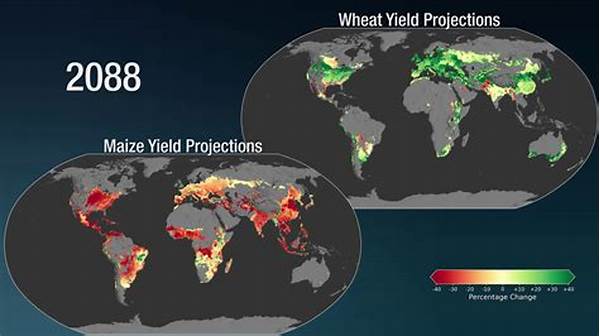
The Interrelationship Between Crop Yield and Climate Change
The impact of climate change on crop yield has become an increasingly pertinent topic in agricultural and environmental discussions. Climate change, characterized by shifts in temperature, precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events, poses significant risks to agricultural productivity. These changes disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystems in which crops are grown, potentially leading to reduced yields globally. Climate change can cause heat stress on crops, alter pest and disease cycles, and create water scarcity, all of which contribute to fluctuations in crop yield. For instance, higher temperatures can accelerate crop maturation, reducing the grain filling period, thereby affecting crop yield quantity and quality. Additionally, altered precipitation patterns can lead to droughts or floods, further stressing crop systems. Therefore, understanding the interrelationship between crop yield and climate change is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate these adverse effects and ensure food security.
Read Now : Strategies For Improving Research Quality
Efforts to adapt to these challenges include breeding crop varieties that are more resilient to heat and drought, optimizing irrigation practices, and employing advanced farming technologies. Researchers and policymakers are increasingly focused on developing sustainable agricultural practices to enhance crop yield while also mitigating the effects of climate change. These practices may include the use of climate-smart agriculture techniques, which focus on increasing productivity sustainably, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing resilience to climate change. As we move forward, integrated approaches that take into account both crop yield and climate change will be essential for creating a sustainable and secure food supply.
To better grasp the future outlook, it is necessary to conduct comprehensive research and implement policies that encourage innovation in the agricultural sector. Collaboration between governments, scientists, and farmers will be key in addressing the intertwined challenges posed by crop yield fluctuations and climate change. Only through such united efforts can we hope to sustain and potentially enhance global agricultural productivity in the face of growing environmental uncertainties.
Factors Influencing Crop Yield and Climate Change
1. Temperature Variability: Temperature fluctuations, caused by climate change, significantly influence crop yield. Higher temperatures can lead to heat stress, affecting crop development phases and ultimately reducing yield.
2. Precipitation Changes: Altered rainfall patterns due to climate change can lead to droughts or floods, disrupting the water supply crucial for optimal crop yield.
3. Pest and Disease Proliferation: Climate change may extend the geographical range and lifespan of pests and diseases, thereby increasing their influence on crop yield.
4. Soil Degradation: Climate change impacts soil health and fertility, which are vital for sustaining crop yield. Erosion and nutrient depletion are key concerns.
5. Adaptation Strategies: Adopting new agricultural practices, such as crop rotation and conservation tillage, helps in mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on crop yield.
Socio-Economic Impacts of Crop Yield and Climate Change
The intersection of crop yield and climate change has profound socio-economic implications. A decline in crop yields can lead to increased food prices, affecting food affordability for populations globally. This is particularly significant in developing countries, where agriculture constitutes a major part of the economy, and a substantial portion of the population relies on farming for their livelihood. Additionally, reduced crop yield due to climate change can lead to food scarcity, necessitating imports and straining national budgets. Governments may face challenges in ensuring food security and social stability, with the rural poor being the most vulnerable to these fluctuations.
On the economic front, crop yield declines could disrupt supply chains, affecting multiple industries from agriculture to retail. Businesses may experience higher operational costs, potentially leading to reduced competitiveness in the global market. In response, policymakers are encouraged to invest in agricultural research and technology, aiming to enhance crop yield resilience to climate change. Efforts such as improving infrastructure, providing farmer education, and supporting technological innovation in agriculture can play a critical role in adapting to these changes. Furthermore, international cooperation on climate policies can provide a framework for shared solutions, helping to stabilize both crop yield and global markets in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Scientific R&D in Crop Yield and Climate Change
1. Genetic Engineering: Advances in genetic engineering focus on developing crop varieties with enhanced resistance to climate change impacts, preserving yield stability.
2. Precision Agriculture: The adoption of precision agriculture technologies allows for more efficient resource use, leading to optimized crop yield despite climate pressures.
3. Soil Health Technologies: Innovations to maintain soil health, critical for sustaining crop yield, are being developed to combat adverse effects of climate change.
4. Water Management Solutions: Advanced irrigation and water management techniques are crucial for conserving water resources and ensuring consistent crop yield amidst changing precipitation patterns.
5. Carbon Sequestration Practices: Implementing practices that enhance carbon sequestration in agricultural lands can mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, complementing efforts to stabilize crop yield.
Read Now : Features Of Open-source Monitoring Platforms
6. Alternative Cropping Systems: Research into alternative cropping systems aims to diversify production and increase resilience to climate change.
7. Weather Forecasting Tools: Enhanced weather prediction tools provide farmers with the data needed to make timely decisions to protect crop yield.
8. Integrated Pest Management: Developing integrated pest management approaches minimizes pest impact while preserving environmental integrity, supporting crop yield.
9. Climate-Resilient Policies: Policymaking informed by climate science seeks to establish guidelines that maintain crop yield despite climate challenges.
10. Agroforestry Practices: Implementing agroforestry can enhance biodiversity and improve crop yield resilience to climate change.
Strategic Policy Formulation for Crop Yield and Climate Change
To effectively address the challenges posed by climate change on crop yield, strategic policy formulation is imperative. Policymakers must prioritize integrating climate change considerations into agricultural development plans. This involves implementing adaptive practices that are both sustainable and economically viable. Investments in agricultural research and development, focused on uncovering innovative solutions to adapt crops to changing climatic conditions, are of utmost importance. By supporting the development and distribution of climate-resilient crop varieties, governments can help farmers safeguard their yields against adverse climatic impacts.
In addition to research investments, educational initiatives to improve farmer awareness and skills in climate-smart agriculture techniques are essential. Providing subsidies or incentives for adopting such practices could further drive large-scale change. Policymakers should also focus on enhancing infrastructure to facilitate efficient resource distribution and access to markets. International collaboration plays a vital role in sharing knowledge and resources, allowing countries to jointly combat the threat that climate change poses to crop yields. Regional climate models and forecasting tools should be leveraged to support timely decision-making processes at both local and national levels. Establishing a coherent national framework that aligns with global climate goals will foster resilience within the agricultural sector while ensuring a stable crop yield in the long term.
The Future of Crop Yield and Climate Change
As climate change continues to exert pressure on global agriculture, the future of crop yield remains uncertain, necessitating robust strategies to mitigate potential risks. Embracing technological advancements, such as precision agriculture, can significantly enhance efficiency and resilience in farming operations. By utilizing data-driven tools, farmers can optimize inputs, reduce waste, and ensure sustainable crop yield practices. Genetic engineering also holds promise, offering avenues to develop crop varieties capable of thriving amidst adverse climate scenarios, thereby securing future food supplies.
Collaboration across international borders is increasingly important, as sharing advancements in technology and strategies contributes to the resilience of global agriculture. Research institutions, governments, and private entities must unite in efforts to prioritize climate-smart agricultural techniques and policies. These collective actions will play a pivotal role in securing an adaptive and sustainable approach to managing crop yields in the wake of climate change. Therefore, a concerted focus on innovation, policy alignment, and cross-border cooperation will be critical in navigating the complex challenges presented by climate change, ensuring that future generations can sustainably meet the global demand for food.
Conclusion
In summary, the intricate relationship between crop yield and climate change demands a multi-faceted and strategic approach to ensure food security in the coming years. As climate change intensifies, its effects on crop yield are becoming increasingly apparent, necessitating immediate actions to mitigate adverse impacts. By supporting research initiatives that develop climate-resilient crop varieties and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, stakeholders can significantly reduce vulnerability to climatic fluctuations. In addition, enhancing educational campaigns to promote awareness of climate-smart agriculture will empower farmers and increase adaptive capacity at the grassroots level.
Furthermore, creating integrated policies that align with both national and international climate change goals will enhance cooperative efforts, facilitating resource sharing and joint research endeavors. By embedding climate considerations into agricultural planning and decision-making processes, policymakers can build resilient systems capable of withstanding the unpredictability brought about by climate change. Hence, a synergistic approach, combining technological innovation, policy support, and international collaboration, is essential for maintaining stable crop yields and ensuring sustainable agricultural productivity in an era characterized by environmental change.