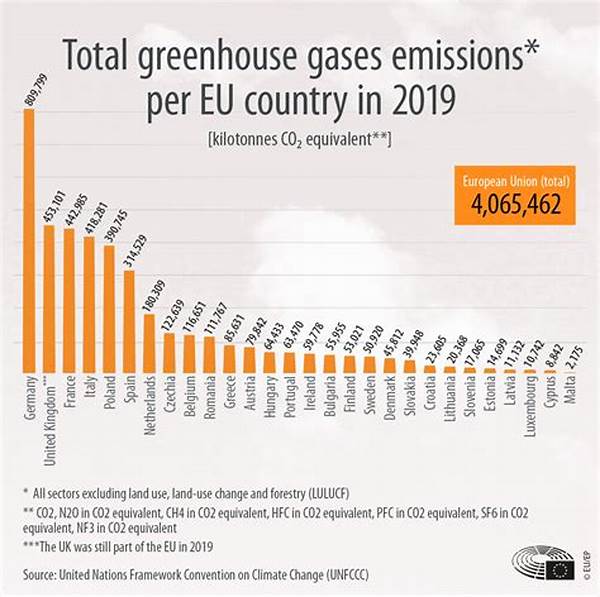
Understanding Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The term “greenhouse gas emissions analysis” refers to a comprehensive study of the gases emitted into the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect. This analysis is crucial for understanding the impact of human activities on climate change. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases, each having varying degrees of impact on warming the Earth’s surface. The primary sources of these emissions include industrial activities, agriculture, deforestation, and burning of fossil fuels. By conducting a detailed greenhouse gas emissions analysis, it becomes possible to identify key emission sources, quantify their contributions, and strategize mitigation efforts.
Read Now : “systematic Literature Review Methodologies”
Greenhouse gas emissions analysis serves as a foundation for setting emission reduction targets and developing policies to address climate change. Through such analysis, policymakers can identify sectors with the highest emission levels and prioritize interventions. Furthermore, it highlights trends over time, enabling the assessment of progress in emission reduction efforts. Given the global nature of climate challenges, international cooperation, supported by robust greenhouse gas emissions analysis, is essential for coordinated action. By leveraging this data, countries can fulfill their commitments under international agreements such as the Paris Agreement, ultimately striving towards a sustainable future.
Methods of Analyzing Emissions
Conducting greenhouse gas emissions analysis involves using systematic data collection and evaluation techniques. Atmospheric measurements and remote sensing technology play pivotal roles in tracking emissions. Advanced modeling tools are employed to simulate emission scenarios and predict future trends. This detailed analysis aids in crafting effective climate policies.
Another approach in greenhouse gas emissions analysis is life cycle assessment (LCA), which considers emissions from all stages of a product’s life from production to disposal. LCA helps identify carbon-intensive processes and enables the formulation of strategies aimed at minimizing emissions throughout the entire lifecycle.
Inventories of greenhouse gas emissions are essential tools for comprehensive analysis. These inventories categorize emissions by source and sector, providing a detailed overview of the emission landscape. This information is crucial for developing targeted strategies to reduce emissions and monitor the effectiveness of mitigation measures.
Policy-oriented greenhouse gas emissions analysis focuses on evaluating the impact of specific regulations and initiatives. By assessing the outcomes of current policies, analysts can recommend adjustments and improvements, enhancing policy design to achieve desired environmental goals effectively.
Finally, the integration of socio-economic factors into greenhouse gas emissions analysis helps to understand the implications of emissions on communities and economies. This holistic approach ensures that mitigation strategies are equitable and consider the needs and capacities of all stakeholders involved.
The Importance of Emissions Data
Greenhouse gas emissions analysis is instrumental in crafting a sustainable and environmentally conscious future. Accurate emissions data is critical for nations to benchmark their progress against established targets, ensuring accountability. Understanding the magnitude and sources of emissions empowers governments and organizations to make informed decisions that align with environmental commitments.
The transparent dissemination of this data allows for public engagement and fosters a collaborative approach to addressing climate change. It also enables the private sector to innovate and implement green technologies and business practices. Furthermore, the credibility of greenhouse gas emissions analysis relies on standardized methodologies and verified data, which provides a consistent baseline against which progress can be measured.
The increasing frequency and severity of climate-related impacts, such as extreme weather events, underscore the urgency of effective greenhouse gas emissions analysis. By understanding emissions at a granular level, policymakers and scientists can model future scenarios and adapt strategies to ensure climate resilience. Ultimately, comprehensive greenhouse gas emissions analysis is a linchpin of efforts to mitigate climate change and protect the planet for future generations.
Challenges in Data Collection and Analysis
Conducting greenhouse gas emissions analysis poses several challenges, including the accurate collection of data across diverse sectors. Variation in data quality and methodology can lead to inconsistent results. Ensuring international standardization and collaboration can mitigate these discrepancies.
Limited resources and technical capacity in many regions hinder comprehensive greenhouse gas emissions analysis. Investing in technology and capacity-building initiatives is crucial to enhance data collection and analysis capabilities globally.
Emissions from certain activities, such as deforestation and land-use changes, are challenging to quantify due to their diffuse nature. Improving remote sensing technologies and satellite imagery can enhance the accuracy of greenhouse gas emissions analysis in these areas.
Data availability is often a significant barrier, with some regions lacking comprehensive records of their emissions. Enhancing data sharing and transparency initiatives can improve the availability and reliability of information for greenhouse gas emissions analysis.
Analyzing emissions in rapidly changing environments requires adaptive methodologies that account for economic, technological, and social shifts. Developing dynamic models that integrate multiple factors is essential for effective greenhouse gas emissions analysis.
Incorporating feedback from diverse stakeholders, including local communities, industries, and policymakers, is vital to ensure that greenhouse gas emissions analysis leads to inclusive and practicable mitigation strategies.
Read Now : Quality Advancements In Research Via Benchmarking
The global nature of emissions requires coordinated international efforts to standardize data collection and reporting practices. By fostering collaboration through platforms such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), greenhouse gas emissions analysis can be enhanced.
Public awareness and education regarding the significance of greenhouse gas emissions analysis are crucial for fostering support for emission reduction initiatives. Encouraging citizen engagement and understanding can drive grassroots actions that contribute to broader environmental goals.
Advancements in data analytics and machine learning offer potential to enhance the precision and scalability of greenhouse gas emissions analysis. Leveraging these technologies can provide deeper insights and more accurate projections for future emission trends.
Finally, bridging the gap between scientific research and policy implementation remains a challenge in greenhouse gas emissions analysis. Strengthening the science-policy interface can ensure that evidence-based strategies effectively inform decision-making and drive sustainable outcomes.
Evaluating Mitigation Strategies through Emissions Analysis
Developing effective climate mitigation strategies relies heavily on comprehensive greenhouse gas emissions analysis. A detailed understanding of emissions patterns enables the identification of high-impact sectors and regions, guiding targeted interventions. By determining the sources of emissions, analysts can prioritize actions that maximize reduction potential while considering economic and social implications.
The evaluation of current and proposed policies using greenhouse gas emissions analysis serves to refine and optimize mitigation efforts. Policymakers can assess the efficacy of implemented measures, ensuring that resources are efficiently allocated towards initiatives that demonstrably contribute to emission reductions. Adjustments to strategies based on analytical findings increase the likelihood of achieving climate commitments.
Moreover, emissions analysis supports transparent communication with stakeholders, including the public, businesses, and international partners. Sharing the outcomes of mitigation strategies fosters accountability and encourages collaboration. Entities across various sectors can align their actions with scientifically-backed objectives, facilitating a unified approach to combating climate change.
Projection of future scenarios through greenhouse gas emissions analysis is also a key aspect of strategy evaluation. By simulating the potential impacts of different policies and technologies, decision-makers can anticipate challenges and make informed choices. This forward-looking perspective reduces the risk of unintended consequences and builds resilience against climatic shifts.
Importantly, robust greenhouse gas emissions analysis empowers continuous improvement in mitigation strategies. As new technologies and methodologies emerge, incorporating these advances ensures that strategies remain effective and adaptive to changing conditions. This dynamic approach is crucial to maintaining momentum towards global sustainability goals.
Summary of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Analysis
In summary, greenhouse gas emissions analysis is a critical component of global efforts to address climate change. By providing in-depth insight into emission sources and trends, it forms the backbone of strategic planning for emission reductions. The comprehensive data garnered through such analysis empowers stakeholders, from governments to industries, to implement informed and impactful measures.
Despite the challenges inherent in data collection, consistency, and international cooperation, advancements in technology and methodology continue to enhance the accuracy and applicability of greenhouse gas emissions analysis. As new insights are gained, strategies can be refined to reflect the most effective pathways for mitigating emissions, thereby achieving international climate goals.
Moving forward, fostering collaboration between scientific, policy, and community stakeholders remains pivotal to the success of emission reduction initiatives. Public engagement and transparency in greenhouse gas emissions analysis can catalyze a collective response to climate challenges, promoting sustainable practices across the globe.
Through ongoing innovation and commitment to rigorous analysis, the global community can significantly advance efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions. By ensuring that mitigation strategies are informed by robust data and assessments, there is a greater opportunity to safeguard the environment for future generations while addressing the pressing realities of climate change.