Understanding Agile Test-Driven Development
Agile test-driven development processes represent an innovative approach that marries the agile methodology with the rigor of test-driven practices. This fusion aims to enhance the adaptability and quality of software development. Agile principles emphasize flexibility, customer collaboration, and iterative progress, which aligns seamlessly with the test-driven development (TDD) practice of writing tests prior to developing code. This harmony ensures that every piece of code is validated against test cases, promoting reliability and robustness. Moreover, agile test-driven development processes encourage close collaboration among cross-functional teams, allowing them to respond swiftly to changes in project requirements. Such processes not only facilitate the early detection of defects but also foster a culture of continuous improvement, thus accelerating the overall development lifecycle.
Read Now : Next-generation Api Management
The integration of agile test-driven development processes supports a more manageable and efficient development environment. Teams are able to deliver smaller, incremental improvements more frequently, which aids in minimizing the risk of significant defects by maintaining focus on quality at every stage. Test cases outlined during the initial phases help developers understand requirements clearly, gearing development efforts toward achieving precise outcomes. Consequently, this enhances the software’s stability and decreases post-release defects. Agile test-driven development processes embody a proactive approach that harmonizes the discipline of TDD with the agility needed to accommodate evolving client needs and technological advances. Through this synergy, organizations can achieve enhanced alignment between business objectives and software deliverables.
Advantages of Agile Test-Driven Development Processes
1. Agile test-driven development processes enhance software quality by ensuring that code passes all outlined tests before implementation. This builds a framework of reliability.
2. By promoting early detection of defects, agile test-driven development processes enable a decrease in debug time, which subsequently improves development efficiency.
3. Repetitive testing enforced by agile test-driven development processes results in faster feedback cycles, facilitating immediate adjustments to the codebase.
4. Agile test-driven development processes reduce overall project risk and cost by maintaining quality control and preventing extensive rework down the line.
5. Enhanced collaboration among teams is a significant advantage of agile test-driven development processes, fostering open communication and collective responsibility for project success.
Implementing Agile Test-Driven Development Processes
The implementation of agile test-driven development processes requires a holistic shift in how teams approach software creation. This involves ingraining the tenets of both agile and TDD within the organizational culture. Initially, it is essential to ensure all team members grasp the core principles of TDD and agile methodologies. Regular training sessions and workshops should be conducted to facilitate this understanding. Additionally, cultivating a mindset that prioritizes testing ahead of coding is crucial. This requires setting a clear vision where the emphasis lies on creating comprehensive test cases before any code is developed, thus embedding quality into the heart of the design process.
Teams must also establish effective communication channels to support continuous collaboration, a cornerstone of agile test-driven development processes. Implementing agile ceremonies such as daily stand-ups and retrospectives can be instrumental in addressing issues in real-time and leveraging collective problem-solving. Additionally, adopting agile tools and frameworks that support test-driven development will aid in the seamless execution of this integrated approach. By fostering an environment that embraces change and prioritizes iterative improvement, organizations can effectively harness the power of agile test-driven development processes to deliver software solutions that not only meet current demands but also possess the flexibility to adapt to future changes.
Exploration of Agile Test-Driven Development Practices
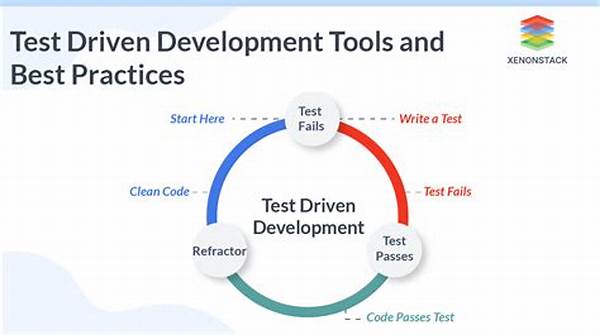
Agile test-driven development processes are grounded in a set of practices that emphasize quality and adaptiveness. Here are ten key aspects:
1. Test First: Writing tests precedes the development of code.
2. Incremental Development: Development is achieved in small, manageable increments.
3. Refactoring: Continuous improvement of code without changing its functionality.
4. Automation: Leveraging automated tests to streamline the process.
Read Now : “economic Impact Of Artificial Intelligence”
5. Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback loops to ensure alignment.
6. Collaboration: Promoting cross-functional team cooperation.
7. Iteration: Promotes flexible response to change.
8. Visibility: Constant tracking of progress against goals.
9. Quality Control: Commitment to maintaining high quality.
10. Documentation: Keeping concise and relevant documentation.
The Role of Testing in Agile Test-Driven Development
Agile test-driven development processes place a substantial emphasis on testing, a strategic move that influences the overall efficiency and effectiveness of software delivery. At the core of these processes is TDD, which mandates the creation of unit tests before the development of functional code. This pre-emptive strategy encourages developers to thoroughly contemplate the expected outcomes of their software components and validate whether the ensuing code meets these expectations. Through rigorous testing, agile test-driven development processes minimize the chances of introducing defects, resulting in higher code reliability.
Furthermore, testing in agile test-driven development processes does not halt at unit tests alone; it spans integration and system testing to confirm interoperability across the entire application stack. The early involvement of testing ensures that feedback is swifter, promoting a more adaptive development environment that can effectively respond to changes in requirements or rectification of errors. Additionally, automation of tests plays a pivotal role, reducing manual effort and providing comprehensive coverage. This empowers teams to focus on creativity and problem-solving. Ultimately, through its ingrained prioritization of testing, agile test-driven development processes promote a culture where quality is embedded at every level of the software lifecycle.
Challenges in Agile Test-Driven Development
Implementing agile test-driven development processes presents several challenges that organizations must navigate to realize their full potential. A fundamental challenge lies in shifting the mentality from traditional development practices to one where testing leads the process. This shift requires convincing stakeholders of the long-term benefits of this approach, as the upfront investment in creating extensive test cases may seem daunting. Furthermore, agile test-driven development processes rely heavily on team collaboration, and establishing a culture that embraces shared responsibility and open communication can be arduous, especially in organizations with deeply ingrained silos.
Another challenge is the dependency on automation tools, which necessitates initial investments in both time and resources. Teams need to choose appropriate tools that align with the project’s needs and integrate seamlessly into existing systems. Additionally, maintaining these automated tests can become cumbersome, particularly as the application grows in complexity. Thus, organizations must be prepared to continuously adapt and refine their practices to overcome these obstacles. Despite these challenges, the strategic adoption of agile test-driven development processes can lead to significant improvements in software quality and project delivery timelines, ultimately justifying the initial hurdles faced during implementation.