Understanding Resilience Theory in Ecology
Resilience theory in ecology refers to the capacity of an ecosystem to absorb disturbances while maintaining its basic structure and function. This concept is crucial in assessing how ecosystems respond to changes such as climate variations, human activities, and natural disasters. The theory emphasizes the significance of understanding processes that allow systems to recover and adapt to unexpected shocks. Resilience theory in ecology is gaining increasing relevance in ecological management and conservation strategies as it provides insights into the sustainability of ecosystems amidst growing environmental challenges.
Read Now : Machine Learning For Moisture Analysis
The application of resilience theory in ecology aids in predicting the thresholds beyond which ecosystems may shift to an entirely different state, often with reduced biodiversity and altered functions. By identifying these thresholds, conservationists and policymakers can implement strategies to maintain or enhance the resilience of various ecosystems. For example, preserving biodiversity, which acts as a buffer, can enhance an ecosystem’s ability to withstand and recover from disturbances.
As human activities continue to impact natural landscapes, resilience theory in ecology offers a framework to guide sustainable management practices. Ecologists and environmental managers can use this theory to devise adaptive management strategies that involve learning from past disturbances and planning for future uncertainties. Hence, resilience theory in ecology remains an essential tool in promoting environmental resilience in the face of anthropogenic and natural pressures.
Key Concepts of Resilience Theory in Ecology
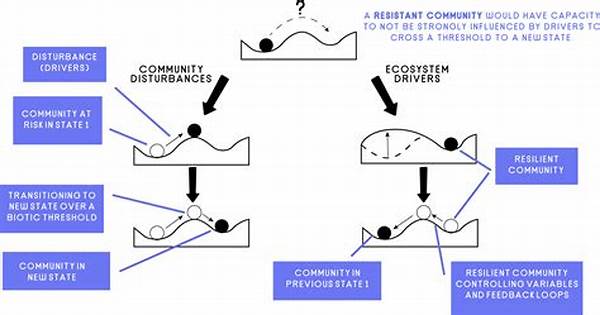
1. Resilience theory in ecology is about understanding how ecosystems can absorb shocks and still maintain their structure and functions.
2. By employing resilience theory in ecology, researchers can identify systems’ thresholds leading to significant state changes.
3. Such theory assists in guiding sustainable practices that enhance ecosystems’ recovery capabilities.
4. Resilience theory in ecology underlines the importance of biodiversity in stabilizing ecosystems against disturbances.
5. This approach informs the creation of policies that support ecological sustainability in changing environments.
The Importance of Resilience Theory in Ecology
The importance of resilience theory in ecology cannot be overstated, as it provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating ecosystem stability and adaptability. With the increasing frequency and intensity of both natural and anthropogenic disruptions, it becomes imperative to understand the resilience of ecological systems. By examining how different ecosystems respond to such changes, ecologists can better predict future outcomes and devise strategies to mitigate adverse impacts.
Furthermore, resilience theory in ecology facilitates a move beyond traditional conservation approaches that often focus solely on preserving current states. Instead, it advocates for adaptive management that considers the dynamic nature of ecosystems. This involves continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment of management practices to cope with new challenges as they arise. By fostering ecosystems’ natural resilience, this theoretical approach promotes sustainability and long-term ecological health, making it indispensable to current and future environmental management strategies.
Practical Applications of Resilience Theory in Ecology
1. Resilience theory in ecology helps in landscape restoration by emphasizing ecosystem functions and processes over rigid endpoint targets.
2. The theory guides the design and implementation of conservation strategies by identifying critical areas that require protection to buffer against disturbances.
3. Utilizing resilience theory in ecology can foster the development of sustainable agricultural practices that maintain soil health and biodiversity.
4. It informs urban planning by integrating green spaces that support ecological resilience and enhance community well-being.
Read Now : Comparison Of E-learning Technologies
5. Resilience theory aids in the anticipatory planning of climate change impacts, allowing for proactive adaptation measures.
6. The theory enhances disaster preparedness by promoting the diversification of species and genetic resources in ecosystems.
7. It facilitates collaboration among stakeholders by providing a common language and framework to address ecological challenges.
8. The theory supports the creation of marine protected areas tailored to maintain or increase the resilience of marine ecosystems.
9. Resilience theory in ecology provides insights into invasive species management by understanding ecosystem thresholds and potential shifts.
10. Implementing the principles of resilience theory can lead to the recovery of degraded ecosystems through adaptive management and restoration efforts.
Challenges and Future Directions in Resilience Theory in Ecology
The application of resilience theory in ecology presents several challenges, primarily due to the inherent complexity and variability of ecosystems. Identifying critical thresholds and predicting system responses require extensive research and data collection, often hindered by practical and financial constraints. Additionally, the dynamic and interconnected nature of ecological systems implies that changes in one component can lead to unforeseen impacts elsewhere. Thus, developing comprehensive models that accurately capture these interactions remains a significant scientific endeavor.
Despite these challenges, resilience theory in ecology holds great promise for future ecological management and policy-making. Advances in technology and computational power offer new opportunities to process large datasets, enhancing our understanding of ecosystem dynamics. Moreover, international collaboration and knowledge-sharing further aid in refining the theory’s applications across different ecological contexts. As environmental pressures continue to mount, resilience theory in ecology will increasingly guide the development of innovative solutions to preserve ecosystem services and promote biodiversity.
Resilience Theory in Ecology: Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, resilience theory in ecology serves as a vital tool in understanding and managing ecosystems amidst the ever-growing environmental challenges. By focusing on ecosystems’ capacity to absorb disturbances and maintain functionality, this theory encourages adaptive management and proactive planning. It emphasizes the criticality of preserving biodiversity and acknowledging the dynamic nature of ecological systems, fostering sustainable practices both in conservation and land-use planning.
Overall, resilience theory in ecology provides a necessary framework for predicting and mitigating the impacts of disruptions on ecosystems. As society continues to grapple with climate change and habitat degradation, the insights gained from this theory will be instrumental in securing the health and sustainability of our planet’s diverse ecosystems.