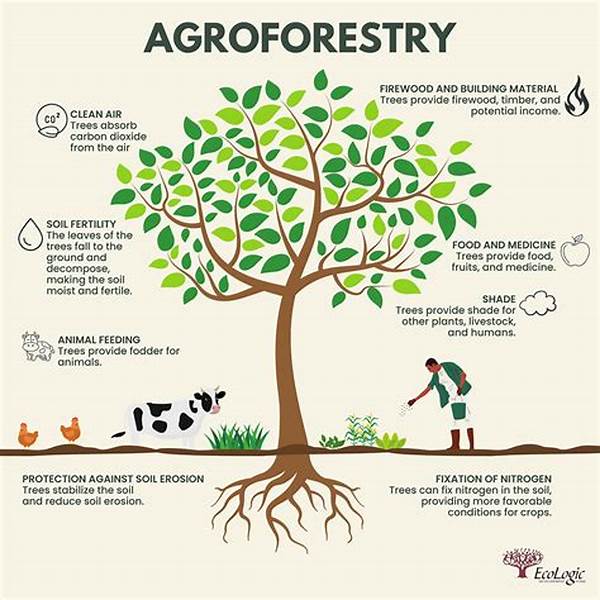
The increasing loss of biodiversity is a global concern, highlighting the urgent need for strategies that integrate environmental sustainability with human agriculture. Agroforestry systems, which blend agricultural and forestry practices, present a viable solution for biodiversity conservation. These systems offer multifaceted benefits by promoting ecological balance, enhancing soil fertility, and providing habitat for diverse species.
Read Now : Network Architecture Review Process
The Role of Agroforestry in Biodiversity Preservation
Agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation are pivotal in maintaining ecological integrity. These systems incorporate trees and shrubs into farming landscapes, creating a diverse array of microhabitats. Such diversity supports a wide range of species, contributing to the complex web of life that underpins ecosystem stability. By integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, agroforestry systems help mitigate the adverse impacts of conventional agricultural practices, which often lead to habitat loss and degradation.
Additionally, agroforestry systems enhance landscape connectivity, facilitating wildlife movement and genetic exchange among populations. This interconnectedness is essential for the resilience and adaptability of species facing challenges such as climate change. Furthermore, agroforestry practices can buffer against environmental extremes, such as floods and droughts, by enhancing soil structure and water retention. Consequently, agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation function as vital tools in the global effort to preserve and enrich biodiversity across varied ecosystems.
Benefits of Integrating Agroforestry Systems
1. Habitat Creation: Agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation create habitats for various species, promoting rich biodiversity.
2. Soil Fertility Improvement: These systems enhance soil health through organic matter and nutrient cycling.
3. Carbon Sequestration: Trees in agroforestry systems capture atmospheric carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
4. Pollinator Support: Diverse plant species offer resources to pollinators, enhancing ecosystem services.
5. Sustainable Land Use: Integrating trees with crops promotes sustainable use of land and resources.
Challenges and Opportunities in Agroforestry Implementation
Agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation face several challenges, including land tenure issues, financial constraints, and a lack of technical knowledge. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from policymakers, researchers, and local communities. Legal frameworks must be strengthened to secure land rights, ensuring that farmers and landowners have the incentive to invest in long-term agroforestry practices. Financial support, in the form of subsidies or incentives, can also encourage the adoption of agroforestry.
Moreover, education and extension services play a crucial role in empowering farmers with the knowledge needed to implement and manage agroforestry systems effectively. Collaboration among stakeholders can facilitate the exchange of best practices and innovations that optimize the benefits of these systems. Recognizing the potential of agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation can drive their integration into national and international conservation strategies, offering sustainable solutions to the biodiversity crisis while supporting local livelihoods.
Implementing Agroforestry Systems for Biodiversity Success
To maximize the effectiveness of agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation, various strategies must be employed. First, site-specific assessments are crucial. Understanding the unique ecological characteristics and socio-economic conditions of each location guides the selection of appropriate tree and crop species. Moreover, participatory approaches that involve local communities and stakeholders foster inclusive decision-making.
Read Now : Enhancing Middleware Performance With Load Balancing
Second, continuous monitoring and adaptation are indispensable. Monitoring biodiversity outcomes and ecological impacts informs adaptive management practices that refine agroforestry techniques. Thirdly, scaling up successful models through knowledge sharing and policy advocacy can amplify the conservation benefits. By fostering partnerships among governments, NGOs, and farmers, agroforestry systems can be more widely adopted as a nature-based solution for biodiversity conservation.
Advancing Agroforestry for Future Generations
Agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation are not merely an academic or theoretical endeavor; they constitute a practical approach to addressing pressing environmental challenges. Through interdisciplinary research and innovative practices, agroforestry evolves as a dynamic strategy for biodiversity preservation. Efforts to harness its potential must align with broader goals such as food security, climate resilience, and sustainable livelihoods.
Critically, it is essential to mainstream agroforestry into governmental policies and land management programs. By doing so, agroforestry systems can significantly contribute to achieving international conservation targets and frameworks, including the Aichi Biodiversity Targets and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Engaging youth and training the next generation of conservationists ensure the continuity and advancement of agroforestry practices. Ultimately, recognizing the role of agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation is integral to securing a sustainable and biodiverse future for all.
Economic and Ecological Synergies in Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation offer a confluence of ecological and economic benefits. As these systems enhance biodiversity, they also provide economic incentives through increased agricultural productivity and diversified income streams. The integration of trees and crops yields a variety of products, from timber and fruit to medicinal plants, which can be marketed locally or internationally.
The economic viability of agroforestry systems encourages widespread adoption, generating environmental and socio-economic returns. Farmers practicing agroforestry benefit from greater resilience to market fluctuations and climate variability, ensuring food security and livelihoods. Moreover, ecosystem services such as pollination, soil fertility, and watershed protection, offered by agroforestry, contribute to the reduction of agricultural inputs and costs. Through holistic management and strategic planning, agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation serve as a bridge between ecological health and economic prosperity.
Conclusion: Embracing Agroforestry for a Sustainable Tomorrow
In conclusion, agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation represent a forward-thinking approach to harmonizing human activities with nature. These systems not only address the immediate concerns of biodiversity loss but also offer long-term solutions for sustainable land use and resource management. The positive impact of agroforestry on biodiversity is manifold, enhancing both ecological integrity and human well-being.
The journey towards widespread implementation of agroforestry requires collaboration and commitment from all sectors of society. Policymakers, researchers, and practitioners must work synergistically to remove barriers and create an enabling environment for agroforestry adoption. Empowering local communities through education and capacity-building initiatives ensures the resilience and sustainability of these systems. By embracing agroforestry systems for biodiversity conservation, we can pave the way for a harmonious and thriving planet, fostering a legacy of sustainability for future generations.