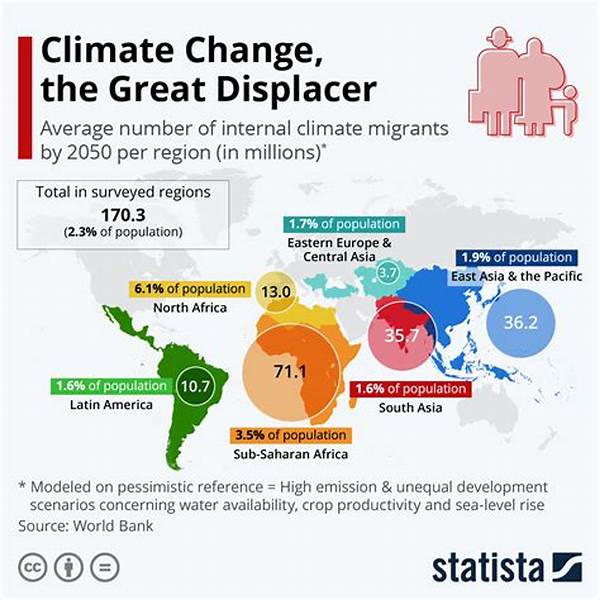
Understanding Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
Climate-induced migration and displacement have emerged as significant challenges in the modern era, driven largely by the impacts of climate change. The increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters, such as floods, droughts, and hurricanes, along with gradual environmental changes like rising sea levels and desertification, have forced many communities to leave their homes in search of safety and better living conditions. These movements, often involuntary, place considerable strain on both the displaced populations and the host communities that receive them.
Read Now : Water-efficient Irrigation Techniques
The consequences of climate-induced migration and displacement are profound and multifaceted. Affected individuals face not only the immediate loss of shelter and livelihoods but also long-term socio-economic challenges. Displacement disrupts traditional ways of life and places additional pressure on urban areas, often leading to conflicts over resources and socio-economic tensions. Developing strategies to address these challenges is crucial for ensuring sustainable and peaceful coexistence between affected populations and host communities.
To effectively manage climate-induced migration and displacement, it is imperative to implement comprehensive policies and frameworks at both national and international levels. These should include preventive strategies that focus on building resilience within vulnerable communities, enhancing early warning systems, and improving infrastructure to withstand climatic impacts. International cooperation is also essential in providing financial and technical support to the most affected regions, ensuring that migration and displacement occur under humane and organized conditions.
Causes and Impacts of Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
1. Climate change, through its effects on environmental degradation, is a primary driver of climate-induced migration and displacement. As climates alter, ecosystems become uninhabitable, prompting migration.
2. Severe weather events, intensified by climate change, contribute significantly to climate-induced migration and displacement, as they destroy homes and livelihoods, forcing populations to move.
3. Rising sea levels, resulting from global warming, threaten coastal communities, leading to climate-induced migration and displacement as inhabitants seek safer, inland locations.
4. Droughts and desertification, exacerbated by climate change, render agricultural lands barren, driving rural populations to urban areas and causing climate-induced migration and displacement.
5. The reduced availability of water resources due to climate change impacts agricultural productivity and daily living, which in turn results in climate-induced migration and displacement as affected populations relocate.
Challenges and Solutions for Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
Addressing climate-induced migration and displacement requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses environmental, social, and economic dimensions. One of the primary challenges lies in identifying and documenting the scale and scope of these movements. Accurate data collection and analysis are essential to understand the patterns and predict future trends, enabling effective planning and response strategies.
Solutions must also focus on enhancing the resilience of communities vulnerable to climate-induced migration and displacement. Investing in sustainable infrastructure, such as improved housing, transportation, and water management systems, can mitigate the impacts of climate change and reduce the necessity for relocation. Additionally, implementing early warning systems and educating communities about adaptive agricultural practices can help in minimizing displacement due to environmental changes.
Another critical aspect is the need for international collaboration in managing climate-induced migration and displacement. Countries and regions must work together to share knowledge, resources, and best practices. Establishing legal frameworks that recognize climate-displaced individuals as refugees could offer them protection and access to aid. Furthermore, facilitating dialogue between migrants and host communities can foster mutual understanding and cooperation, paving the way for peaceful coexistence and integration.
Policy Measures and Frameworks for Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
1. National governments need to formulate policies aimed specifically at managing climate-induced migration and displacement by predicting vulnerable zones and planning preemptive evacuations.
2. International legal frameworks, akin to those protecting war refugees, could be established to ensure the rights and welfare of climate-displaced individuals.
3. Regional cooperation is vital for providing financial and logistical support to heavily impacted areas, thereby aiding in managing climate-induced migration and displacement.
4. Developing robust disaster response frameworks can minimize harsh impacts on affected populations, thus preventing forced climate-induced migration and displacement.
5. Raising public awareness on climate-induced migration and displacement can foster community-level resilience and preparedness against environmental changes.
Read Now : Indexing Academic Journal Articles
6. Infrastructure development, particularly in at-risk areas, can enhance community resilience and reduce the need for climate-induced migration and displacement.
7. Establishing clear pathways for integrating displaced individuals into host communities can aid in managing the social impacts of climate-induced migration and displacement.
8. Investment in education and skills training for displaced populations can mitigate the socio-economic impacts of climate-induced migration and displacement.
9. Implementing sustainable land use practices can reduce environmentally induced pressures that lead to migration and displacement.
10. Encouraging private sector engagement in addressing climate-induced migration and displacement can unlock innovative solutions and additional resources.
Socio-Economic Dimensions of Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
The socio-economic implications of climate-induced migration and displacement are vast and complex. Displaced populations often face significant hurdles in rebuilding their lives, including access to employment, education, and essential services. This involuntary movement disrupts traditional livelihoods, leading to potential competition for resources and employment opportunities with host communities. Consequently, it is crucial to devise socio-economic strategies that support the seamless integration of displaced individuals.
One effective approach is to provide skills training and education for displaced populations, equipping them for new job markets and facilitating economic self-reliance. Tailored educational programs can help bridge skill gaps and enable affected individuals to contribute positively to their new communities. Moreover, establishing clear legislative frameworks that protect the rights of climate-displaced individuals can prevent exploitation and discrimination, ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Additionally, facilitating inclusive dialogue between displaced populations and host communities is vital for fostering mutual understanding and collaboration. Such engagement can mitigate potential conflicts and promote social cohesion. Encouraging host communities to participate in resettlement planning processes can also enhance acceptance and support for displaced populations, creating a harmonious environment conducive to long-term prosperity.
Investing in Resilience for Climate-Induced Migration and Displacement
Investments in resilience-building measures are key to addressing climate-induced migration and displacement. Enhancing infrastructure, such as flood defenses and drought-resistant agriculture, can reduce the vulnerability of at-risk areas, lessening the likelihood of displacement. Moreover, adopting sustainable environmental practices helps in maintaining ecological balance, thereby minimizing the drivers of migration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, climate-induced migration and displacement present substantial challenges that require immediate attention and comprehensive strategies. These phenomena, spurred by environmental changes, demand coordinated efforts across multiple sectors and stakeholders to address both the causes and consequences. Effective management hinges on a deep understanding of the socio-economic, legal, and environmental dimensions involved.
The international community must collaborate to develop frameworks that protect and support displaced populations, ensuring that climate-induced migration and displacement occur under humane conditions. By promoting resilience within vulnerable communities and facilitating the integration of displaced individuals into host regions, we can work towards sustainable solutions that uphold human dignity and foster peaceful coexistence.
The complexities inherent in climate-induced migration and displacement underscore the need for innovative and proactive policy-making. Governments, NGOs, and the private sector must engage in joint efforts to devise long-term strategies that mitigate the impacts of environmental change. Through inclusive and coordinated action, we can pave the way for a more resilient future, safeguarding communities and preserving ecosystems.