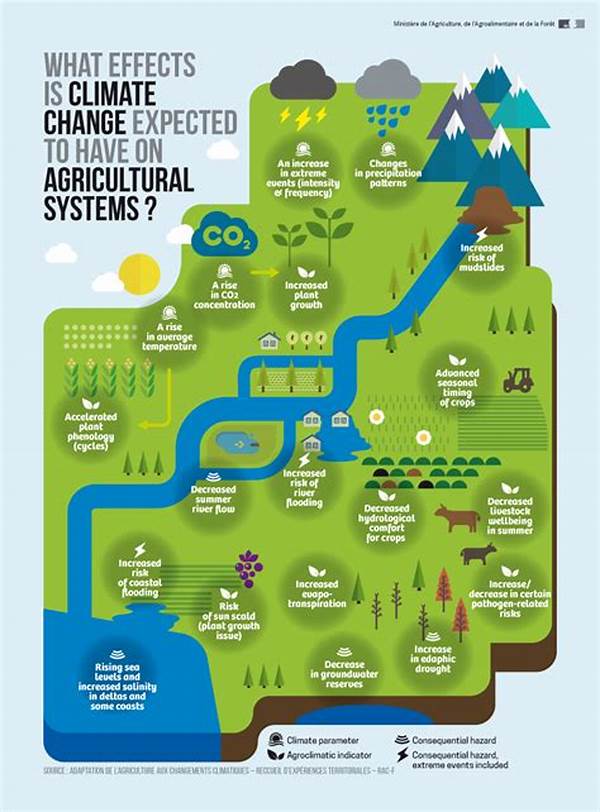
Challenges in Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
Agricultural adaptation to climate variability represents a crucial focal point within contemporary agronomic research and policy development. As the global climate continues to exhibit unprecedented variability, farmers worldwide are compelled to continually adjust their practices in response to climatic fluctuations. This adaptive process involves the integration of advanced technologies and methodologies, including precision agriculture, the development of climate-resilient crop varieties, and the adoption of diversified cropping systems. The implementation of such strategies not only aims at mitigating the adverse effects of climate change but also seeks to enhance the resilience and sustainability of agricultural practices. Through international collaboration and shared knowledge, agricultural adaptation to climate variability is being addressed as a collective effort toward sustainable development.
Read Now : Database Optimization And Indexing
Government policies also play a pivotal role in facilitating agricultural adaptation to climate variability. Regulatory frameworks and support systems designed to promote research, development, and the dissemination of adaptive practices are paramount. Financial incentives, such as subsidies for adopting sustainable practices or investing in drought-resistant technologies, are critical in encouraging farmers to adapt to changing climatic conditions. Additionally, investments in infrastructure, particularly in irrigation systems and water management, are essential in addressing water scarcity issues, often exacerbated by climate variability. Enhanced strategies and government intervention can effectively bolster the capacity of the agricultural sector to withstand climatic challenges.
Community education and awareness are equally vital components in the successful implementation of agricultural adaptation to climate variability. Empowering local communities with knowledge about sustainable practices and potential climate threats equips them with the necessary tools to make informed decisions concerning agricultural practices. Educational workshops, farmer-to-farmer knowledge exchange programs, and access to climate information services are effective means of fostering resilience at the grassroots level. By promoting a culture of adaptive learning, communities can better anticipate and respond to the challenges posed by climate variability, ultimately securing food security and livelihood sustainability.
Strategies for Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
1. Precision agriculture utilizes technology to optimize irrigation and fertilization, enhancing agricultural adaptation to climate variability by increasing resource efficiency.
2. Developing climate-resilient crops through genetic modification and breeding supports agricultural adaptation to climate variability by ensuring crop survival under adverse conditions.
3. Diversifying cropping systems contributes to agricultural adaptation to climate variability, reducing the risk of crop failure due to climate extremes.
4. Water management strategies, such as rainwater harvesting and improved irrigation, are essential for agricultural adaptation to climate variability, addressing water scarcity challenges.
5. Government policies promoting sustainable practices incentivize agricultural adaptation to climate variability, ensuring long-term sector resilience.
The Role of Technology in Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
Technological advancements are pivotal in the ongoing efforts of agricultural adaptation to climate variability. Innovations such as precision agriculture have revolutionized the way farmers interact with their crops and the environment. By employing data-driven approaches, farmers can make informed decisions to enhance crop yield and minimize resource wastage. Precision agriculture utilizes sensors, satellite imagery, and data analytics to provide accurate information on soil health, moisture levels, and crop conditions. Such technological interventions facilitate timely interventions, ultimately contributing to the sustainability and efficiency of agricultural practices amid climatic changes.
Furthermore, the use of biotechnology in developing climate-resilient crops is a significant milestone in agricultural adaptation to climate variability. Through genetic modification and advanced breeding techniques, researchers can produce crop varieties capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, drought conditions, and pest infestations. By increasing the resilience of crop yields, biotechnology contributes not only to food security but also to the economic stability of farming communities. The integration of technology within the agricultural sector is, therefore, a cornerstone in navigating the complexities of climate variability, ensuring that farming initiatives remain resilient, productive, and sustainable in the face of environmental challenges.
Collaborative Efforts in Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
1. International partnerships foster shared knowledge on agricultural adaptation to climate variability, promoting global resilience.
2. Research institutions contribute to agricultural adaptation to climate variability by developing innovative practices and solutions.
3. Farmers’ cooperatives facilitate agricultural adaptation to climate variability through collective resource management and information dissemination.
4. Financial institutions support agricultural adaptation to climate variability by providing funding for sustainable farming initiatives.
Read Now : “contemporary Research Analysis Trends”
5. NGOs actively engage in agricultural adaptation to climate variability, offering technical support and advocacy.
6. Educational institutions play a role in agricultural adaptation to climate variability by training future generations of climate-smart agricultural professionals.
7. Public-private partnerships enhance agricultural adaptation to climate variability by pooling resources and expertise.
8. Government agencies implement policies to guide agricultural adaptation to climate variability efficiently.
9. Local communities’ participation is vital for agricultural adaptation to climate variability, ensuring grassroots-level implementation.
10. Climate information services empower stakeholders with data essential for agricultural adaptation to climate variability decision-making.
Long-term Impacts of Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
Agricultural adaptation to climate variability yields numerous long-term impacts that touch on environmental, economic, and social dimensions. Environmentally, adaptation strategies such as sustainable farming practices, conservation agriculture, and integrated pest management contribute to biodiversity conservation and soil health improvement. These practices help mitigate land degradation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thus promoting ecological balance. Long-term environmental benefits ensure that agricultural ecosystems remain robust and productive amid climate challenges.
Economically, agricultural adaptation to climate variability enhances the resilience of farming businesses, stabilizing yields, and ensuring food security. By adopting resilient and efficient farming practices, agricultural enterprises can offset potential losses from climate-induced disruptions, maintaining profitability. Improved economic stability for farmers translates into strengthened rural economies, increased investment opportunities, and reduced vulnerability to market fluctuations. For governments, investing in adaptation strategies can lead to substantial economic returns through increased agricultural productivity and reduced costs associated with climate-related agricultural losses.
Socially, agricultural adaptation to climate variability fosters community resilience and food security, which are crucial for sustaining livelihoods. By empowering communities with adaptive knowledge and practices, stakeholders can enhance individual and collective capacities to anticipate and respond to climatic threats. This empowerment leads to improved social cohesion and community engagement, contributing to a broader sense of security and well-being. As a result, societies become more adaptive and robust in the face of climate variability, securing long-term sustainability and resilience for future generations.
Education and Capacity Building in Agricultural Adaptation to Climate Variability
Education and capacity building are fundamental to effective agricultural adaptation to climate variability. Training programs and workshops that focus on sustainable agriculture practices equip farmers with practical skills necessary for adaptive approaches. By integrating modern technologies and climate-smart practices into educational curricula, future generations of farmers can be better prepared to tackle climate-related challenges. Education facilitates a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, which is integral to evolving agricultural practices.
Moreover, capacity-building initiatives aimed at empowering local communities and institutions are essential for strengthening resilience. Programs that provide access to climate information services enable farmers and stakeholders to make informed decisions based on real-time data. Engagement in farmer-to-farmer knowledge exchange enhances community learning and promotes the dissemination of innovative practices. Through such efforts, agricultural adaptation to climate variability becomes an inclusive endeavor that leverages the collective knowledge and experience of diverse stakeholders, ensuring a comprehensive and sustainable response to climatic changes.