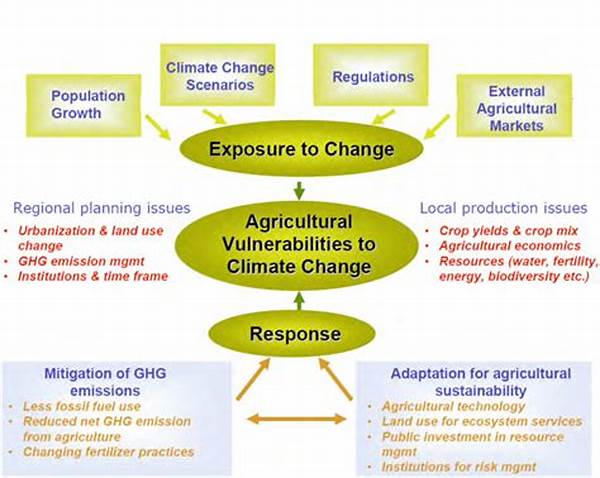
The increasing volatility in climatic conditions presents significant challenges to the agricultural sector, requiring systematic analysis and forward-thinking strategies to mitigate potential adverse effects. Agricultural climate risk assessment has emerged as an essential tool in addressing these challenges. This method evaluates and anticipates the impact of climate change on agricultural productivity, helping stakeholders make informed decisions and develop sustainable farming practices. By understanding the risks posed by changing climatic variables—such as temperature fluctuations, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events—farmers, policymakers, and researchers can work together to build resilient agricultural systems.
Read Now : “future Developments In Api Protection”
Importance of Agricultural Climate Risk Assessment
In recent years, agricultural climate risk assessment has gained prominence due to its vital role in ensuring food security and sustainable agricultural development. Understanding climatic impacts allows for better resource allocation and the implementation of effective risk management strategies. Through comprehensive data analysis and scenario modeling, agricultural climate risk assessment enables stakeholders to predict potential disruptions and plan accordingly. It provides a scientific basis for designing policies that foster climate-resilient agricultural practices, thereby safeguarding livelihoods and ecosystems. The proactive approach inherent in agricultural climate risk assessment is indispensable for adapting to a rapidly changing environmental landscape.
Key Aspects in Implementing Agricultural Climate Risk Assessment
1. Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering and interpreting climate data is foundational for agricultural climate risk assessment, aiding in the identification of trends and potential risks.
2. Stakeholder Involvement: Engaging farmers, researchers, and policymakers ensures a comprehensive understanding of regional challenges and fosters collaboration in developing adaptive strategies.
3. Scenario Modeling: This process helps forecast future climatic conditions and their potential impacts, guiding the creation of long-term mitigation and adaptation plans.
4. Resource Allocation: Effective agricultural climate risk assessment supports the efficient distribution of resources to vulnerable areas, enhancing resilience.
5. Policy Formulation: Detailed assessments inform the development of policies aimed at promoting sustainable agricultural practices and mitigating climate-related risks.
Challenges in Agricultural Climate Risk Assessment
While the benefits of agricultural climate risk assessment are apparent, its successful implementation faces several challenges. First, the complexity of climatic systems and agricultural responses necessitates sophisticated modeling techniques and reliable datasets, which can be resource-intensive and technically demanding. Moreover, the variability in local contexts—such as geographical conditions, crop types, and sociopolitical factors—complicates the creation of universally applicable assessment models. Additionally, the dynamic nature of climate change requires continuous updates and refinements to existing risk assessment frameworks. Addressing these challenges demands coordinated efforts across sectors and scales, emphasizing the need for continued research, investment, and capacity-building to enhance the efficacy of agricultural climate risk assessment initiatives.
The Role of Technology in Agricultural Climate Risk Assessment
1. Remote Sensing: Advanced satellite technology offers precise data on climatic variations and agricultural yields, crucial for effective risk assessment.
2. Big Data Analytics: Agricultural climate risk assessment benefits from analyzing vast datasets to recognize patterns and anticipate future risks.
3. Climate Models: Simulations provide insights into potential climate scenarios, guiding proactive decision-making in agricultural planning.
4. GIS Tools: Geographic Information Systems facilitate spatial analysis and visualization of climate impacts, enhancing risk communication.
Read Now : Securing Restful Api Endpoints
5. Blockchain Technology: Ensures transparency and security in data sharing among stakeholders involved in agricultural climate risk assessment.
6. IoT Solutions: Internet of Things devices monitor environmental conditions and offer real-time data feeds to improve assessment accuracy.
7. Machine Learning: Algorithms predict climate impacts on agriculture, assisting in developing adaptive strategies.
8. Mobile Applications: Mobile platforms extend the reach of agricultural climate risk assessment tools to remote and underserved areas.
9. Drones: Provide aerial views and data collection for precision agriculture, aiding risk assessment and management.
10. Crowdsourced Data: Engaging communities in data collection enriches the quality of agricultural climate risk assessment.
Benefits of Agricultural Climate Risk Assessment
Agricultural climate risk assessment provides significant benefits to various stakeholders within the agricultural value chain. Primarily, it empowers farmers with the knowledge to anticipate and adapt to climatic fluctuations, thereby safeguarding crop yields and livelihoods. For policymakers, it presents a basis for crafting robust policies that underpin agricultural sustainability and resilience. Researchers benefit from detailed insights that guide further studies and foster innovation in agricultural practices. Moreover, investors gain confidence in supporting agriculture ventures as comprehensive risk assessments reduce uncertainties associated with climatic impacts. In essence, agricultural climate risk assessment not only aids in overcoming immediate threats but also contributes to the long-term sustainability and stability of the agricultural sector.
Conclusion
As the agricultural sector continues to grapple with the escalating threats posed by climate change, the need for comprehensive agricultural climate risk assessment becomes increasingly paramount. By integrating advanced technologies and collaborative approaches, this method offers a pathway to sustainable and resilient agricultural practices. Despite the inherent challenges, the benefits of agricultural climate risk assessment—ranging from enhanced food security to economic stability—underscore its crucial role in shaping the future of global agriculture. Therefore, it is imperative for stakeholders across all sectors to prioritize the development and implementation of effective risk assessment frameworks as a foundational element in their response to climate change.
Summary
In conclusion, agricultural climate risk assessment serves as a critical instrument in managing the uncertainties associated with climate change impacts on agriculture. It equips stakeholders with essential information to make informed decisions, develop adaptive strategies, and design resilient agricultural systems. Engaging various stakeholders, from farmers to policymakers, ensures a holistic approach to risk assessment and mitigation. By leveraging technologies and fostering multi-disciplinary collaborations, agricultural climate risk assessment not only addresses immediate climatic challenges but also paves the way for sustainable agricultural development. As global climate dynamics continue to evolve, the importance of agricultural climate risk assessment in securing food systems and supporting rural livelihoods cannot be overstated.