The agricultural sector plays a vital role in global food security and economic development. However, it is also a significant contributor to environmental challenges, particularly through emissions that exacerbate climate change. Understanding the emission sources in agriculture sector is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. This article explores various factors contributing to emissions within this sector, detailing their impacts and potential solutions.
Read Now : Behavior Analysis In Cybersecurity
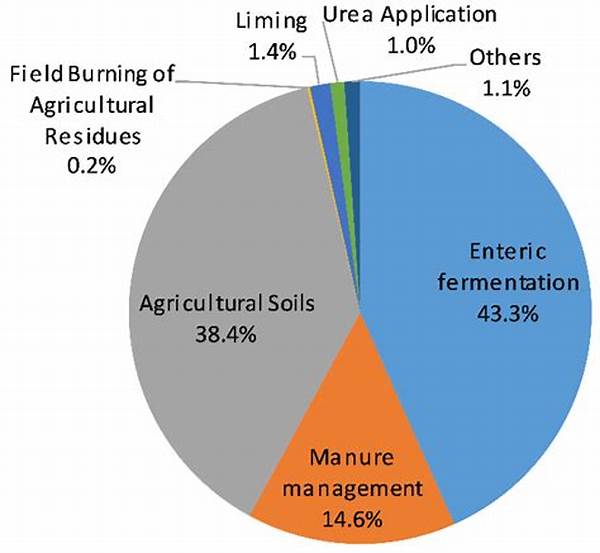
Main Contributors to Emissions in Agriculture
The emission sources in the agriculture sector are diverse and multifaceted. Predominantly, they stem from enteric fermentation, a natural digestive process in ruminant animals, resulting in methane emissions. Livestock manure management also plays a substantial role by releasing both methane and nitrous oxide. Synthetic fertilizers used to enhance crop productivity release nitrous oxide during application. Moreover, rice cultivation in flooded fields generates methane emissions. These sources contribute significantly to the overall greenhouse gas emissions, necessitating targeted mitigation practices to reduce their environmental impact. Sustainable practices and innovations in agricultural methods can help in mitigating these emissions, thereby aiding in the global effort to combat climate change.
Detailed Examination of Emission Sources
1. Enteric Fermentation: A primary emission source in agriculture sector, stemming from the digestive processes of livestock, particularly cattle. It produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
2. Manure Management: This process involves handling animal waste, which releases both methane and nitrous oxide, lengthy overlooked emission sources in agriculture sector.
3. Synthetic Fertilizers: These are widely utilized to boost crop yield but are notable emission sources in agriculture sector due to nitrous oxide release.
4. Rice Cultivation: Methane emissions result from anaerobic conditions in flooded rice paddies, marking them as a significant emission source in the agriculture sector.
5. Deforestation for Agriculture: Clearing land for farming contributes to carbon dioxide emissions, representing another notable emission source in agriculture sector.
Mitigation Strategies for Agricultural Emissions
Addressing emission sources in agriculture sector requires a comprehensive approach involving technological, managerial, and policy interventions. Promoting precision agriculture technologies can optimize input usage, thus minimizing emissions. The implementation of integrated livestock and feed management practices can reduce methane emissions from enteric fermentation and manure. Switching to organic fertilizers or enhancing fertilizer application techniques can reduce nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils. Additionally, adopting agroforestry practices and promoting sustainable land management can mitigate carbon emissions associated with deforestation and land-use changes. Achieving these reductions will require coordinated efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and farmers, emphasizing education, financial incentives, and supportive policy frameworks to ensure sustainability and effectiveness in reducing emissions within the agriculture sector.
Innovations and Technological Advances
1. Precision Agriculture: Utilizes technology to optimize resource use, reducing undue emissions.
2. Feed Alternatives: Development of new feed types can limit methane production in livestock digestion.
3. Biogas Technology: Converts manure into a renewable energy source, reducing methane release.
4. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Practices that enhance the ability of soil to store carbon.
5. Agroforestry: Integrating trees within farmland for carbon absorption.
Read Now : Broad-based Educational Evaluation Standards
6. Methane Inhibitors: Compounds that reduce enteric methane production from livestock.
7. Improved Water Management: Can decrease emissions in rice cultivation.
8. Reduced Tillage: Limits soil disturbance, helping maintain soil carbon levels.
9. Cover Cropping: Utilized to enhance soil health and reduce emissions.
10. Satellite Monitoring: Helps in better management and monitoring of agricultural activities to mitigate emissions.
Policy and Institutional Frameworks
To effectively curb emission sources in the agriculture sector, comprehensive policy and institutional frameworks must be established. Governments play a critical role in setting regulations that limit greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. The introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms can incentivize reductions in emissions by making it financially beneficial for farmers to adopt environmentally friendly practices. Furthermore, funding research and development in agricultural technology can provide new methods for reducing emissions. International cooperation is also vital, as it allows for the sharing of knowledge and resources across borders, ensuring that both developed and developing countries can participate in the mitigation process effectively.
Coordinated efforts at the national and international levels are necessary to manage emission sources in the agriculture sector. Through supportive policies and frameworks, countries can achieve a balance between economic productivity and environmental sustainability. This requires active participation from multiple stakeholders, including farmers, industry experts, policymakers, and environmental organizations. Education and awareness campaigns can facilitate the adoption of sustainable practices by informing stakeholders of the environmental impacts associated with agriculture, as well as the benefits of mitigation strategies. By prioritizing emission reductions, the agricultural sector can continue to fulfill its crucial role in feeding the global population while minimizing its environmental footprint.
Conclusion on Emission Reduction
In conclusion, addressing emission sources in the agriculture sector is imperative for achieving sustainability and combating climate change. The sector’s contribution to global emissions is significant, resulting from various activities such as livestock rearing, fertilizer application, and land-use changes. Targeted interventions including advanced technological solutions, changes in management practices, and policy frameworks are essential to mitigate these emissions effectively. These strategies, combined with international cooperation and education, offer viable means to reduce the environmental impacts of agriculture while sustaining its role in global food security.
Achieving emissions reduction in the agriculture sector necessitates a multidisciplinary approach that involves environmental scientists, agriculturalists, policymakers, and the farming community. The transition to sustainable practices not only aids in emission reductions but also enhances agricultural resilience and productivity. By recognizing and addressing the emission sources in agriculture sector, we can work towards a future where agricultural activities contribute to environmental conservation and climate action, with benefits for present and future generations.