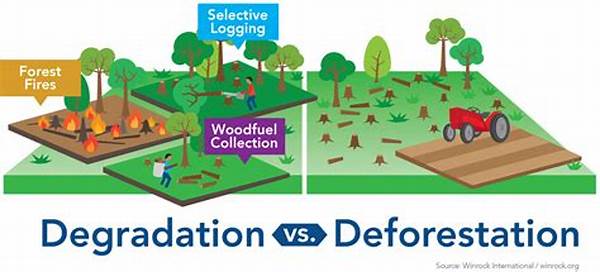
In recent years, the global discourse surrounding agriculture and environmental conservation has increasingly highlighted the crucial need for sustainable farming practices. This conversation often juxtaposes such practices against deforestation, which is largely driven by agricultural expansion. Sustainable farming versus deforestation presents a dichotomy where the former seeks to maintain ecological balance, and the latter results in significant environmental degradation. It is imperative to examine these two opposing forces to understand their respective impacts on the environment and food security.
Read Now : “modern Research Analysis Techniques”
The Environmental Impact of Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
Sustainable farming emphasizes eco-friendly techniques, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and water conservation, to maintain soil health without degrading natural resources. By contrast, deforestation, primarily induced by the need to make way for expansive agricultural land, results in biodiversity loss and increased carbon emissions. While sustainable farming practices aim to preserve the environment for future generations, deforestation remains one of the leading causes of global ecological deterioration. Sustainable farming versus deforestation thus highlights a pivotal environmental issue, as sustainable methods prove beneficial not only for the current ecosystem but also for mitigating climate change effects.
Efforts to promote sustainable farming versus deforestation also include integrating agroforestry, which combines agriculture with tree cultivation. This practice not only enhances biodiversity but also improves soil fertility and water retention. Consequently, when considering sustainable farming versus deforestation, it appears that a transition towards sustainable agricultural practices may offer a more viable solution to addressing environmental challenges. Furthermore, the reduction of deforestation can also lead to the preservation of vital rainforests, which act as crucial carbon sinks and biodiversity hotspots, underscoring the environmental dichotomy of sustainable farming versus deforestation.
Economic Implications of Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
1. Economic Sustainability: Sustainable farming versus deforestation has vast economic implications. Sustainable practices often lead to reduced costs in the long term due to less reliance on synthetic inputs, while deforestation can initially boost production but may result in long-term ecological and economic harm.
2. Resource Management: Effective management of resources is a critical component of sustainable farming. By employing practices that conserve water, soil, and biodiversity, sustainable farming versus deforestation represents a more balanced and economically viable approach to agriculture.
3. Market Access: As consumers become more environmentally conscious, products derived from sustainable farming often gain better market access compared to those from deforested lands. Sustainable farming versus deforestation highlights a trend towards greater demand for ‘green’ products.
4. Employment Opportunities: In promoting sustainable farming versus deforestation, there is potential to create diverse employment opportunities in fields like eco-tourism and organic agriculture, compared to the shrinking options associated with deforested lands.
5. Government Policies and Incentives: Governments can encourage sustainable farming versus deforestation through policies and incentives that support eco-friendly agricultural practices, potentially leading to sustainable economic growth and development.
Social Dimensions of Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
The social impact of sustainable farming versus deforestation is profound, affecting communities, health, and cultural practices. In many developing nations, deforestation has disrupted the livelihoods of indigenous populations who depend on forests for their sustenance and cultural practices. Conversely, sustainable farming practices offer pathways to nourishing local economies while preserving cultural heritage. Sustainable farming versus deforestation, therefore, encapsulates a social dilemma that affects not just the environment but also human rights and social equity.
Communities practicing sustainable farming often enjoy better health outcomes due to decreased exposure to harmful chemicals and pesticides. The sustainable farming versus deforestation debate also extends to educational opportunities, as farmers engaged in sustainable practices often require retraining in eco-friendly agriculture techniques. Such educational programs may empower communities, providing them with the knowledge and skills necessary to engage in sustainable agricultural practices that balance economic needs with environmental stewardship.
Technological Innovations in Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
1. Precision Agriculture: Leveraging technology to optimize crop yields while minimizing environmental impact represents a critical aspect of sustainable farming versus deforestation.
2. Agroforestry Systems: Implementing agroforestry, which integrates trees into farming landscapes, is a key component of sustainable farming versus deforestation, promoting biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
3. Biotechnology: Utilizing biotechnology in sustainable farming offers potential solutions to combat crop diseases and improve yields without resorting to deforestation.
4. Irrigation Management: Efficient water use through advanced irrigation systems underscores sustainable farming versus deforestation, leading to enhanced soil conservation and productivity.
Read Now : Innovative Approaches To Research Analysis
5. Renewable Energy: Incorporating renewable energy sources into farming operations reduces reliance on deforestation-driven fuel sources, aligning with sustainable farming principles.
6. Soil Health Monitoring: Sustainable farming versus deforestation involves continuous monitoring of soil health to ensure long-term viability and productivity.
7. Climate-Resilient Crops: Developing crops resistant to changing climatic conditions helps underscore the significance of sustainable farming in the sustainable farming versus deforestation debate.
8. Organic Farming Techniques: Organic farming eliminates the dependence on synthetic chemicals, positioning sustainable farming versus deforestation as a preferable alternative.
9. Sustainable Supply Chains: Establishing sustainable supply chains reflects the importance of sustainable farming versus deforestation in ensuring ethical production practices.
10. Community-Based Initiatives: Engaging communities in sustainable agricultural practices highlights the social and environmental benefits of sustainable farming versus deforestation.
Policy and Governance in Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
In discussing sustainable farming versus deforestation, a critical examination of policy frameworks and governance structures is indispensable. Good governance can bridge the gap between sustainable farming practices and deforestation prevention. Governments play a pivotal role through legislation and regulation that promote sustainable agriculture while curbing deforestation. Sustainable farming versus deforestation requires a cohesive policy approach that incentivizes eco-friendly practices and penalizes illegal deforestation activities.
Policy interventions should also focus on providing subsidies for sustainable farming practices and enforcing strict monitoring of land use changes. International cooperation is equally critical, considering deforestation’s global impact on climate change and biodiversity. Sustainable farming versus deforestation thus represents an opportunity for nations to collaboratively fortify their agricultural policies, ensuring that they align with global sustainability goals. By fostering partnerships across borders, countries can exchange knowledge and technologies that enhance sustainable farming capabilities and mitigate the adverse effects of deforestation on a global scale.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives on Sustainable Farming Versus Deforestation
The ongoing dialogue surrounding sustainable farming versus deforestation underscores the complexity of balancing agricultural productivity with environmental stewardship. By prioritizing sustainable farming practices, societies can better preserve ecosystems, bolster economic resilience, and foster social equity. As technological advancements continue to emerge, they provide practical pathways for enhancing sustainable farming methodologies that stand in stark contrast to the repercussions of deforestation.
Ultimately, the pressing need to address global food security and environmental preservation remains at the forefront of sustainable farming versus deforestation discussions. As governments, organizations, and communities unite to implement and advocate for sustainable farming practices, there is a promising opportunity to reduce deforestation rates and safeguard our planet for future generations. Sustainable farming versus deforestation embodies a crucial effort to redefine agriculture in a manner that respects both human needs and the integrity of our natural world.