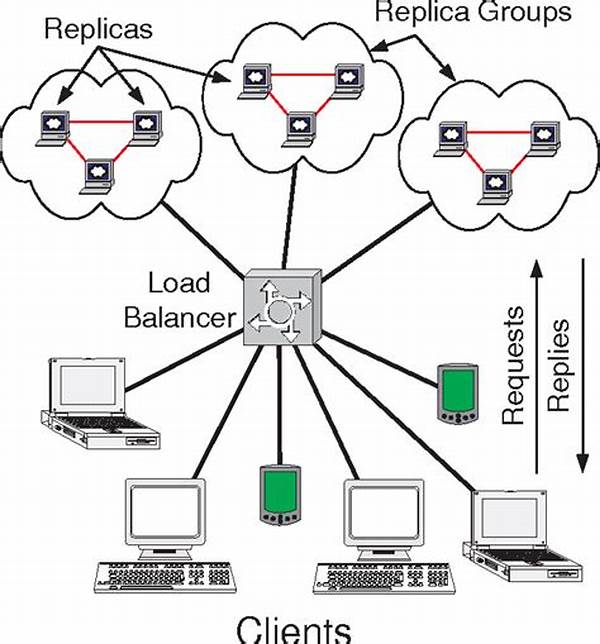
In the ever-evolving realm of information technology, the efficiency and responsiveness of middleware are paramount for the seamless operation of complex systems. The concept of middleware performance boost via load distribution has garnered significant attention for optimizing system functionalities. Load distribution, by balancing the workload across multiple resources, ensures that the system’s throughput and response time are maintained at optimal levels. This strategic approach enhances not only the middleware’s performance but also the overall system’s reliability and availability. The intricate nature of today’s IT ecosystems necessitates innovative solutions, such as load distribution, to address the burgeoning demand for robust performance and scalability.
Read Now : “data Visualization With Neural Networks”
Importance of Load Distribution in Middleware
The implementation of load distribution in middleware systems is a critical strategy that significantly facilitates a middleware performance boost via load distribution. By intelligently distributing incoming requests or workloads across multiple servers or processing units, companies can effectively prevent overloading any single resource. This approach not only mitigates potential bottlenecks but also maximizes resource utilization, contributing to enhanced system performance. Moreover, load distribution aids in maintaining system stability and scalability, accommodating increased demand without compromising on efficiency. Therefore, as organizations strive to navigate the complexities of modern IT landscapes, the adoption of load distribution mechanisms becomes an indispensable component for achieving superior middleware performance.
Key Strategies for Middleware Optimization
1. Implementing dynamic load balancing algorithms can result in a significant middleware performance boost via load distribution. These algorithms adapt to real-time changes in workload, ensuring efficient task allocation.
2. Use of predictive analytics plays a pivotal role in achieving a middleware performance boost via load distribution. It forecasts load trends and adjusts distribution strategies accordingly.
3. The integration of cloud-based solutions facilitates a middleware performance boost via load distribution by providing elastic resources that automatically scale to meet demand.
4. The deployment of microservices architecture supports a middleware performance boost via load distribution by decentralizing tasks and reducing single points of failure.
5. Real-time monitoring systems can substantially contribute to a middleware performance boost via load distribution by identifying potential issues and reallocating resources swiftly.
Technological Advancements Supporting Load Distribution
Advancements in technology have significantly empowered organizations to achieve a middleware performance boost via load distribution. The proliferation of cloud computing and virtualization technologies has introduced new paradigms for resource allocation and task distribution. By leveraging these tools, enterprises can dynamically allocate resources according to demand, ensuring that middleware systems operate efficiently even under peak loads. Furthermore, developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning have enabled predictive load balancing, which anticipates traffic spikes and redistributes workload preemptively. As a result, enterprises can achieve higher reliability and performance, ultimately fostering improved user satisfaction.
Read Now : Improving Accuracy In Study Results
Another facet of technological advancement is the integration of containerization technologies. Containers encapsulate middleware applications and their dependencies, allowing for more efficient scaling and load distribution. This approach leads to seamless middleware performance boost via load distribution as applications can be deployed consistently across various environments. Meanwhile, service mesh architectures provide enhanced observability and control, allowing for more granular load balancing at the service level. Collectively, these technological improvements ensure that middleware can handle the dynamic and demanding nature of modern applications, safeguarding performance and enhancing business continuity.
Middleware Load Distribution Techniques
The Evolution and Future of Middleware Load Distribution
The principles underlying a middleware performance boost via load distribution have continually evolved, reflecting advancements in technology and shifting industry needs. Initially, simple techniques like static load balancing sufficed; however, with the explosion of internet usage and complex enterprise applications, more sophisticated solutions became necessary. The trajectory of load distribution is guided by innovations such as artificial intelligence, which promises even more intelligent and adaptive load balancing methodologies. Future advancements may focus on predictive distribution, autonomously adjusting loads based on machine learning insights to avoid latency and downtime proactively.
The future of load distribution also sees a greater emphasis on integration with cloud-native technologies. As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud environments, traditional methods must be adapted to support containers and serverless architectures. This evolution ensures that middleware performance boost via load distribution remains relevant and effective, delivering unparalleled performance irrespective of workload changes. Companies will need to invest in automated and intelligent distribution systems to remain competitive. Ultimately, this evolution signifies a commitment to maintaining high levels of performance while maximizing resource efficiency, thus advocating future-ready middleware solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
While a middleware performance boost via load distribution offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. The complexity of implementing sophisticated load balancing technologies requires perpetual fine-tuning and investment in skilled personnel. Organizations must consider data security, as distributing loads across multiple servers can sometimes expose systems to vulnerabilities. Additionally, the assessment of network latency and bandwidth limitations remains crucial, as these factors can impede performance. Therefore, while the correct application of these strategies fosters improved middleware operations, a nuanced understanding and meticulous execution are necessary for success.
In conclusion, a middleware performance boost via load distribution holds transformative potential for organizations seeking improved efficiency, scalability, and reliability. Through a comprehensive understanding of load distribution mechanisms and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies, businesses can not only enhance middleware performance but also sustain competitive advantage. However, navigating the complexities associated with these strategies requires careful planning and expertise to harness their full potential effectively. Ultimately, as technology continues to progress, the adoption of innovative load distribution approaches becomes indispensable in maintaining robust and responsive middleware systems.