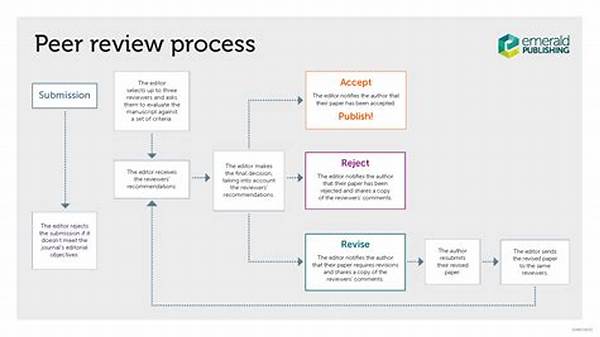
Over the decades, the academic and research communities have continuously refined the peer review system to ensure the integrity and quality of scholarly publications. As scientific knowledge expands rapidly, the traditional structures of peer review systems face unique challenges, prompting the need for substantial evolutions in how peer review processes are conducted. This article endeavors to explore these transformative changes, delving into the dynamics shaping the modern peer review landscape.
Read Now : Transformative Approaches In Data Study
Evolution of Peer Review Systems
Changes in peer review systems are driven by the need to address biases, inefficiencies, and technological advancements. Traditionally, peer reviews have been double-blind or single-blind, which, while maintaining author anonymity, often result in prolonged review cycles. The rise of open peer review, incorporating transparency and accountability, is becoming attractive for many journals. This change aims to counteract possible biases by making the identities of reviewers and authors mutually visible.
Technological innovation has also played a pivotal role in these changes. Automation and AI tools are increasingly employed to assist editors by providing initial manuscript assessments, thus accelerating the review process. Additionally, online platforms enhance reviewer collaboration, allowing for broader participation in the peer review process. These technological integrations are essential, as they not only bolster efficiency but also accommodate the growing volume of submissions.
The changes in peer review systems also extend to the criteria and standards imposed on reviewers. In light of ever-evolving scientific discoveries, there is a need for continuous training and updating of reviewers’ expertise, ensuring that they remain equipped to evaluate cutting-edge research effectively. Journals are increasingly investing in reviewer development programs, fostering a culture of rigorous yet fair evaluation processes.
Factors Influencing Changes in Peer Review Systems
1. Technological Advancements: The integration of AI and online platforms exemplifies crucial changes in peer review systems, enhancing speed and reliability.
2. Reviewer Training: Continuous training and development programs for reviewers are vital changes in peer review systems to maintain evaluative precision.
3. Open Peer Review: This approach marks significant changes in peer review systems, promoting transparency and reducing bias in scholarly evaluations.
4. Editorial Modifications: Changes in peer review systems frequently involve adjusting editorial policies to align with the evolving nature of scientific inquiry.
5. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging interdisciplinary insights is among the notable changes in peer review systems, aiming to enrich the evaluative scope.
The Role of Technology in Peer Review Systems
A pivotal factor driving changes in peer review systems is the integration of technology. The advent of artificial intelligence and machine learning offers transformative mechanisms for handling submissions, enabling automated checks on plagiarism and data authenticity. By providing instantaneous insights into the technical validity of manuscripts, these technologies contribute to reducing the workload of human reviewers and editors, consequently expediting the peer review process.
Leveraging technology, online platforms have enhanced collaborative efforts among reviewers, enabling collective assessments and shared expertise across geographical boundaries. These platforms facilitate seamless communication and coordination, mitigating delays traditionally associated with physical correspondence. Through technological innovations, publishers can now ensure an equitable, efficient, and reliable peer review process, essential for keeping pace with the accelerating publication demands in academia.
Benefits of Changes in Peer Review Systems
1. Enhanced Efficiency: Changes streamline processes, reduce waiting times, and increase publication speed.
2. Increased Transparency: Improvements allow for visibility in decision-making, encouraging accountability.
3. Greater Inclusivity: Diverse and global perspectives are facilitated through technology.
4. Bias Reduction: Transparency and structured guidelines mitigate subjective bias.
Read Now : Ecological Resilience And Adaptation
5. Quality Assurance: Technological checks ensure high standards of published research.
6. Reviewer Recognition: Systems now better acknowledge reviewers’ contributions.
7. Adaptability: Flexible systems adjust to the evolving research landscape.
8. Precision: Specialized training programmes equip reviewers with updated knowledge.
9. Feedback Mechanisms: Continuous feedback loops are established for ongoing system refinement.
10. Ethical Compliance: Peer review changes ensure adherence to ethical publication standards.
Challenges in Implementing Changes in Peer Review Systems
Implementing changes in peer review systems does not come without challenges. Institutions must overcome resistance to adopting new practices, as traditionalists may view such changes with skepticism. Moreover, the financial investments required for technological upgrades and training programmes can be substantial, posing budgetary constraints for many institutions. There is also a learning curve associated with familiarizing reviewers and editors with new technologies and processes, which can temporarily disrupt established workflows.
However, overcoming these challenges is essential for maintaining relevance in the rapidly evolving academic world. Institutions and publishers must prioritize open dialogues with stakeholders to address apprehensions regarding these changes, explaining their long-term benefits to ensure smooth transitions. By doing so, they can implement these changes while maintaining the quality and integrity of scholarly publications, ultimately strengthening the peer review systems on a global scale.
Technological Investments in Peer Review
The integral role of technology in transforming peer review systems cannot be understated. Investments in robust AI and machine learning algorithms facilitate efficient manuscript evaluations, drastically reducing the burden on human reviewers. Furthermore, changes in peer review systems include adopting secure, cloud-based platforms that ensure data integrity and facilitate international reviewer collaboration. Such infrastructure advancements are crucial for adapting to the dynamic needs of peer review processes.
Conclusion: Navigating Future Changes
In summary, changes in peer review systems are vital for addressing the complex challenges faced by the academic publishing industry. Balancing technological advancements with human oversight, these changes foster an environment of accountability, efficiency, and inclusivity. As publications globally strive for excellence, embracing these developments is indispensable for ensuring that peer review remains a cornerstone of scientific integrity.
Future directions in peer review must also incorporate adaptable frameworks, supporting interdisciplinary research and diverse voices within academia. While the journey towards refining peer review systems poses challenges, the potential benefits underscore the necessity for ongoing innovation. Commitment to an evolving peer review system will yield a more equitable and insightful platform for academic discourse, benefiting researchers and the broader society alike.