The Interconnection between Climate Change and Poverty Increase
Climate change is an escalating global issue that profoundly affects economic and social stability, particularly in impoverished regions. The adverse impacts of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns, increased frequency of natural disasters, and shifts in agricultural productivity, exacerbate the living conditions of vulnerable populations. This environmental phenomenon has created a vicious cycle where poverty increase is both a consequence of and a contributor to climate change.
Read Now : Challenges In Peer Review Coordination
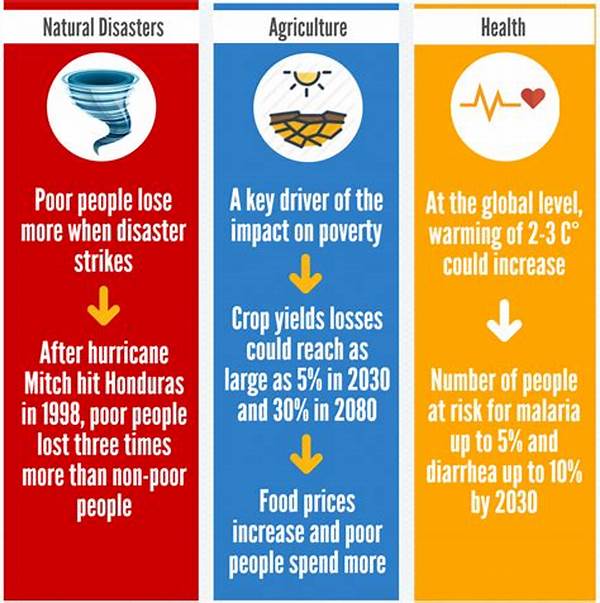
The relationship between climate change and poverty increase is particularly evident in regions where communities heavily rely on agriculture for their livelihoods. Changes in climate conditions, such as droughts and floods, directly affect crop yields, leading to food scarcity and economic instability. As agricultural productivity diminishes, so too do income opportunities for farmers and rural workers, resulting in a deepening of poverty. Furthermore, the financial strain on governments in developing nations to mitigate the effects of climate change diverts resources from essential services, such as education and healthcare, further exacerbating poverty levels.
Moreover, those living in poverty are often the least equipped to adapt to the impacts of climate change. Limited access to financial resources, technology, and infrastructure impedes their ability to recover from environmental shocks. This lack of resilience perpetuates a cycle where climate change continuously undermines economic growth and development, leading to a persistent poverty increase. It is imperative that global strategies encompass both climate change mitigation and poverty alleviation to break this cycle and promote sustainable development.
Factors Contributing to Climate Change and Poverty Increase
1. Agricultural Vulnerability: Climate change disproportionately impacts low-income populations dependent on agriculture, leading to poverty increase as crop failures become more frequent.
2. Economic Disparity: The widening gap between wealthy and poor nations is exacerbated by climate change, fostering conditions that lead to further poverty increase.
3. Natural Disasters: Increased intensity and frequency of natural disasters due to climate change displace communities and elevate poverty increase rates due to destroyed infrastructure.
4. Resource Depletion: Climate change-induced depletion of natural resources harms economic opportunities and heightens poverty increase among already vulnerable populations.
5. Health Impacts: Climate change contributes to health issues that disproportionately affect impoverished communities, compounding the poverty increase due to decreased productivity.
Addressing the Dual Crisis of Climate Change and Poverty Increase
The complex interplay between climate change and poverty increase demands comprehensive policy responses that integrate environmental and socioeconomic considerations. Mitigating the effects of climate change requires international cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices. Equally important is the development of adaptive strategies that bolster the resilience of vulnerable communities to climate-related challenges. This approach involves financial support for sustainable agriculture, investment in renewable energy, and infrastructure development to withstand environmental impacts.
Addressing poverty increase within the context of climate change necessitates targeted interventions that improve access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Empowering communities through skills development and technological access can enhance their adaptive capacity, reducing the detrimental effects of climate change on their livelihoods. Furthermore, policies that ensure equitable resource distribution and prioritize sustainable development goals can help break the cycle of poverty increase and environmental degradation.
Socioeconomic Implications of Climate Change and Poverty Increase
1. Economic instability perpetuated by climate change leads to a poverty increase, hindering national and international growth.
2. Populations in poverty are disproportionately affected by climate change, making them more vulnerable to economic shocks.
3. Deteriorating living conditions due to climate change lead to migration, intensifying poverty increase in urban areas.
4. Limited access to resources reduces adaptive capacity to climate change impacts, exacerbating poverty increase.
5. Food insecurity driven by climate change-induced agriculture issues contributes significantly to poverty increase.
6. Insufficient healthcare facilities in impoverished areas lead to greater health impacts from climate change, amplifying poverty increase.
Read Now : **sampling Bias Minimization Strategies**
7. Educational disruptions due to climate-related disasters result in a poverty increase by limiting future economic opportunities.
8. Government resources stretched thin by climate change mitigation lead to decreased funding for poverty alleviation programs.
9. Intergenerational poverty increase is accelerated by the continual environmental impacts of climate change.
10. Global economic policies must consider the interrelation of climate change and poverty increase to foster sustainable development.
Strategies for Overcoming Climate Change and Poverty Increase
The dual challenge of climate change and poverty increase represents a critical global concern requiring urgent attention. A multifaceted approach is necessary to address the intertwined issues effectively. At the international level, stronger commitments to reducing carbon emissions and fostering technological innovations are needed to counteract climate change. Financial mechanisms that support sustainable development in low-income countries should be prioritized to mitigate poverty increase driven by environmental factors.
National governments play a pivotal role in implementing policies that integrate climate resilience with economic empowerment strategies. By investing in renewable energy infrastructure and promoting sustainable agricultural practices, nations can create job opportunities that simultaneously address climate change and poverty increase. Additionally, improving social safety nets and providing access to healthcare and education will strengthen communities’ resilience against climate disruptions.
On a community level, grassroots initiatives that involve local populations in climate adaptation efforts have proven effective at reducing poverty increase. Community-based projects that focus on resource conservation, disaster preparedness, and sustainable livelihoods can create adaptive frameworks to withstand the impacts of climate change. Empowering local communities with information and resources to engage in climate action not only alleviates poverty but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards environmental stewardship.
The Path Forward: Integrating Solutions to Combat Climate Change and Poverty Increase
Collaborative Efforts for Sustainable Development
Global partnerships are essential in addressing the complex interrelation between climate change and poverty increase. International organizations, governments, and local communities must work together to implement comprehensive solutions that address both environmental and socioeconomic challenges. Collaborative efforts are critical to ensure the transfer of technology, expertise, and financial resources to the most affected regions, enabling sustainable development and poverty alleviation.
Building Resilient Communities
Resilience-building is a crucial aspect of combating climate change and poverty increase. Empowering communities with the tools and knowledge to adapt to changing conditions enhances their capacity to withstand environmental and economic shocks. Investment in education, infrastructure, and health services forms the foundation for resilient communities capable of thriving amidst climate challenges. Strategies that promote inclusivity and equitable access to resources ensure that no group is left behind in the fight against poverty and climate change.
Enhancing Policy Frameworks
Robust policy frameworks that integrate climate change mitigation with poverty alleviation are vital for sustainable development. Governments must prioritize policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions while simultaneously addressing the social determinants of poverty increase. This involves ensuring resource allocation toward renewable energy, promoting sustainable industry practices, and implementing social programs that support vulnerable populations. By aligning economic and environmental incentives, policymakers can create a cohesive strategy that addresses climate change and poverty increase.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Climate Change and Poverty Increase
Addressing the dual challenges of climate change and poverty increase requires a holistic approach that integrates environmental sustainability with socioeconomic development. This multifaceted strategy involves collaboration across international, national, and local levels, ensuring that efforts to mitigate climate change are aligned with poverty alleviation initiatives. Prioritizing resilience-building within vulnerable communities will enable them to adapt to the adverse effects of climate change and foster long-term development.
While climate change intensifies existing socioeconomic inequalities and propels poverty increase, targeted interventions can reverse this trend. By investing in sustainable technologies, education, infrastructure, and health, societies can build a resilient future that simultaneously combats climate change and reduces poverty. It is imperative that global actors unite in their commitment to addressing these interconnected challenges, promoting a sustainable and equitable development trajectory for future generations.