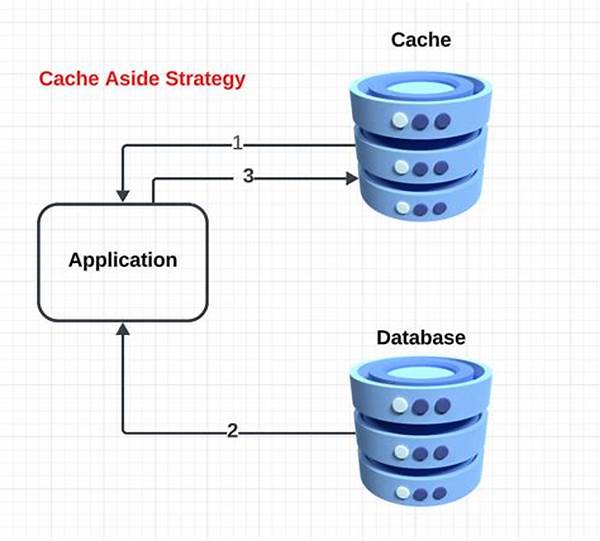
In the realm of database management, the importance of efficient database cache strategies cannot be overstated. As databases continue to grow in size and complexity, the need for robust caching solutions to enhance performance and reduce latency is paramount. With advancements in technology and an ever-expanding pool of data, database administrators are constantly seeking innovative ways to optimize performance. Implementing efficient database cache strategies is a critical component in ensuring that systems are responsive, reliable, and scalable. This article explores various approaches and methodologies that can be employed to optimize caching mechanisms within database environments.
Read Now : Methods For Benchmarking Research Quality
Understanding Efficient Database Cache Strategies
Efficient database cache strategies are integral to modern database architectures. By leveraging caching, systems can store frequently accessed data temporarily, thereby reducing the time needed to retrieve it from the database itself. This not only accelerates query performance but also minimizes the load on the database, allowing it to focus on more intensive operations. Efficient database cache strategies involve selecting the appropriate caching layer and technology, such as in-memory caches or distributed caching solutions. In-memory caches provide rapid access by storing data close to the processor, while distributed caches offer scalability by spreading the load across multiple nodes. The selection of a suitable caching strategy is contingent upon the specific requirements and constraints of the database environment, including the nature of the workload, the volume of data, and the acceptable latency levels.
To construct efficient database cache strategies, database administrators must conduct a thorough analysis of usage patterns. Identifying frequently accessed datasets can inform the prioritization of cache storage, ensuring that the most critical data is readily available. Additionally, automation tools can be employed to monitor cache performance, allowing for real-time adjustments to the caching strategy as needed. Efficient database cache strategies also involve maintaining cache coherence, ensuring that data remains consistent across both the cache and the database. This can be achieved through techniques such as cache invalidation and synchronization protocols, which update cached data when changes occur in the database.
Ultimately, the implementation of efficient database cache strategies demands a balanced approach that considers both technological and operational aspects. While technology provides the tools to enhance performance, it is the strategic application of these tools, informed by comprehensive data analysis, that yields optimal results. As databases continue to evolve, so too must the strategies that underpin their operation, ensuring that they remain capable of meeting the demands of an increasingly data-driven world.
Key Elements of Efficient Database Cache Strategies
1. Understanding usage patterns is essential for developing efficient database cache strategies, as it aids in identifying the most accessed datasets. By prioritizing these datasets for caching, database administrators can decrease query time and reduce database strain significantly.
2. Incorporating automation in cache management enhances efficient database cache strategies. Automation allows for continuous monitoring and real-time adjustments, ensuring optimal cache utilization. By leveraging automation tools, database systems can dynamically adapt to changing demands and maintain optimal performance levels.
3. Cache coherence maintenance is a crucial aspect of efficient database cache strategies. Techniques such as cache invalidation and synchronization protocols ensure data consistency between the cache and the database. This coherence guarantees that users receive accurate and up-to-date information, even in rapidly changing data environments.
4. Selecting the appropriate caching technology is vital for efficient database cache strategies. In-memory caches provide rapid access times, ideal for high-speed applications, whereas distributed caches offer scalability and load balancing. The choice depends on the specific needs of the database system, including data volume and expected latency.
5. Efficient database cache strategies must also measure cache performance metrics to ensure effectiveness. By regularly analyzing performance indicators such as hit ratios and cache latency, database administrators can identify bottlenecks and optimize caching strategies for better efficiency and reliability.
The Impact of Efficient Database Cache Strategies
Incorporating efficient database cache strategies can drastically enhance the performance of database systems. One of the primary benefits is the substantial reduction in data retrieval times. By storing frequently accessed data in a cache, systems can furnish responses to queries with significantly reduced latency. This ensures that end-users experience faster transaction times, enhancing overall user satisfaction. Another advantage is the reduction in load on the primary database. Since cached data alleviates the need for repeated database queries, the server can allocate more resources to complex operations, thereby improving system scalability and robustness.
Furthermore, efficient database cache strategies facilitate more consistent data access patterns, which can also result in cost savings. By minimizing read and write operations on the central database, organizations can lessen hardware and maintenance costs. This aspect is particularly beneficial for enterprises managing large volumes of data daily, as it permits them to optimize their resources efficiently. Efficient database cache strategies also play a pivotal role in ensuring data consistency, a critical aspect of database management. By implementing protocols such as cache invalidation and synchronization, organizations can guarantee that the information retrieved is up-to-date and reliable, reducing the risk of errors and discrepancies.
In conclusion, efficient database cache strategies serve as a cornerstone of modern database management practices. They do more than merely enhancing performance; they contribute to greater reliability, scalability, and cost-efficiency. As businesses continue to expand their digital operations and data requirements evolve, the adoption of these strategies will be indispensable. Organizations that prioritize efficient caching mechanisms will better position themselves to respond rapidly to user requirements and technological advancements, maintaining their competitive edge in increasingly data-driven marketplaces.
Read Now : **api Data Performance Optimization**
Exploring Caching Technologies
Within the spectrum of database management, numerous caching technologies can be leveraged to build efficient database cache strategies. Technologies such as Redis serve as in-memory data structures, providing exceptionally rapid data access due to their proximity to the processor. Redis excels in handling small, frequently accessed datasets, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring high-speed data retrieval. Conversely, Memcached offers a distributed memory object caching framework aimed at reducing database load by caching data and objects directly within memory. This reduces the time spent on database reads, significantly improving application speed.
Varnish Cache is another potent tool, primarily for web applications. Acting as an HTTP accelerator, Varnish diminishes backend server loads by serving cached version of web pages. It employs an efficient database cache strategy by storing copies of pages after initial requests. Additionally, Apache Ignite is a powerful open-source distributed database, providing an in-memory data grid with strong caching capabilities. Ignite offers seamless integration into existing databases, enhancing speed and resilience through its distributed architecture. Amazon ElastiCache brings hosted caching to the cloud, supporting both Redis and Memcached frameworks.
Efficient database cache strategies employ these technologies based on context and specific application requirements. Selection often depends on individual database architecture, data patterns, and application objectives. The understanding and implementation of these technologies are crucial to optimizing caching and improving database efficiency across diverse environments.
The Importance of Cache Invalidation
In the landscape of database caching, cache invalidation is a critical consideration within efficient database cache strategies. Cache invalidation ensures that changes made to the primary database are reflected promptly in the cached data, thus maintaining data accuracy and reliability. Proper invalidation mechanisms prevent stale or outdated data from being delivered to the end user, which is essential for applications where real-time accuracy is paramount. For example, in e-commerce platforms, the availability or price of a product can change frequently. Ensuring that the cache reflects these updates in near real-time is crucial to prevent erroneous transactions or user misinformation.
Efficient database cache strategies incorporate various invalidation techniques, such as time-to-live (TTL) mechanisms, where cached data is set to expire after a specific duration. Alternatively, write-through and write-behind caching strategies synchronize the cache and database concurrently, ensuring real-time data consistency. TTL is straightforward and effective for data that can tolerate brief inconsistencies, while the other methods are more complex but offer more immediate data updates.
While designing these strategies, it’s vital to acknowledge that the effectiveness of cache invalidation is partly determined by the balance achieved between data freshness and the overhead of constantly updating cache entries. Over-aggressive invalidation can strain resources, but inadequate invalidation can lead to data discrepancies. Therefore, efficient database cache strategies must be meticulously designed, considering both system load and the accuracy requirements of the cached data.
Balancing Efficiency and Resource Allocation
Efficient database cache strategies must adequately balance system performance with resource allocation. This balance involves tuning the caching layer to enhance performance while ensuring that resources such as memory and processing power are not disproportionately consumed. Optimization is key; failing to effectively allocate resources can lead to diminished returns on caching efforts or bottlenecks that impede overall system performance. For instance, overly aggressive caching can demand excessive memory usage, reducing the availability of resources for other critical operations.
Implementing efficient database cache strategies also involves setting appropriate threshold values for cache utilization. By monitoring cache performance metrics, such as hit ratios and cache latency, appropriate adjustments can be determined to fine-tune cache resource expenditure effectively. Resource allocation strategies must evolve with the database landscape since data growth and usage patterns can significantly change over time. It is especially crucial for enterprises experiencing rapid data expansion, requiring constant reevaluation of their caching strategies to align with data loads.
Strategic resource allocation embodied within efficient database cache strategies is vital for sustaining long-term performance enhancements. The right configuration can deliver substantial improvements, accommodating scaling demands while fostering data consistency. Constant surveillance and adaptation are fundamental to striking a harmonious convergence of efficient cache strategies and robust resource management, ensuring databases operate at optimal levels within a fluctuating data landscape.