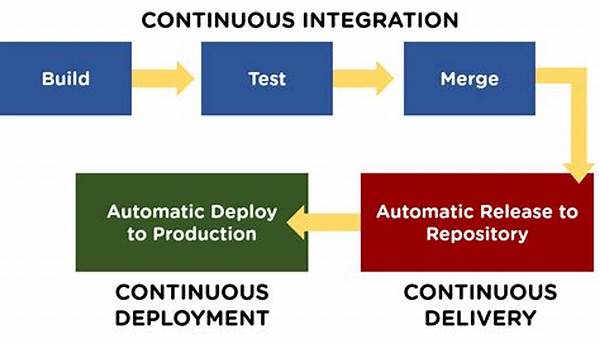
The evolution of software development processes has been significantly influenced by the adoption of microservices architecture. Microservices allow for modular, scalable, and efficient service updates, which are vital in today’s fast-paced development environment. However, managing these services requires more advanced methodologies, and one of the most critical among them is continuous integration (CI). CI has become an indispensable practice in microservices development, streamlining code integration, enhancing code quality, and simplifying deployment pipelines. Continuous integration for microservices development ensures that updates and integrations are handled smoothly, minimizing disruptions and maintaining system stability.
Read Now : Enhancing Business Through Api Implementation
The Significance of Continuous Integration in Microservices Architecture
Continuous integration for microservices development plays a pivotal role in maintaining service integrity and efficiency. Microservices, by their nature, involve multiple independent components that must work seamlessly together. Implementing CI facilitates the automated testing and merging of code changes, reducing the probability of integration issues. It allows developers to detect errors early in the cycle, preventing flawed code from progressing. This practice also promotes a culture of regular updates, ensuring that codebases are always up-to-date and aligning with the latest development practices. Furthermore, CI optimizes resource management by automating repetitive tasks, allowing developers to focus on creating innovative solutions rather than mundane integration issues. In essence, continuous integration for microservices development enhances developmental agility and robustness.
Another aspect where continuous integration for microservices development excels is in its support for collaborative work environments. In a setting where numerous developers are working on various components of a microservices architecture, CI serves as a cohesion point. It ensures that code from different team members integrates without conflict, fostering a cohesive development atmosphere. By automating integrations, the process becomes more predictable, providing a reliable foundation for collaborative efforts. This shared framework reduces the dependency on manual interventions, allowing for consistent and reliable integrations. Hence, continuous integration for microservices development not only serves a technical purpose but also strengthens team collaboration and synergy.
Moreover, continuous integration for microservices development is crucial for delivering quality user experiences. With its ability to streamline the integration process, CI ensures that end-users receive clean, error-free software updates. The automated checks and balances enabled by CI detect discrepancies promptly, safeguarding the user experience against unforeseen disruptions. By maintaining service continuity, CI helps in building user trust and satisfaction, which are vital for the service’s reputation and success. Thus, continuous integration for microservices development not only optimizes backend operations but also serves a significant role in enhancing the user interface and experience.
Implementing Continuous Integration for Microservices Development
1. Automation: Continuous integration for microservices development leverages automation to streamline integration processes. Automated builds, tests, and deployments minimize human error and ensure consistency throughout the development lifecycle, enhancing the system’s reliability.
2. Scalability: The CI approach in microservices supports scaling with ease. As systems grow, continuous integration facilitates seamless addition and management of new services, ensuring that scaling operations do not disrupt existing functionalities.
3. Version Control: Effective version control is a cornerstone of continuous integration for microservices development. It enables developers to manage multiple code versions efficiently, allowing for swift rollbacks and error resolution without compromising system integrity.
4. Collaboration: CI fosters a collaborative environment among developers. By consistently integrating updates into a shared repository, team members remain aligned with the project’s progress, reducing conflicts and improving overall team synergy.
5. Quality Assurance: Continuous integration for microservices development integrates real-time testing as part of the development process. This ensures that any new code integrates correctly and functions as intended, thereby upholding the quality and reliability of the software.
Challenges in Continuous Integration for Microservices Development
Despite the many advantages, implementing continuous integration for microservices development presents its own set of challenges. One significant challenge is managing the complexity of the pipeline itself. Each microservice has its own unique dependencies, which must be addressed during the integration process. CI pipelines can become intricate, needing meticulous configuration to handle each service’s individual requirements effectively. Developers must be vigilant to ensure that changes in one service do not inadvertently affect the performance or stability of others, which demands a robust and comprehensive testing strategy.
Additionally, continuous integration for microservices development requires a cultural shift within organizations. Teams need to embrace a mindset of collaboration, frequent communication, and joint responsibility for code quality across all services. The siloes that often exist in traditional development models must be broken down to facilitate seamless integration efforts. This cultural transformation is not instantaneous and requires concerted efforts in team-building and process adjustments. It is essential for organizations to invest in training and support systems to help teams adapt to this new method of working effectively. In doing so, they can unlock the full potential of continuous integration for microservices development.
Moreover, the tools and technologies used in CI need to be carefully selected and implemented to align with the organization’s specific needs. New tools continuously emerge, offering varied functionalities and benefits, which can be overwhelming. It is crucial for organizations to assess these tools and choose those that best fit their existing infrastructure and future goals. The effectiveness of continuous integration for microservices development largely depends on leveraging advanced tools that improve pipeline efficiency and integration accuracy. Careful planning and execution of these aspects can lead to successful CI implementation, enhancing both microservices’ functionality and the development process as a whole.
Key Considerations for Continuous Integration in Microservices
1. Service Isolation: Ensuring that each microservice is thoroughly isolated to avoid cross-dependencies during integration is fundamental to successful CI implementation.
2. Automated Testing: Comprehensive automated tests that cover unit, integration, and functional testing are vital in CI to ensure code quality and integration reliability.
3. Monitoring and Logging: Continuous integration for microservices development benefits from robust monitoring and logging to quickly identify and resolve integration issues.
4. Incremental Deployment: Employing incremental deployment strategies, such as canary releases, aids in minimizing the impact of new service integrations on the overall system.
Read Now : Gesture Recognition In Virtual Reality
5. Feedback Loops: Establishing effective feedback mechanisms allows developers to receive immediate insights on integration successes or failures, promoting timely corrections.
6. Security: Maintaining security protocols within the CI pipeline ensures that integrations are performed without exposing the system to vulnerabilities.
7. Dependency Management: Proper management of microservice dependencies is crucial to prevent conflicts and ensure smooth CI operations.
8. Tool Compatibility: Selecting CI tools that align with the technology stack of the microservices architecture is crucial for streamlined integrations.
9. Documentation: Maintaining clear and comprehensive documentation of CI processes helps in onboarding new team members and maintaining system consistency.
10. Scalability Planning: Ensuring that CI infrastructure can scale along with the growth of the microservices is essential for sustained system performance.
Continuous Integration Tools and Technologies in Microservices
In the thriving landscape of software development, selecting appropriate tools and technologies for continuous integration in microservices is critical for achieving an optimized workflow. The variety of existing tools offers different benefits, and choosing the right ones can significantly influence the efficiency of the integration process. Jenkins, Bamboo, and GitLab CI/CD are some of the prominent tools widely adopted due to their comprehensive capabilities in managing build, testing, and deployment processes. These tools provide automation and scalability, integral to supporting the dynamic nature of microservices development.
Moreover, containerization technologies, such as Docker and Kubernetes, complement continuous integration for microservices development by providing isolated environments that replicate production settings. These tools not only simplify deployments but also ensure consistency across environments, mitigating the risk of discrepancies between development, testing, and production stages. Their integration with CI pipelines enhances the overall reliability and stability of the software being developed. Furthermore, adopting monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana allows for in-depth analysis of integration processes, offering timely insights into performance metrics and potential bottlenecks, thereby facilitating proactive management and optimization of the CI environment.
The choice of tools must also align with the specific requirements of the development team and the organization as a whole. Flexibility, ease of use, and integration capabilities are some of the factors that influence these decisions. Continuous integration for microservices development thrives on a tailored toolset that not only automates the integration process but also propels the development lifecycle towards enhanced agility and performance. Thus, careful consideration and assessment during tool selection contribute to building robust CI practices that support the holistic growth and efficiency of microservices architectures.
Conclusion: The Future of Continuous Integration in Microservices
The future of continuous integration for microservices development holds immense potential, driven by ongoing technological advancements and a growing emphasis on automation. As organizations strive for more agile and efficient development processes, CI will continue to evolve, incorporating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These innovations promise to further streamline integration tasks by automating decision-making processes and refining predictive analytics for identifying potential integration issues before they arise. Such advancements will enhance the stability and robustness of microservices, ensuring seamless integration and high-quality delivery.
In addition, the increasing adoption of DevOps culture will further bolster continuous integration practices. By integrating development and operations teams, organizations can achieve more cohesion and transparency across the development lifecycle, breaking down traditional silos that have hindered seamless integration efforts. DevOps, in conjunction with CI, will empower teams to deliver software at higher velocities, maintaining a continuous feedback loop that drives constant improvements and optimizes performance.
As continuous integration for microservices development continues to mature, its central role in achieving technical excellence and operational efficiency becomes more pronounced. Organizations that embrace these advancements will position themselves at the forefront of innovation, maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving digital landscape. The fusion of advanced technologies and collaborative methodologies will redefine how microservices are developed and integrated, ensuring seamless delivery and exceptional user experiences. Thus, continuous integration will remain a cornerstone of successful microservices development strategies, driving sustainable growth and innovation in the software industry.