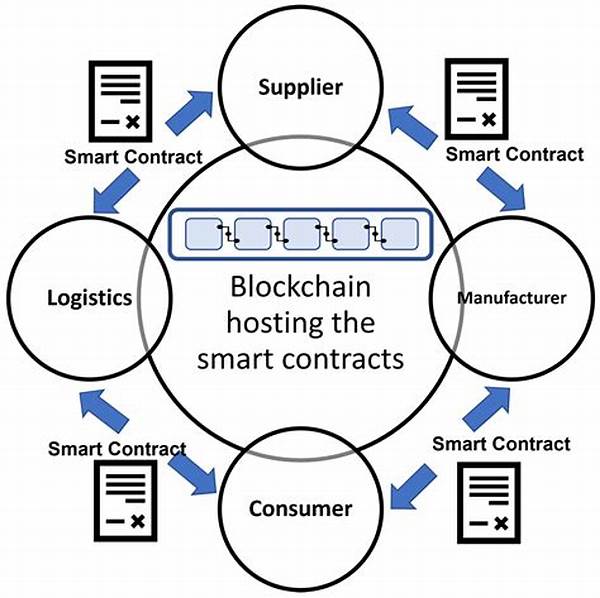
Blockchain-based smart contracts have emerged as a pivotal technological innovation, transforming the landscape of digital transactions. They promise a secure, efficient, and autonomous mechanism for executing agreements, thereby minimizing the need for intermediaries. As the global economy increasingly embraces digital solutions, understanding the intricacies of blockchain-based smart contracts becomes essential for businesses and individuals alike, offering unparalleled transparency and security in digital agreements.
Read Now : Technology-driven Climate Adaptation Farming
The Functionality of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based smart contracts function by encoding contractual terms into software code, which is then stored on a blockchain. Once deployed, these smart contracts autonomously execute pre-defined actions when certain conditions are met. This automation not only reduces the potential for manual error but also ensures compliance with the agreed terms. Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that the data within the smart contracts is immutable and verifiable by all relevant parties, thereby providing an unmatched level of transparency. Furthermore, because blockchain-based smart contracts operate independently of a central authority, they minimize reliance on third parties, further streamlining the transaction process and reducing associated costs. As this technology matures, it holds the potential to revolutionize numerous industries by offering a reliable alternative to traditional contract execution mechanisms.
Advantages of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
1. Security: Blockchain-based smart contracts offer heightened security through cryptographic algorithms, ensuring data integrity and protection from unauthorized tampering.
2. Transparency: The decentralized nature of blockchain provides all parties involved in the contract with complete visibility and access to the contractual terms and execution processes.
3. Efficiency: By automating the execution of contractual terms, blockchain-based smart contracts significantly reduce the time and resources required for manual contract management.
4. Immutability: Once recorded on a blockchain, the data in blockchain-based smart contracts cannot be altered, providing a reliable audit trail of all transactions.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: By minimizing the need for intermediaries, blockchain-based smart contracts reduce transaction costs and enhance financial efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
Despite their potential, implementing blockchain-based smart contracts is not without challenges. One notable concern is the complexity of coding and deploying these contracts, which requires a high level of technical expertise. Errors in the code can lead to undesirable outcomes, emphasizing the importance of rigorous testing and validation. Additionally, the legal status and enforceability of blockchain-based smart contracts remain subject to regulatory developments in various jurisdictions. As governments and legal institutions grapple with these new digital instruments, the need for clear and consistent regulatory frameworks becomes paramount. Organizations considering the adoption of blockchain-based smart contracts must remain vigilant and adaptable to these evolving legal landscapes to fully capitalize on their potential benefits.
Read Now : Scalability In Distributed Computing Systems
Applications of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
The versatility of blockchain-based smart contracts extends across diverse sectors. In the financial industry, they streamline processes such as trading, escrow services, and loan agreements by executing pre-defined terms without manual intervention. Supply chain management also benefits, as blockchain-based smart contracts enhance traceability and automate the execution of shipping and payment conditions. In healthcare, they ensure secure sharing and accessibility of patient records while maintaining privacy. Real estate transactions are simplified and secured through automation of title transfers and agreements. The insurance sector implements these smart contracts for automating claims processing, reducing fraud and inefficiencies. In digital content, creators are empowered to define and enforce usage terms for their work. Furthermore, decentralized applications (DApps) are built on these contracts, enabling new business models and innovation in the tech ecosystem.
Future Prospects of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
As blockchain technology evolves, it is expected that blockchain-based smart contracts will play an increasingly prominent role in the digital economy. Businesses across sectors are actively exploring potential applications, and new use cases continue to emerge. The growing interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) further highlights the transformative impact of blockchain-based smart contracts. However, for these contracts to reach their full potential, it will be necessary to address and overcome various technological and regulatory challenges. Continued collaboration between technology developers, legal experts, and regulators will be key in shaping a future where blockchain-based smart contracts are integrated seamlessly into the fabric of global commerce.
Theoretical Underpinnings of Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts
The conceptual foundation of blockchain-based smart contracts lies in the intersection of blockchain technology and traditional contract law. Cryptographic principles ensure the security of these contracts, leveraging distributed ledger technology to achieve consensus and validate transactions. This blend of technological innovation and legal theory provides a novel framework for digital agreements. As blockchain-based smart contracts continue to evolve, their theoretical basis is expected to broaden, incorporating advances in fields such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advancements will likely further enhance the functionality and adaptability of blockchain-based smart contracts, solidifying their role as a cornerstone of future economic activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain-based smart contracts represent a pioneering step toward a more decentralized and efficient future for contractual agreements. By automating processes and enhancing security, they offer substantial benefits over traditional contracts. However, the implementation and adoption of blockchain-based smart contracts require careful consideration of technical and legal challenges. By fostering innovation and collaboration across industries and domains, stakeholders can unlock the transformative potential of blockchain-based smart contracts, unlocking new possibilities for economic growth and innovation in the digital age. The future of blockchain-based smart contracts is promising, with opportunities to reshape how we conduct business and interact in the digital world.