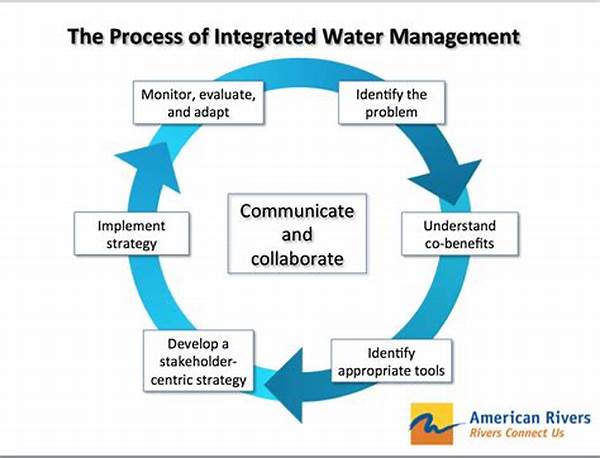
Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) represents a paradigm shift in how water resources are developed, managed, and protected. This holistic framework emphasizes the need to consider the interconnectedness of hydrological systems, balancing social, economic, and environmental objectives. By integrating various sectors, stakeholders, and policies, IWRM aims to promote sustainable water use while ensuring equitable access and maintaining ecosystem integrity. Its success hinges on comprehensive planning, participatory decision-making, and adaptive management, requiring stakeholders to navigate complex interactions and uncertainties. This article delves into the various strategies and principles underpinning integrated water resources management approaches.
Read Now : “impact Of Climate Change On Biodiversity”
The Principles of Integrated Water Resources Management
Integrated Water Resources Management approaches emphasize three core principles: economic efficiency, social equity, and environmental sustainability. Economic efficiency involves optimizing water use to maximize benefits within the constraints of available resources. Social equity focuses on fair and inclusive access to water, ensuring that marginalized and vulnerable communities are not disadvantaged. Environmental sustainability addresses the preservation of ecosystems and the services they provide, recognizing their crucial role in maintaining hydrological balances. These principles are interdependent and necessitate cooperation among sectors such as agriculture, industry, and domestic water use. Successful implementation of IWRM relies on the active participation of stakeholders, adaptive policies, and the integration of scientific knowledge with traditional practices. Moreover, IWRM acknowledges the dynamic nature of water systems and the need for flexible management to address changing conditions and uncertainties, such as climate change and population growth.
Strategies for Implementing IWRM
1. Developing Collaborative Governance Structures: Integrated water resources management approaches prioritize the establishment of participatory governance frameworks that include all relevant stakeholders to ensure transparent and inclusive decision-making.
2. Utilizing Basin-Level Management: Adopting a basin-level perspective is crucial in integrated water resources management approaches, as it allows for a comprehensive understanding of hydrological processes and the effective allocation of water resources.
3. Enhancing Data Collection and Monitoring: Integrated water resources management approaches depend on robust data collection systems to inform decision-makers and enable adaptive management practices through accurate assessments.
4. Promoting Capacity Building and Education: Integrated water resources management approaches stress the importance of capacity building among stakeholders, fostering a thorough understanding of water systems and promoting informed participation.
5. Integrating Technological Innovations: Leveraging technological advancements, such as remote sensing and data analytics, is vital within integrated water resources management approaches to improve water resource monitoring and management strategies.
Challenges in IWRM Implementation
Implementing integrated water resources management approaches presents various challenges, primarily due to the complexity and diversity of water systems and stakeholders involved. One major obstacle is the resistance to change from established practices and institutional inertia. Traditional water management systems often operate in silos, leading to fragmented efforts and inefficiencies. Transitioning to an integrated approach necessitates overcoming these barriers through effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and restructured governance frameworks. Additionally, financial constraints pose significant hurdles, as adequate funding is critical for the development and maintenance of integrated water resources management infrastructures. Furthermore, data insufficiency and lack of technical expertise can hinder accurate assessments and informed decision-making. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from governments, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector. By fostering collaboration and leveraging financial and technical resources, integrated water resources management approaches can be more effectively implemented. Overcoming these challenges is key to realizing the potential of IWRM in achieving water security, sustainability, and resilience.
Read Now : Tools For Research Impact Evaluation
Technological Advances in IWRM
The role of technology in facilitating integrated water resources management approaches cannot be overstated. Technological advances continually reshape the landscape of water resource management, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges. Remote sensing technologies, for instance, provide invaluable data on water availability, quality, and usage, which is essential for informed decision-making. Similarly, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enable the spatial analysis of water systems, supporting the design of effective management strategies. Additionally, data analytics and modeling tools offer predictive insights into hydrological changes, allowing for proactive management in the face of climate variability and unexpected events. The integration of these technologies within IWRM streamlines processes, enhances efficiency, and fosters more robust and responsive water management frameworks. However, the full potential of technology can only be realized when complemented by comprehensive training programs, ensuring that stakeholders possess the necessary skills to utilize these tools effectively. Balancing technological advancements with traditional knowledge and practices remains crucial in achieving sustainable and inclusive integrated water resources management approaches.
Future Perspectives of Integrated Water Resources Management
Looking ahead, integrated water resources management approaches must evolve to address emerging challenges and opportunities. Climate change represents a critical factor influencing water availability, demanding adaptive strategies to manage variability and water scarcity. The evolving political and socio-economic landscapes also necessitate adaptive governance structures that are responsive to changing stakeholder needs and geopolitical dynamics. Additionally, the intersection of urbanization and water management presents both challenges and opportunities within the IWRM framework. Rapid urban growth exacerbates water demand, pollution, and flood risks, requiring integrated planning that encompasses urban, peri-urban, and rural areas. Harnessing the power of interdisciplinary research remains pivotal in refining IWRM approaches, enabling the integration of novel insights from fields such as economics, ecology, and social sciences. The continuous engagement of local communities, governments, and international organizations is required to drive systemic change and ensure the long-term sustainability and resilience of water resources. Through concerted efforts, integrated water resources management approaches can pave the way for a future where water resources are managed holistically, equitably, and sustainably.
Key Components of IWRM
Successful Integrated Water Resources Management approaches are founded on several key components. Collaborative governance structures ensure inclusive stakeholder participation and decision-making, enabling diverse voices to be heard. The integration of scientific research with traditional knowledge forms the backbone of informed and culturally sensitive strategies. Robust data collection and analysis are essential in developing adaptive policies that respond to dynamic water systems. Monitoring and evaluation frameworks provide insights into the effectiveness of implemented measures, facilitating continuous improvement. Financial mechanisms, such as public-private partnerships, offer the funding necessary for sustainable infrastructure development and maintenance. Lastly, education and capacity building empower communities to actively engage in water management processes, enhancing the resilience and adaptability of IWRM approaches. Together, these components constitute a comprehensive blueprint for managing water resources effectively and equitably.
Conclusion of Integrated Water Resources Management Approaches
In conclusion, Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) represents a transformative approach to water resource management that aligns with global sustainability goals. By fostering collaboration, inclusivity, and adaptability, IWRM holds the potential to address the multifaceted challenges of water management in the 21st century. Its holistic framework prioritizes the equitable sharing of benefits, the preservation of ecosystems, and the efficient use of resources across sectors and regions. While numerous challenges exist, from financial constraints to governance complexities, the successful implementation of IWRM requires coordinated efforts and a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation. As we navigate an increasingly uncertain climate and socio-economic landscape, integrated water resources management approaches offer a viable path towards achieving water security, sustainability, and resilience for future generations. It is imperative that all stakeholders, including governments, communities, and organizations, actively engage in and support these approaches, ensuring that holistic water management becomes a cornerstone of sustainable development worldwide.