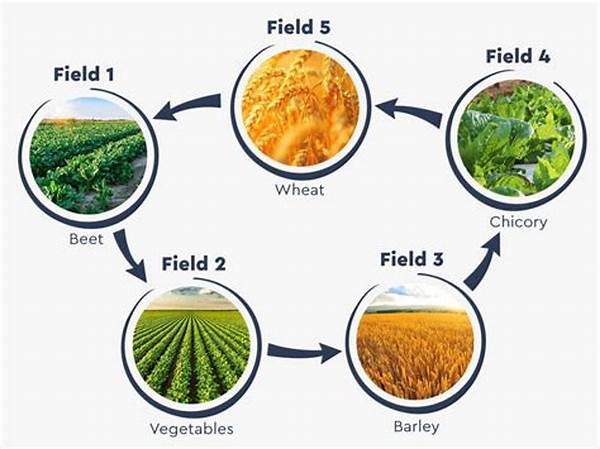
The practice of crop rotation, a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, offers numerous advantages that contribute significantly to long-term environmental health and agricultural productivity. By systematically alternating the types of crops grown on a particular piece of land, farmers can optimize the use of nutrients, control pests and diseases, and improve soil structure. This agricultural technique has been recognized for its potential to enhance food security and protect ecosystems, making it an essential strategy in sustainable farming practices.
Read Now : Dynamic Systems For Assessing Scientific Research
The Role of Crop Rotation in Enhancing Soil Health
Crop rotation benefits for sustainability are prominently reflected in the enhancement of soil health. By rotating different crops, particularly those with varying nutrient requirements and root structures, farmers can prevent the depletion of essential soil nutrients. Leguminous crops, such as beans and peas, naturally fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, the variation in root depths promotes better soil aeration and structure, facilitating improved water retention and drainage. The cumulative effects of these practices significantly reduce soil erosion and degradation, creating a more resilient agricultural system that can withstand climatic and environmental challenges.
Another important aspect of crop rotation is its ability to disrupt the life cycles of pests and pathogens. By changing the crops grown in a particular field, the specific environmental conditions that pests thrive in are altered. This natural method of pest control reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, which often have detrimental impacts on both biodiversity and human health. Consequently, crop rotation plays a vital role in promoting ecological balance and fostering a healthier agricultural environment. Given these multifaceted benefits, employing crop rotation is pivotal for achieving and maintaining sustainable agricultural practices.
Economic and Environmental Advantages
1. Nutrient Optimization: Crop rotation benefits for sustainability involve effective nutrient use, allowing a balance between nutrient absorption and replenishment, consequently reducing chemical input dependency.
2. Pest Management: By rotating crops, farmers disrupt pest breeding cycles, lowering pest populations in a natural manner and reducing pesticide use.
3. Reduced Soil Erosion: Diverse root structures in crop rotation help improve soil integrity, thus mitigating erosion and preserving farmland health.
4. Biodiversity Enhancement: Crop rotation fosters biodiversity by encouraging a variety of plant and animal species, strengthening ecosystem resilience.
5. Increased Yield Stability: Crop rotation contributes to more stable yields by cultivating healthier soil and reducing pest and disease pressures.
Crop Rotation and Climate Change Mitigation
The crop rotation benefits for sustainability are not limited to soil health. This agricultural method plays an essential role in climate change mitigation. By enhancing soil organic matter content through diversified cropping systems, carbon sequestration in soils is promoted. Increased carbon storage not only contributes to improving soil fertility but also helps in reducing the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide, a leading greenhouse gas. This practical application of crop rotation serves as a powerful tool for farmers seeking to lower their carbon footprint and adapt to changing climatic conditions.
Moreover, adopting crop rotation practices can lead to decreased fossil fuel dependency. As reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides diminishes, the energy consumption associated with their production, transportation, and application decreases. This transition toward more sustainable energy practices is crucial in the global effort to address climate change. Additionally, the increased resilience of crops to extreme weather events resulting from enhanced soil health can aid in ensuring food security amidst growing unpredictability in weather patterns. Thus, crop rotation remains a vital practice in sustainable agriculture with far-reaching benefits beyond immediate agricultural productivity.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Crop Rotation
While the crop rotation benefits for sustainability are substantial, several challenges must be considered.
1. Planning Complexity: Developing an effective crop rotation schedule requires careful planning considering factors such as crop compatibility and market demand.
2. Economic Constraints: Transitioning to crop rotation systems may entail upfront costs and require continued investment for monitoring and adjusting practices.
3. Knowledge and Training: Effective implementation relies heavily on farmer education and access to the latest agricultural research and practices.
4. Market Variability: Changes in market demand for specific crops can affect rotation choices, impacting farm income.
Read Now : Streamlining Support Processes Via Apis
5. Land Availability: Limitations in available land may restrict the ability to implement diverse crop rotation systems fully.
6. Infrastructure Needs: Adequate infrastructure for dealing with diverse crops, including storage and transportation, is necessary for successful rotation practices.
7. Pest and Disease Management: While rotation aids in reducing pest pressures, it is not a standalone solution and should be integrated with other management practices.
8. Soil Type Variation: Diverse soil types within a region may require tailored rotation plans, complicating implementation.
9. Climate Conditions: Regional climate conditions may limit the types of crops suitable for rotation.
10. Regulatory Frameworks: Legal and policy considerations can impact the feasibility and attractiveness of crop rotation systems.
Future Prospects for Crop Rotation Practices
The future of agriculture lies significantly in the adoption of sustainable practices such as crop rotation. As global demand for food continues to rise alongside environmental concerns, the crop rotation benefits for sustainability offer a viable solution to these pressing issues. By emphasizing agricultural practices that prioritize the health of the soil and the environment, farmers can achieve a balance between productivity and ecological preservation. The potential for technological advancements to enhance crop rotation techniques further underscores the importance of ongoing research and development in this field.
Investing in training programs and increasing accessibility to resources for farmers are critical steps toward realizing the full potential of crop rotation. Collaboration between governments, research institutions, and the agricultural community can drive innovation and provide the support needed for widespread adoption. As society becomes increasingly aware of the necessity of sustainable practices, policies that promote and incentivize crop rotation are likely to gain traction, thus ensuring its place at the forefront of modern agriculture. In sum, crop rotation represents a promising pathway toward achieving sustainability in agriculture, with benefits that extend to the global environment, economy, and society as a whole.
Conclusion: A Move Towards Comprehensive Agricultural Reform
The myriad crop rotation benefits for sustainability underscore the necessity of integrating this practice into the core of agricultural reform.
The collaborative efforts among policymakers, agricultural scientists, and farmers play an indispensable role in the successful implementation of crop rotation systems. By advocating for policies that encourage research and support the transition towards more sustainable practices, the agricultural sector can evolve to meet the challenges of the 21st century. These initiatives, coupled with education and training, can empower farmers to adopt crop rotation techniques that benefit the environment while ensuring long-term productivity and stability.
Moreover, as awareness grows regarding the critical importance of sustainable practices, the global agricultural community is poised to leverage the crop rotation benefits for sustainability to address broader ecological and economic goals. By fostering resilience and adaptability within farming systems, crop rotation can lead to significant advancements in environmental conservation while simultaneously supporting the livelihoods of farmers worldwide. The integration of these practices marks a progressive step toward a more sustainable and equitable agricultural future.