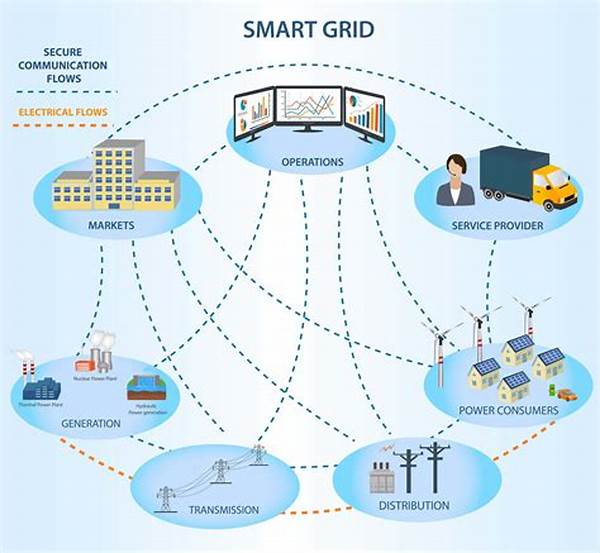
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy distribution, the advent of smart grid resource management systems marks a pivotal shift. This technological advancement not only optimizes energy efficiency but also ensures a sustainable future for generations to come. Through the integration of sophisticated algorithms and real-time data analytics, these systems provide a robust framework for managing energy resources with unparalleled precision. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of smart grid resource management systems, we uncover the transformative potential they hold for modern society.
Read Now : Reducing Data Payload Size
Integration of Advanced Technologies
Smart grid resource management systems are at the forefront of technological integration in the energy sector. By harnessing the power of machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and predictive analytics, these systems ensure that energy distribution is both efficient and reliable. The implementation of smart grid resource management systems facilitates a dynamic energy environment where supply and demand are continuously balanced to avoid wastage and stabilize energy costs. Moreover, the real-time monitoring capabilities inherent to these systems allow stakeholders to identify anomalies swiftly, thereby enhancing the resilience of the energy grid. As the world increasingly shifts towards renewable energy sources, smart grid resource management systems play a crucial role in enabling the seamless transition by providing the necessary infrastructure to support distributed energy resources.
Key Features of Smart Grid Resource Management Systems
1. Real-Time Data Processing: Smart grid resource management systems leverage real-time data to optimize energy distribution efficiently.
2. Predictive Analytics: These systems utilize predictive models to anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions in energy supply.
3. Scalability: The adaptable nature of smart grid resource management systems accommodates future expansions in energy infrastructure.
4. Enhanced Consumer Interaction: These systems empower consumers by providing detailed energy usage insights and control mechanisms.
5. Sustainability Compliance: By optimizing resource allocation, smart grid resource management systems contribute significantly to sustainability goals.
Challenges and Solutions
One of the most pressing challenges faced by smart grid resource management systems is cybersecurity. As these systems rely heavily on digital infrastructure and interconnected networks, they are susceptible to cyber-attacks that can disrupt energy distribution and compromise sensitive data. In response to these threats, robust security protocols and encryption technologies are implemented to safeguard the integrity of the systems. Furthermore, collaboration between industry experts and governmental bodies is crucial in establishing standardized security measures. Another challenge is the integration of variable renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, which require sophisticated algorithms to manage their intermittent nature effectively. Smart grid resource management systems address this by employing advanced forecasting techniques to predict energy generation patterns and adjust grid operations accordingly, ensuring a stable energy supply.
Future Prospects of Smart Grid Resource Management Systems
The future of smart grid resource management systems is inextricably linked to the advancement of renewable energy technologies and smart cities. As urban areas continue to expand, the demand for efficient energy management grows, propelling the development of next-generation smart grid systems. These systems are poised to incorporate artificial intelligence and blockchain technology to further enhance their operational capabilities. As a result, smart grid resource management systems will play an instrumental role in developing resilient and adaptive energy networks that cater to a diversified energy landscape. The integration of these systems with electric vehicle infrastructure also presents an exciting opportunity to create a more sustainable transportation system, actively contributing to emissions reduction efforts on a global scale.
Innovative Approaches in Energy Management
1. IoT Implementation: IoT devices are vital in collecting and transmitting data for smart grid resource management systems, ensuring real-time responsiveness.
2. Decentralized Grids: Future smart grid resource management systems promote decentralized grids for enhanced energy distribution and resilience.
3. Energy Storage Solutions: Advanced storage technologies are incorporated to store excess energy and balance supply with consumption demands.
Read Now : Inclusive Teaching Evaluation Methods
4. Blockchain Utilization: Blockchain technology offers a secure framework for transactions and data integrity within smart grid resource management systems.
5. Demand Response Programs: Demand response initiatives incentivize consumers to adjust their energy usage during peak periods, facilitated by smart grid resource management systems.
6. Data Analytics Integration: Complex data analytics enable predictive assessments and strategic energy optimization within smart grid resource management systems.
7. Grid Automation: Automation technologies enhance the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution via smart grid resource management systems.
8. Collaborative Platforms: Stakeholders engage in collaborative platforms enabled by smart grid resource management systems to optimize grid operations.
9. Sustainability Initiatives: Sustainable practices are embedded in smart grid resource management systems, promoting energy efficiency and environmental conservation.
10. Policy Alignment: Smart grid resource management systems align with regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance and facilitate global energy standards.
Conclusion and Implications
In conclusion, smart grid resource management systems represent a paradigm shift towards a more efficient and sustainable energy future. These systems have significantly transformed the energy sector through innovative technologies and strategic resource allocation. The implications of their widespread adoption are profound, impacting everything from reducing environmental footprints to enhancing the reliability of energy supply. As stakeholders continue to embrace these systems, a concerted effort is required to address the challenges associated with cybersecurity, interoperability, and regulatory compliance. The continued investment in research and development will inevitably yield more advanced solutions, paving the way for a resilient and adaptive energy ecosystem that aligns with global sustainability objectives. As we move forward, the role of smart grid resource management systems will be pivotal in shaping the future of energy systems worldwide.
Strategies for Implementation
Successful implementation of smart grid resource management systems depends on several strategic factors. First, it is essential to establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks that provide guidelines for system integration and operation. Governments play a critical role in facilitating this process by offering incentives and support for smart grid initiatives. Furthermore, fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and research institutions is crucial in driving innovation and enhancing system capabilities. Investments in workforce training and development will also equip professionals with the necessary skills to operate and maintain these sophisticated systems. Lastly, engaging consumers through awareness campaigns and feedback mechanisms can promote public acceptance and participation, ultimately driving the success of smart grid resource management systems in achieving their intended goals.