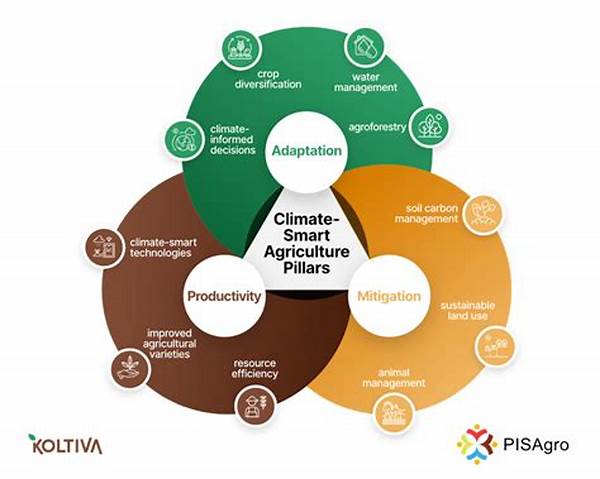
In the face of growing environmental challenges, climate-adaptive agricultural strategies have emerged as essential for ensuring food security. These strategies are tailored to account for changing weather patterns, ensure sustainable farming practices, and improve crop resilience. The necessity for these strategies becomes even more apparent as the impacts of climate change continue to intensify, disrupting traditional agricultural practices. Recognizing the importance of adapting to these changes, stakeholders across the globe are increasingly investing in research and development to create more robust agricultural systems. By integrating innovative technologies and traditional knowledge, climate-adaptive agricultural strategies aim to provide long-term solutions.
Read Now : Best Strategies For Integrated Evaluation
Importance of Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
Climate-adaptive agricultural strategies are crucial to combating the adverse effects of climate change on food production. With unpredictable weather patterns posing significant risks, these strategies prioritize the development of resilient crops and farming systems. By implementing adaptive technologies, farmers can better manage resources, control pests, and enhance soil health. Furthermore, these strategies emphasize the importance of community involvement, ensuring that local knowledge is leveraged to create culturally sensitive solutions. Policymakers are also encouraged to promote climate-adaptive practices through funding and educational programs, thus fostering a more sustainable agricultural sector. In sum, the holistic approach of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies seeks to secure food systems against climate-induced vulnerabilities.
Implementing Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
1. Climate-adaptive agricultural strategies involve utilizing drought-resistant crop varieties to withstand variable precipitation levels.
2. These strategies often integrate precision agriculture technologies to efficiently use water and nutrients, reducing waste and increasing output.
3. Encouraging agroforestry is another measure, focusing on the symbiotic relationship between crops and trees to enhance biodiversity.
4. Implementing climate-adaptive agricultural strategies also requires the support of policies that incentivize sustainable farming practices.
5. Additionally, fostering community training programs aids in disseminating knowledge about effective adaptation techniques.
Challenges in Adopting Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
Despite the apparent benefits, the adoption of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies is not without challenges. Smallholder farmers, often the most affected, may lack the financial resources or technical know-how to implement these strategies. Furthermore, the cost of research and development in creating resilient crop varieties and innovative technologies can be prohibitive. Additionally, there is the challenge of harmonizing traditional farming methods with new practices, which may sometimes lead to resistance from local communities. Governments and organizations must, therefore, work towards creating supportive frameworks that provide financial aid, education, and infrastructure development. Overcoming these barriers is essential for the widespread adoption of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies, ensuring food security for future generations.
Innovative Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
1. Vertical farming utilizes controlled environments, reducing reliance on climate variables and optimizing space.
2. Climate-adaptive agricultural strategies include breeding salt-tolerant crops to combat soil salinity.
3. The implementation of digital tools for weather forecasting assists farmers in planning and decision-making.
4. Intercropping improves soil fertility and reduces pest infestation, aligning with climate-adaptive agricultural strategies.
5. Regenerative agriculture focuses on rehabilitating ecosystems, fostering long-term sustainability.
Read Now : Public Policy And Inequality
6. Biochar application improves soil health, acting as a carbon sink in climate-adaptive agricultural strategies.
7. Water-efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation, are critical components of these strategies.
8. Conservation agriculture maintains soil cover and promotes minimal soil disturbance.
9. Utilizing genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to withstand extreme weather is part of modern strategies.
10. Climate-adaptive agricultural strategies often include diversification to minimize risk and stabilize income.
Future Directions for Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
The future of agriculture in a climate-affected world relies heavily on the successful implementation and evolution of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies. As we advance, it is vital to blend cutting-edge technology with time-tested traditional knowledge. The role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in real-time data collection and analysis cannot be overstated. These technologies provide precise weather forecasts and tailored recommendations, enabling farmers to make informed decisions. Similarly, blockchain technology is expected to enhance transparency and efficiency in supply chains, ensuring that products reach market more effectively. Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and the private sector are crucial for supporting these technologies and ensuring they are accessible to all.
The potential of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies is immense, but their success depends on collaborative efforts. Training programs and workshops play a pivotal role in educating farmers and empowering communities to adopt new practices. Additionally, building resilient infrastructure, such as climate-smart storage facilities and transport systems, is necessary for reducing post-harvest losses and maintaining food quality. To ensure these strategies reach their fullest potential, continuous assessment and adaptation based on feedback and results are required. Ultimately, the goal of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies is not only to protect against climate threats but to construct an agricultural system that thrives in harmony with the environment.
Community Engagement in Climate-Adaptive Agricultural Strategies
Community engagement forms a cornerstone of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies, recognizing that sustainable solutions require input and cooperation from those who are directly affected. By fostering participatory approaches, strategies benefit from local knowledge and expertise, ensuring they are culturally relevant and practical. Establishing agricultural cooperatives can facilitate the sharing of resources and information, empowering communities to experiment with various adaptive tactics. Moreover, engaging younger generations through educational initiatives can inspire long-term commitment to sustainable practices, ensuring the continuity of adaptive strategies.
Involvement in the decision-making process helps build ownership and accountability, which are critical for the success of climate-adaptive agricultural strategies. Workshops and seminars serve as platforms for dialogue, where stakeholders can discuss challenges and opportunities. Tailoring outreach programs to address specific local needs ensures that strategies are not only reactive to climate threats but also proactive in strengthening community resilience. Encouraging collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and farmers will foster an environment where innovative solutions can be developed and implemented efficiently. By prioritizing community engagement, these strategies promise to build sustainable agricultural systems that are robust against the challenges posed by climate change.