The significance of understanding latency differences in REST and SOAP is paramount for businesses aiming to optimize their web services. As the digital landscape evolves, choosing the right protocol can be a determinant of success. REST and SOAP, the two most prevalent web service protocols, differ significantly in their architectural approach and performance metrics, particularly in terms of latency.
Read Now : “optimizing Performance Using New Api Techniques”
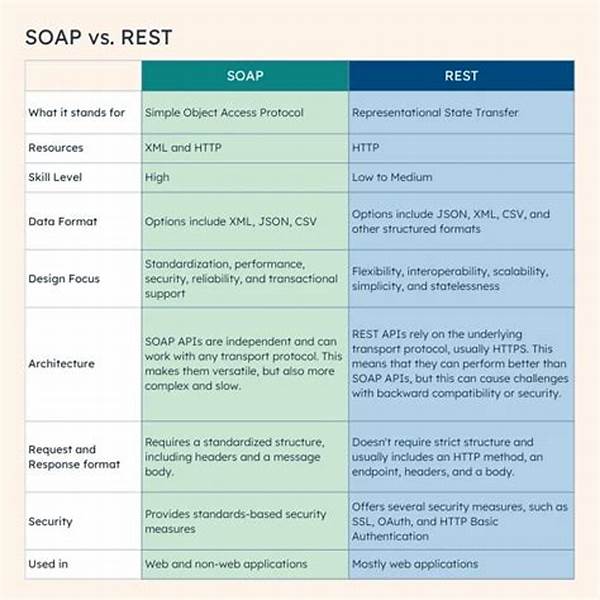
Comparative Analysis of Latency: REST vs. SOAP
In the realm of web services, the latency differences in REST and SOAP are substantial and worthy of in-depth exploration. REST, or Representational State Transfer, is an architectural style that relies on a stateless, client-server communication model, making it lightweight and faster in execution. Conversely, SOAP, or Simple Object Access Protocol, is a protocol with an extensive set of standards and features. It supports ACID transactions, security features, and a stricter form of messaging, which contributes to a more considerable overhead, resulting in higher latency compared to REST.
The latency differences in REST and SOAP impact various performance metrics significantly. REST’s use of lighter payload formats such as JSON, as opposed to SOAP’s heavy XML format, further contributes to its faster response time. This speed advantage is crucial in an era where user experience and agility are prioritized. Additionally, the stateless nature of REST reduces the server’s load, diminishing latency. Meanwhile, SOAP’s additional features, such as built-in error handling and security protocols like WS-Security, often result in increased processing time, manifesting in latency differences that professionals must consider when selecting the appropriate web service protocol for their applications.
Key Factors Contributing to Latency Differences
1. Architectural Design: The architectural design of REST and SOAP contributes to latency differences. REST’s stateless model and simplified data exchange ensure efficient performance, while SOAP’s complex structure and stateful operations often result in increased latency.
2. Data Format: REST typically uses JSON, a lightweight format, which facilitates faster processing. In contrast, SOAP employs XML, a verbose format, leading to latency differences due to the need for increased parsing efforts.
3. State Management: REST’s stateless nature reduces server-side workload, decreasing latency. SOAP, with its capability to maintain state across transactions, adds to latency, particularly in operations demanding high processing.
4. Security Features: SOAP’s comprehensive security protocols, such as WS-Security, introduce latency differences. These features, although beneficial for secure communications, require additional processing time, unlike REST, which relies on external security measures.
5. Error Handling: SOAP’s built-in error handling contributes to latency differences with REST. The advanced error management in SOAP necessitates additional processing layers absent in REST, thus increasing latency.
Practical Implications of Latency Differences
Understanding the latency differences in REST and SOAP extends beyond theoretical discourse and bears practical implications. For instance, businesses prioritizing rapid development and wide platform support may find REST more appealing due to its speed and agility advantages. The lightweight nature and straightforward implementation of REST make it highly suitable for mobile and web applications where quick response times are crucial.
On the other hand, industries requiring robust transaction support and enhanced security might gravitate towards SOAP. Despite the higher latency resulting from its complex features, SOAP’s framework provides comprehensive options for message integrity, reliability, and security, thus appealing to financial sectors and enterprise-level applications. Therefore, while the latency differences in REST and SOAP can significantly affect application performance, the choice of protocol should align with the specific business needs and technological environments.
Technical Considerations on Latency
1. Integration Complexity: SOAP’s integration of rich standards increases latency and complexity compared to REST, which leverages simple HTTP operations.
2. Customization: REST’s flexibility allows tailored implementations, minimizing latency. SOAP’s rigid framework offers limited customization, resulting in latency differences.
3. Scalability: REST’s scalability supports high-performance demand with reduced latency. SOAP’s overhead can impede efficient scaling, highlighting noticeable latency differences.
4. Compatibility: REST’s compatibility with web technologies leads to smoother integrations and lower latency. SOAP’s detailed protocol specifications might lead to compatibility challenges.
5. Resource Utilization: REST’s efficient resource utilization attributes to lower latency, contrasting SOAP’s resource-intensive operations that contribute to latency differences.
Read Now : **predictive Analytics In Education**
6. Data Validation: SOAP’s stringent data validation processes cause latency differences in REST and SOAP, as they demand additional processing time.
7. Flexibility in Deployment: REST’s simpler deployment can result in reduced latency, as opposed to SOAP’s heavier infrastructure requirement.
8. Standardization Requirements: REST’s minimal standards result in lower latency, while SOAP’s adherence to rigid standards can cause latency differences.
9. Middleware Requirements: The minimal middleware needs for REST often lead to lower latency, compared to SOAP’s complex middleware integrations.
10. Protocol Evolution: REST’s adaptability to new Internet protocols may reduce latency, whereas SOAP’s slower adaptation can maintain latency static.
Strategic Importance in Decision-Making
In the strategic decision-making process, the latency differences in REST and SOAP hold significant weight. Organizations must evaluate the scope of their applications and the environment in which they operate to select the protocol aligned with their objectives. REST, offering speed and simplicity, stands out in environments demanding agility and scalability, such as startups and tech-driven enterprises. Its lower latency contributes to a seamless user experience, crucial in contemporary digital landscapes.
Conversely, organizations prioritizing structured communication and security, such as financial institutions and large corporations, often prefer SOAP. Despite inherent latency differences stemming from its complex feature set, SOAP’s robustness in handling transactions and compliance makes it viable for specific use cases where security and process integrity are paramount. Therefore, when evaluating the latency differences in REST and SOAP, businesses must align their technological choice with operational goals and customer expectations to ensure optimal functionality and service delivery.
Evaluating the Balance Between Performance and Functionality
Achieving a balance between performance and functionality is essential when considering the latency differences in REST and SOAP. REST’s efficiency in data transfer and processing times offers performance benefits that cannot be overlooked in high-demand environments. Its low overhead allows for faster communication between systems, making it advantageous for applications where immediacy is critical.
Conversely, SOAP provides enhanced functionality and exhaustive security features, which, while contributing to higher latency, deliver reliability required in applications needing transactional integrity. The complexity of SOAP lies in its extensiveness, where every detail, from message formatting to processing protocols, is meticulously outlined, causing latency differences compared to the streamlined REST architecture.
Consequently, businesses aiming for optimal web service implementation must weigh these considerations carefully, acknowledging the trade-off between the latency improvements achievable with REST against the comprehensive functionalities of SOAP. By aligning technology strategy with business priorities, the organization can achieve enhanced operational efficiency.
Summary of Latency Differences in REST and SOAP
To summarize, the latency differences in REST and SOAP arise primarily from their foundational differences. REST, with its minimalist architecture and reliance on standard web technologies like HTTP and JSON, outperforms SOAP in terms of speed and agility. This is especially relevant in applications facing high user engagement, where reduced latency translates directly into an improved user experience and satisfaction. REST’s lightweight characteristics ensure minimal processing overhead, advantageous for scaling operations efficiently.
Contrastingly, SOAP’s extensive protocol and security measures underscore its complexity, making it a preference for systems requiring robust security and transactional accuracy. Despite the latency overhead, SOAP offers resilience and stability, which are paramount in sectors like finance and government that handle sensitive data. Therefore, understanding these latency differences is vital for decision-makers tasked with selecting the appropriate web service protocol, ensuring that both performance expectations and functional needs are met within technological and commercial constraints.