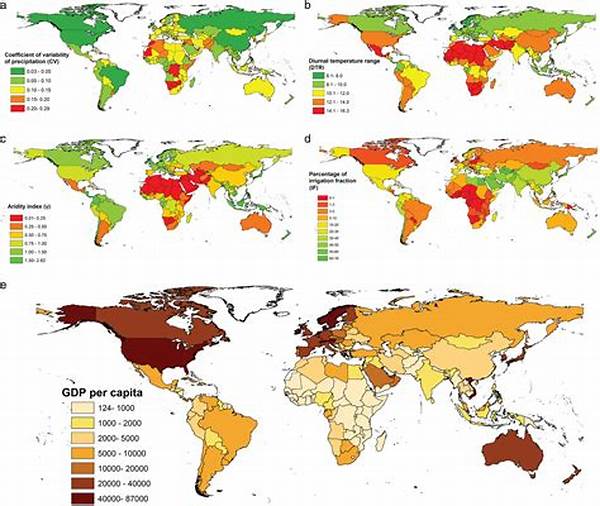
The interplay between rainfall variability and crop yields is a critical concern in the agricultural sector. The unpredictability of rainfall patterns can heavily impact crop production, thereby affecting food security globally. Understanding this relationship is essential in developing strategies to mitigate risks and improve agricultural practices. The following sections will delve into the complexities of rainfall variability and its consequences on crop yields, providing an in-depth analysis of how these factors interrelate and influence agricultural productivity.
Read Now : Enhancing Business With Apis
The Relationship Between Rainfall Variability and Crop Yields
Rainfall variability, characterized by inconsistent precipitation patterns, poses a significant challenge to crop yields. This unpredictability has been exacerbated by climate change, leading to more frequent droughts and floods. Such conditions can severely disrupt the growth cycle of crops, potentially reducing yields. Farmers must adapt by implementing techniques such as water management systems and drought-resistant crops to cope with these challenges. Furthermore, understanding historical rainfall trends can assist in predicting future conditions and preparing accordingly. Governments and agricultural bodies are increasingly focused on research and development to devise effective strategies for minimizing the impact of rainfall variability on crop yields. Improving forecasting technology and investing in resilient agricultural practices are pivotal in ensuring sustainable food production amidst these challenges.
The relationship between rainfall variability and crop yields is complex and multifactorial. Crop growth depends on receiving adequate water at specific growth stages, and any deviation in rainfall can be detrimental. Excessive rainfall leads to waterlogging and nutrient leaching, while insufficient rainfall results in drought stress. Both extremes demand strategic intervention and adaptation by the agricultural sector. Comprehensive understanding of these dynamics can aid in developing robust solutions for ensuring consistent crop yields despite varying rainfall patterns.
Factors Affecting Rainfall Variability and Crop Yields
1. Climate Change: Climate change intensifies rainfall variability, disrupting traditional weather patterns and affecting crop yields.
2. Water Management: Efficient water management systems can mitigate the negative impacts of rainfall variability on crop yields.
3. Technological Advancements: Innovations in agricultural technology can provide solutions to adapt to fluctuating rainfall and maintain crop yields.
4. Soil Quality: Good soil quality can buffer the adverse effects of rainfall variability, supporting stable crop yields.
5. Crop Selection: Choosing the right crop varieties can reduce susceptibility to rainfall variability and optimize yields.
Implications for Agricultural Policy and Planning
Rainfall variability and crop yields are critical considerations for agricultural policy and planning. Policymakers must prioritize investments in research and technology to develop resources that can help farmers adapt to changing weather conditions. This includes enhancing weather prediction models to provide accurate forecasts, which can aid in strategic planting and harvesting decisions. Additionally, policies should focus on promoting sustainable agricultural practices that enhance resilience to rainfall variability. These practices not only ensure food security but also contribute to the economic stability of farming communities.
Investment in education and training for farmers is vital. By equipping them with knowledge and skills on managing the effects of rainfall variability on crop yields, farmers can make informed decisions. This involves understanding which crops are more resilient and implementing suitable irrigation techniques. Also, collaboration between governments, research institutions, and the private sector can further drive innovation in sustainable agricultural practices. Ultimately, such efforts could lead to enhanced food production capacity while maintaining environmental integrity.
Read Now : Advanced Mobile Application Security Features
Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Rainfall Variability on Crop Yields
Mitigating the impact of rainfall variability on crop yields necessitates a multifaceted approach. First, enhancing irrigation infrastructure can provide reliable water sources during dry spells, ensuring consistent crop growth. Second, adopting drought-resistant crop varieties can enhance resilience to water scarcity. Third, employing water conservation techniques, such as rainwater harvesting, can reduce dependence on erratic rainfall. Fourth, precision agriculture technologies can optimize water usage and improve crop yields. Fifth, integrating crop rotation and polyculture systems can enhance biodiversity and soil health, reducing susceptibility to rainfall variability. Sixth, advanced weather forecasting systems can aid in timely agricultural planning. Seventh, promoting agroforestry can provide ecological benefits that mitigate climatic impacts. Eighth, governmental subsidies and financial support can encourage farmers to adopt resilient practices. Ninth, education and awareness programs can empower farmers with knowledge and tools to cope with rainfall variability. Lastly, international collaboration in research and resource sharing can foster adaptive strategies on a global scale.
Economic Impacts of Rainfall Variability on Crop Yields
The economic ramifications of rainfall variability on crop yields are profound, influencing both local farming livelihoods and global food markets. Unpredictable rainfall can lead to crop failures, diminishing farm incomes and exacerbating poverty, particularly in regions heavily reliant on agriculture. Conversely, favorable rainfall conditions can boost crop yields, fostering economic growth and stability. However, the uncertainty surrounding rainfall patterns necessitates risk mitigation strategies to safeguard against potential economic losses. Investment in insurance schemes, government support, and technological innovations can provide financial resilience against the adverse effects of rainfall variability on crop yields. Furthermore, understanding the economic implications facilitates informed policy decisions that can optimize resource allocation and enhance agricultural productivity. As the world grapples with climate change, addressing the economic challenges posed by rainfall variability will be crucial in securing a sustainable future for agricultural economies.
Conclusion on Rainfall Variability and Crop Yields
The dependency of crop yields on stable and predictable rainfall patterns cannot be overstated. Rainfall variability introduces complexities that can jeopardize food production and economic stability. Therefore, a concerted effort is necessary to mitigate these challenges. By advancing research in weather patterns and agricultural technologies, society can better anticipate and adapt to the effects of rainfall variability, securing food supply chains.
Moreover, cooperation at multiple levels—from local farmers to international bodies—is essential in developing resilient agricultural frameworks. Integrating traditional knowledge with modern technologies enables a more flexible response to fluctuating weather conditions. Ensuring that all stakeholders are engaged in the conversation will provide a comprehensive approach to safeguarding agricultural productivity against rainfall variability.
Summary of Rainfall Variability and Crop Yields
Rainfall variability presents a formidable challenge to sustaining crop yields globally. The irregularity of precipitation patterns, driven in part by climate change, requires adaptive strategies to maintain food security. The potential for both droughts and excessive rainfall requires a balanced approach in agricultural planning, encompassing technological, environmental, and policy-driven solutions. A shift towards sustainable and resilient farming practices is essential.
The multifaceted nature of rainfall variability’s impact on crop yields demands a holistic response. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and farmers will be integral to developing innovative solutions. Staying ahead of these challenges means enhancing forecasting capabilities, investing in sustainable technologies, and promoting education and awareness. Ultimately, by adopting a proactive stance, societies can better navigate the complexities of rainfall variability and secure a stable food supply for future generations.