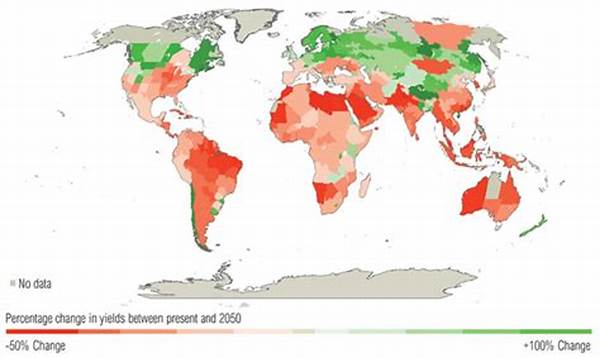
The agricultural sector, crucial for global food security and economic stability, is significantly influenced by various environmental conditions, especially weather. As the climate undergoes changes on both local and global scales, the effects of weather variations on crop yield have become a topic of paramount importance. Understanding these effects is essential for developing adaptive strategies that ensure sustainable agricultural practices. This article delves into the intricate relationship between weather variations and crop yield, exploring multiple perspectives and implications.
Read Now : Peer-reviewed Journal Breakthroughs
Climate Change and Crop Productivity
Climate change introduces variability and unpredictability in weather patterns, severely affecting agricultural productivity. The effects of weather variations on crop yield are evident in terms of altered rainfall patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and shifts in temperature regimes. These changes can lead to both positive and negative impacts on different crops, depending on their specific climatic requirements. For instance, excessive rainfall may lead to waterlogging, affecting root growth and nutrient uptake, while prolonged droughts can cause water scarcity, affecting photosynthesis and biomass production. As such, farmers, researchers, and policymakers must collaborate to devise strategies that mitigate these adverse effects, embracing technologies like drought-resistant crop varieties and improved irrigation systems. The intricate relationship between weather variations and crop yield underscores the need for proactive measures to anticipate and counteract the negative consequences of climate change on agriculture.
Factors Influencing Crop Yield Amidst Weather Variability
1. Temperature Fluctuations: The effects of weather variations on crop yield are significantly influenced by temperature changes. Excessive heat can lead to heat stress, affecting crop metabolism and reducing yields. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can damage crops, particularly those sensitive to frost.
2. Rainfall Patterns: Shifts in rainfall patterns, a direct effect of weather variations, impact crop yield. Inadequate rainfall leads to drought conditions, affecting soil moisture levels and plant growth, while excessive rainfall can cause flooding and soil erosion.
3. Soil Moisture Levels: The effects of weather variations on crop yield are intricately linked to soil moisture levels. Fluctuations in weather can lead to either waterlogging or drought, both of which have detrimental effects on root development and nutrient absorption.
4. Extreme Weather Events: The occurrence of extreme weather events, a manifestation of weather variations, poses significant risks to crop yield. Storms, hail, and strong winds can cause physical damage to crops, impairing their growth and development.
5. Climate Resilience of Crops: The effects of weather variations on crop yield are moderated by the inherent climate resilience of specific crop species. Crops with higher resilience can withstand variable weather conditions better, maintaining higher productivity levels.
Read Now : Protecting Rest Apis From Attacks
Adaptive Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture
Farmers and agricultural stakeholders must adopt adaptive strategies to combat the effects of weather variations on crop yield. Embracing climate-smart agriculture is one such strategy that prioritizes practices enhancing resilience and sustainability. Crop diversification, for example, reduces risks associated with climate variability by spreading the exposure across different crops, thus mitigating potential losses. Additionally, incorporating agroforestry practices enhances soil health and provides microclimates beneficial for crop growth. Investing in advanced technologies, such as precision agriculture and data-driven farming practices, allows for real-time monitoring and appropriate responses to weather changes, enhancing crop yield. Moreover, policies encouraging sustainable water management are crucial, especially in areas prone to drought. By implementing these adaptive strategies, the agricultural sector can better withstand the adverse effects of weather variations on crop yield, ensuring both productivity and sustainability for future generations.
Technological Innovations and Crop Yield
Technological innovations play a pivotal role in counteracting the effects of weather variations on crop yield. The integration of precision agriculture practices, satellite-based weather monitoring, and genetically modified crops designed for resilience to adverse conditions has become increasingly vital. For instance, precision agriculture employs sensors and data analytics to optimize field management in response to specific weather patterns. It allows for precise water and nutrient applications, reducing waste and enhancing crop productivity. Satellite weather forecasting, meanwhile, provides farmers with timely data on imminent weather changes, enabling proactive measures. The development of genetically modified crop varieties engineered for drought resistance and improved disease tolerance stands at the frontier of agricultural innovation. These technologies collectively support farmers in managing the unpredictability of weather, thus minimizing the adverse effects on crop yield. As technology continues to evolve, its integration into agricultural practices offers promising solutions to future challenges posed by climate variability.
Impacts of Meteorological Variability on Harvest
The effects of weather variations on crop yield manifest in various forms, impacting the overall harvest and food supply chain. Temperature extremes can lead to accelerated or hindered growth rates in crops, disrupting their life cycles and affecting yield quality. While moderate temperatures can enhance growth conditions, severe cold or heat can lead to reduced seed germination rates and poor yield. Precipitation variability also directly affects the moisture content necessary for optimal crop growth. In regions experiencing erratic rainfall, crops are often subjected to drought stress or waterlogging, both affecting roots and reducing agricultural outputs. Moreover, extreme weather events like hailstorms, heavy winds, and floods can cause direct physical damage to crops, impacting their structural integrity and health. These effects not only reduce immediate yields but can also lead to long-term soil degradation and fertility loss. In the broader context, the implications of these challenges threaten food security, amplify economic vulnerabilities, and necessitate robust adaptation mechanisms to mitigate the effects of weather variations on crop yield.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effects of weather variations on crop yield present significant challenges to global agriculture, affecting productivity and food security. Understanding the complex interplay between weather and crop performance is crucial for developing adaptive strategies that ensure resilience in the face of climatic change. Through technological innovation, sustainable agricultural practices, and collaborative efforts among stakeholders, the adverse effects of climate variability can be mitigated, paving the way for a more secure and productive future in agriculture.