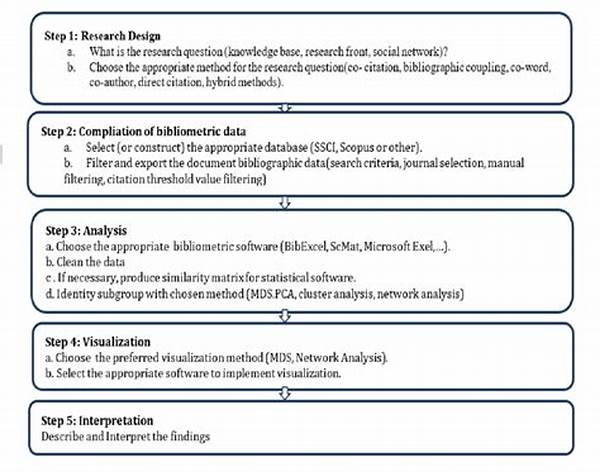
The Importance of Bibliometric Analysis in Academic Research
Bibliometric analysis for academic research has emerged as an indispensable tool in the evaluation of scholarly publications and the mapping of academic landscapes. This analysis involves the quantitative study of academic literature, utilizing various bibliometric indicators to gauge research outputs, impact, and trends. Through bibliometric analysis, researchers can objectively assess the influence of specific works, authors, or journals within a field, thereby guiding strategic decision-making for future research.
Read Now : Revamping Traditional Api Solutions
In addition to evaluating academic contributions, bibliometric analysis for academic research provides invaluable insights into research trends and patterns over time. By examining citation networks and co-authorship patterns, researchers can identify core topics and emergent themes warranting further exploration. This approach not only facilitates the discovery of knowledge gaps but also supports researchers in aligning their work with leading-edge topics, thus enhancing the relevance and impact of their studies on a global scale.
Furthermore, bibliometric analysis for academic research serves an essential role in institutional and funding evaluations. Academic institutions and funding bodies utilize bibliometric indicators as objective measures of research performance, productivity, and collaboration. By leveraging bibliometric analysis, these entities can evaluate the effectiveness of research strategies, allocate resources efficiently, and foster collaborative networks that ultimately lead to more innovative and impactful discoveries.
Advances in Bibliometric Analysis Techniques
1. Citation Analysis: Citation analysis within bibliometric analysis for academic research assesses the frequency and impact of citations to gauge the influence of publications and authors.
2. Co-Authorship Networks: Examining co-authorship networks helps in understanding collaboration patterns, which are crucial in bibliometric analysis for academic research to enhance research partnerships.
3. Co-Citation Analysis: This technique identifies interconnected works through simultaneous citations, enriching bibliometric analysis for academic research by revealing relationships and trends among scholarly texts.
4. Bibliometric Mapping: Utilizing visual tools, bibliometric mapping presents a graphical representation of academic landscapes, a vital aspect of bibliometric analysis for academic research.
5. Altmetrics: By focusing on alternative metrics, bibliometric analysis for academic research incorporates social media mentions and online engagement, evaluating research impact beyond traditional scholarly boundaries.
Bibliometric Analysis Methodologies
Bibliometric analysis for academic research employs a variety of methodologies, each designed to extract specific insights from scientific data sets. Central to these methodologies is citation analysis, which quantifies the impact of scholarly works through citation counts. By identifying frequently cited papers, researchers can gauge the significance and influence of particular studies or authors, thus highlighting pivotal research contributions that have shaped academic discourse over time.
Beyond citation analysis, co-authorship and co-citation analyses form integral parts of bibliometric methodologies. Co-authorship analysis examines authorship patterns to understand collaboration dynamics within academic communities. This approach elucidates essential research networks and potential synergies between researchers. Co-citation analysis, on the other hand, identifies clusters of interconnected scholarly works, revealing underlying relationships and thematic associations valuable in comprehending research trends. Together, these methodologies facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the structural and dynamic characteristics inherent in academic research landscapes.
Read Now : “data Visualization With Neural Networks”
Case Studies of Bibliometric Analysis Applications
Bibliometric analysis for academic research finds its application in diverse case studies, illustrating its adaptability and significance across disciplinary boundaries. One pivotal case study involves analyzing citation trends in the field of environmental science, where bibliometric analysis identified emerging research areas such as climate change mitigation and sustainable energy practices. This insight enabled policymakers to tailor funding strategies aligned with critical research needs, ultimately advancing solutions to pressing environmental challenges.
In the realm of medical sciences, bibliometric analysis for academic research showcased its utility by assessing the impact of collaborative publications in enhancing treatment protocols and patient outcomes. By analyzing co-authorship networks across medical institutions, researchers unveiled patterns of successful collaboration, enabling the replication of effective partnerships. Such findings contributed to elevating the standard of healthcare through the dissemination of innovative medical practices.
Challenges and Future Directions in Bibliometric Analysis
Bibliometric analysis for academic research, while encompassing significant advantages, also poses challenges necessitating careful consideration. One prominent challenge is the accurate interpretation of bibliometric indicators, as citation counts may not fully reflect the quality or significance of a publication. Consequently, researchers must adopt a comprehensive approach, integrating multiple indicators for a more nuanced evaluation of academic contributions. Moreover, variations in citation practices across disciplines can result in improper comparisons, underscoring the need for discipline-specific indicators and benchmarks.
As bibliometric analysis for academic research progresses, future directions point towards the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques. These advancements promise to enhance data processing capabilities, allowing for more precise analysis of large and complex datasets. The development of advanced bibliometric tools equipped with predictive analytics may further facilitate identifying emerging research trends, ultimately guiding researchers towards untapped areas of inquiry and fostering innovative breakthroughs.
Enhancing Research Visibility through Bibliometric Analysis
The application of bibliometric analysis for academic research plays a pivotal role in enhancing the visibility and impact of scholarly works. By providing objective metrics of research productivity and intellectual influence, bibliometric analysis enables researchers to communicate their contributions effectively to a global audience. This heightened visibility not only attracts attention from peers and collaborators but also opens up opportunities for interdisciplinary integration and societal engagement.
Moreover, bibliometric analysis for academic research aligns closely with open access practices, promoting the accessibility and dissemination of research findings. Through the analysis of open access repositories and digital platforms, researchers can evaluate the reach and engagement of their works beyond traditional academic boundaries. This alignment bolsters the democratization of knowledge, ensuring that research benefits society at large, enriching educational practices, and informing evidence-based policy-making.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Bibliometric Analysis
In conclusion, bibliometric analysis for academic research holds enduring value as a critical instrument for assessing and enhancing the quality and impact of scholarly outputs. By providing comprehensive insights into research dynamics and trends, bibliometric analysis facilitates informed decision-making among researchers, institutions, and policymakers. Embracing bibliometric analysis within the academic landscape promises to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and contribute to addressing societal challenges through the strategic advancement of knowledge. As the field continues to evolve, its integration with emerging technologies is poised to unlock new dimensions of understanding and spur the global enhancement of academic research practices.