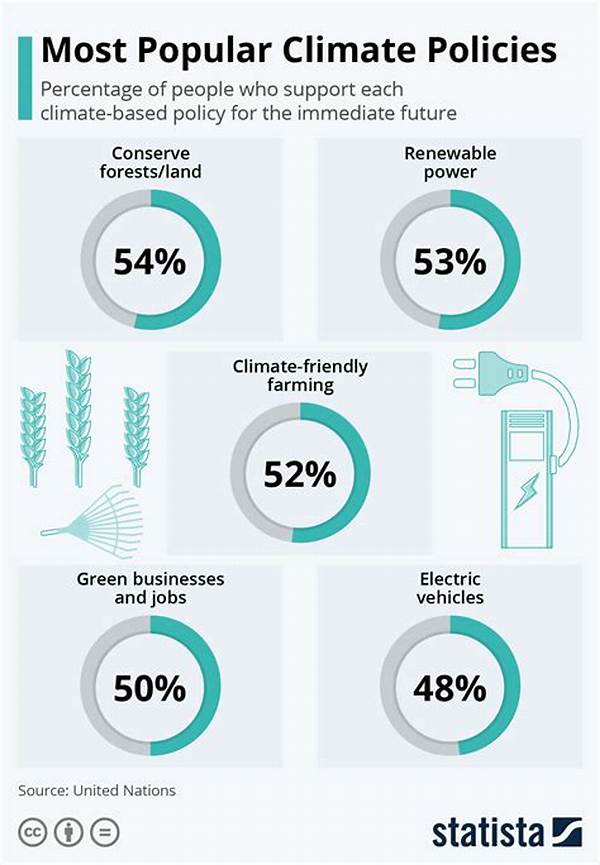
The spectrum of international climate policy developments is vast and intricate, reflecting a concerted global effort to combat environmental changes affecting the planet. These advancements are pivotal, forming the foundation upon which nations collaborate to mitigate adverse climate impacts. Over the years, international climate policy developments have shifted from mere discussions to actionable strategies, emphasizing the necessity for collective action and innovation in addressing climate change.
Read Now : Enhancing Services Through Apis
Progress in Global Climate Agreements
In recent years, international climate policy developments have been significantly influenced by major global agreements. The 2015 Paris Agreement marked a crucial milestone, compelling nations to set achievable targets for reducing carbon emissions. Its emphasis on accountability and transparency has facilitated more robust international climate policy developments. Subsequent conferences, such as the annual United Nations Climate Change Conferences, have furthered these efforts, sustaining momentum and fostering collaboration. Moreover, these agreements have encouraged nations to invest in renewable energy resources, reflecting the widespread nature of international climate policy developments. The persistent dialogue and yearly summits have also provided a platform for reviewing progress, sharing innovations, and optimizing strategies to meet climate targets.
Key Drivers of Climate Policy Developments
1. International climate policy developments are motivated by growing concerns about climate change impacts, urging nations to adopt systemic solutions.
2. Technological advancements play a critical role in shaping international climate policy developments by offering viable alternatives to carbon-intensive processes.
3. Economic incentives underpin international climate policy developments, encouraging investments in sustainable energy and green technologies.
4. Public awareness and activism foster international climate policy developments by demanding accountability and action from governments.
5. International climate policy developments rely on scientific research to provide accurate data and predictions, guiding policy decisions.
The Role of Multilateral Organizations
Multilateral organizations hold a strategic position in steering international climate policy developments. Entities such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provide invaluable frameworks for policy formulation. They orchestrate negotiations, set international standards, and lend support to developing countries, ensuring that international climate policy developments are inclusive and equitable. Furthermore, financial mechanisms facilitated by these organizations enable resource-poor nations to implement necessary initiatives. The global reach and influence of these organizations underpin their ability to drive international climate policy developments, making them instrumental in the collective effort to curb climate challenges. Their emphasis on inclusivity ensures that all nations, irrespective of economic standing, are stakeholders in the climate dialogue.
Read Now : Submission Guidelines Commonly Overlooked
Challenges in Policy Implementation
International climate policy developments face significant hurdles in execution, owing to various socio-economic and political complexities. First, disparities in economic capabilities and priorities among nations can stymie international initiatives. Second, the varying levels of commitment to agreed-upon targets pose challenges to universal compliance and progress. Third, the continuous evolution of scientific data necessitates that international climate policy developments adapt rapidly, which is not always feasible due to bureaucratic inertia. Fourth, geopolitical tensions can impede cooperation, jeopardizing coordinated climate action. Fifth, the transition towards sustainable practices requires substantial funding, technology transfer, and capacity building, especially in developing economies, making comprehensive policy implementation ambitious. Sixth, balancing economic growth with environmental preservation remains a pressing concern for policymakers. Seventh, the increased frequency of natural disasters necessitates a reevaluation of existing protocols to ensure resilience. Eighth, there is a need for robust metrics to measure progress, requiring international consensus and methodologies. Ninth, misinformation and skepticism surrounding climate science challenge the legitimacy of policy actions. Tenth, fostering a proactive global citizenry is vital to supporting and amplifying international climate policy developments.
Future Perspectives
Looking forward, international climate policy developments must evolve to address emergent challenges and harness new opportunities. The integration of digital technologies and data analytics presents a promising avenue for enhancing climate forecasting and policymaking accuracy. Furthermore, harnessing international financial markets can catalyze investments in sustainability, creating a nexus between economic interests and environmental objectives. The success of international climate policy developments will also hinge on fostering public-private partnerships, which can drive innovation and expedite the implementation of solutions. Educational initiatives are critical in cultivating a climate-conscious global populace, ensuring sustained public support for policy measures. Moreover, future international climate policy developments should prioritize equity to ensure that vulnerable communities are not disproportionately affected by climate change or the policies intended to address it.
Collaborative Efforts for Sustainable Development
Effective international climate policy developments are inherently interconnected with the principles of sustainable development. By prioritizing sustainability, policymakers can align climate goals with broader socio-economic objectives, ensuring that interventions yield comprehensive benefits. Collaborative efforts among nations, facilitated by international entities, can foster innovation, sharing of best practices, and pooling of resources. Moreover, strengthening institutional capacities across the globe will enhance resilience against climate impacts, creating a robust global framework for climate governance. Harmonizing efforts in mitigation, adaptation, and resilience-building can catalyze the transformative change necessary to meet climate ambitions.
Conclusion and Implications
In summary, international climate policy developments represent a critical component of global efforts to address climate change. These policies are shaped by a multitude of factors including scientific advancements, economic considerations, and social dynamics. They involve a complex interplay between national interests and global obligations, making the policy landscape particularly dynamic and challenging. The progress made to date underscores the importance of continued collaboration and innovation. It is imperative that stakeholders across sectors and borders maintain momentum, adapting to changing circumstances and embracing opportunities for growth and learning. The path forward will require concerted effort, with all nations playing an integral role in securing a sustainable, resilient future for the planet. International climate policy developments must remain at the forefront of international discourse, guiding actions and decisions that will shape the world for generations to come.