of virtual learning environments suggests, balancing technological innovation with ethical considerations will be crucial in shaping the future of education.
Role of Educational Institutions in Implementing VLEs
Educational institutions play a pivotal role in the successful implementation of virtual learning environments. This review of virtual learning environments examines how institutions can effectively integrate these platforms into their curriculum to enhance educational delivery. Institutions should focus on providing comprehensive training programs for educators to master VLE tools, ensuring they can deliver engaging and effective instruction.
Furthermore, institutions need to facilitate a supportive infrastructure that includes reliable internet access and advanced technological tools, ensuring an equitable educational experience for all students. This review of virtual learning environments also highlights the need for continuous evaluation and adaptation of these platforms to meet the evolving demands of education and the workforce.
Conclusion of the Review of Virtual Learning Environments
In conclusion, this review of virtual learning environments underscores their transformative potential in modern education. By offering flexible, accessible, and interactive learning experiences, VLEs can significantly enhance educational outcomes. However, challenges such as digital equity, engagement, and data security remain, requiring strategic planning and innovation from educational institutions and technology developers.
This review of virtual learning environments suggests that future advancements in technology will only further integrate these platforms into mainstream education, offering more personalized and immersive learning opportunities. By addressing existing challenges and embracing emerging technologies, virtual learning environments can continue to evolve and play a crucial role in shaping the future of education.