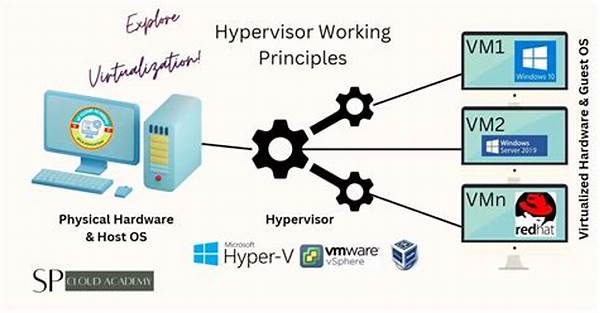
In the realm of information technology, virtualization has emerged as a powerful tool, revolutionizing how resources are managed and allocated. At the heart of this transformation lies the hypervisor, a pivotal component that plays a crucial role in virtualization. The hypervisor serves as an intermediary between the physical hardware and the virtualized environment, enabling multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical machine. This capability not only enhances resource efficiency but also provides scalability and isolation.
Read Now : Blockchain Solutions For Transparent Data
Understanding Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
Hypervisor roles in virtualization are indispensable for the effective deployment of virtual systems. At its core, the hypervisor abstracts the hardware and provides virtual machines with an operating environment that mimics physical hardware. By managing and distributing hardware resources like CPU, memory, and storage among virtual machines, hypervisors ensure that these machines operate independently yet harmoniously on the same physical server. This separation fosters a higher level of security, as one virtual machine’s behavior or failure does not impact others. Furthermore, hypervisors facilitate the migration of virtual machines between hosts, aiding in load balancing and minimizing downtime during maintenance operations. Through these functions, hypervisor roles in virtualization significantly contribute to optimizing resource use and improving system resilience.
Key Functions of Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
1. Resource Allocation: Hypervisor roles in virtualization include allocating and managing resources such as CPU, memory, and storage, ensuring efficient usage.
2. Isolation: One of the hypervisor roles in virtualization is to provide isolation between virtual machines, enhancing security and preventing interference.
3. Migration: Hypervisor roles in virtualization support live migration, allowing virtual machines to move between servers, aiding in load balancing and minimizing downtime.
4. Scalability: By enabling concurrent operations of multiple virtual machines, hypervisor roles in virtualization aid in achieving scalable IT infrastructure.
5. Security Enhancement: Hypervisor roles in virtualization contribute to security by separating virtual machines, reducing the risk of data breaches and system failures.
Types of Hypervisors and Their Roles in Virtualization
Hypervisors are broadly classified into two types: Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct roles in virtualization. Type 1 hypervisors, also referred to as bare-metal hypervisors, operate directly on the host’s hardware, providing superior performance and security. These hypervisors are commonly used in enterprise environments, where performance and efficiency are paramount. Type 1 hypervisors are crucial in environments requiring high availability and robust resource management.
Conversely, Type 2 hypervisors run atop a conventional operating system. These hypervisors are often used in development and testing environments due to their ease of setup and configuration. Despite typically offering lower performance than their Type 1 counterparts, Type 2 hypervisors play a vital role in virtualization by offering flexibility and ease of use. Understanding the distinctive roles of these hypervisors in various environments is essential for deploying optimal virtualization solutions.
Security Aspects of Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
1. Access Control: Hypervisor roles in virtualization include implementing strict access controls, ensuring that only authorized entities have control over virtual machines.
2. Isolation Mechanisms: By maintaining isolation between virtual machines, hypervisor roles in virtualization protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
3. Threat Mitigation: Hypervisor roles in virtualization involve deploying security features to mitigate threats like unauthorized intrusions or malware attacks.
4. Patch Management: A critical aspect of hypervisor roles in virtualization is maintaining up-to-date security patches to safeguard against vulnerabilities.
5. Intrusion Detection: Implementing mechanisms to detect and respond to unauthorized actions forms a part of hypervisor roles in virtualization, enhancing overall security.
Read Now : Improving Accuracy In Study Results
6. Audit Logging: Hypervisor roles in virtualization entail keeping detailed logs of operations to identify and respond to suspicious activities.
7. Data Integrity: Ensuring data integrity within virtual machines falls under hypervisor roles in virtualization, preventing data corruption or loss.
8. Backup and Recovery: Hypervisor roles in virtualization include facilitating backup and recovery processes, ensuring data availability and resilience.
9. Encryption: Implementing data encryption strategies is part of hypervisor roles in virtualization, safeguarding sensitive information.
10. Compliance: Hypervisor roles in virtualization ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards, maintaining organizational trust and credibility.
Challenges and Future Trends in Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
The hypervisor’s evolving role in virtualization presents both challenges and opportunities. Despite their benefits, hypervisors are not without vulnerabilities, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. The challenge lies in continuously enhancing security measures while maintaining performance and efficiency. As virtualization technology advances, new trends are emerging. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with hypervisor roles in virtualization presents possibilities for improved resource management and threat detection.
Moreover, the growing demand for cloud computing and hybrid infrastructure solutions highlights the need for hypervisors to adapt and facilitate seamless integration across diverse environments. Future developments in hypervisor technology will likely focus on enhancing automation capabilities, optimizing resource utilization, and strengthening security frameworks. By staying abreast of these trends and addressing potential challenges, hypervisor roles in virtualization will continue to play a fundamental part in shaping the future of IT infrastructure.
Performance Optimization in Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
Optimizing performance within virtualization environments is a critical aspect of hypervisor roles. Ensuring that virtual machines operate efficiently without infringing on each other’s resources requires meticulous management. Hypervisors play a crucial role in balancing loads, dynamically adjusting resource allocations to prevent bottlenecks and enhance overall performance.
Moreover, hypervisors can leverage features like memory overcommitment and CPU affinity to optimize the usage of available resources. Implementing advanced scheduling algorithms allows hypervisors to efficiently distribute tasks among virtual machines, ensuring optimal performance even under demanding conditions. Through strategic resource allocation and management, hypervisor roles in virtualization contribute significantly to maintaining high-performance computing environments.
Conclusion: The Integral Nature of Hypervisor Roles in Virtualization
In summation, the significance of hypervisor roles in virtualization cannot be overstated. These roles underpin the ability to efficiently manage resources, enhance security, and provide scalable and flexible IT solutions. By isolating virtual environments, hypervisors ensure the reliability and security of systems, while their resource management capabilities optimize performance.
As technology continues to evolve, hypervisor roles in virtualization will adapt, encompassing new innovations and addressing emerging challenges. The future holds promise for continued enhancements in virtualization technology, driven by the critical functions that hypervisors perform. As they continue to facilitate the seamless operation of virtual environments, hypervisors remain an indispensable component in the modern IT landscape.