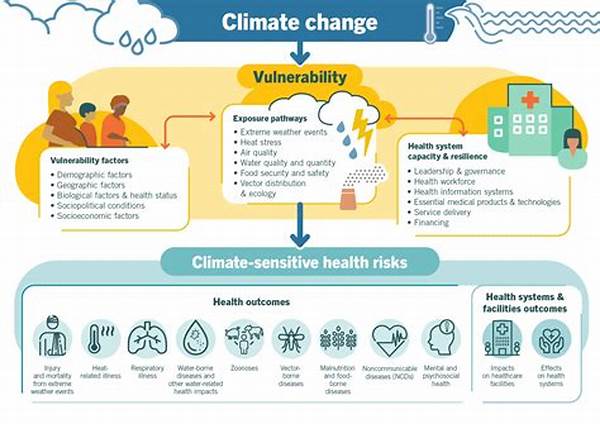
Climate change, an undeniable global phenomenon, is deeply impacting societies by exacerbating existing vulnerabilities. The concept of social vulnerability to climate disruptions refers to the susceptibility of communities to the adverse impacts of climate change, including natural disasters, as well as the ability of these communities to respond, recover, and adapt to these disruptions. Understanding this vulnerability is critical to developing efficient mitigation and adaptation strategies that ensure the safety and well-being of affected populations.
Read Now : Crop Yield And Climate Change
Assessing Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
Social vulnerability to climate disruptions is influenced by a myriad of factors, including socioeconomic status, geographic location, and demographic parameters such as age, gender, and health. These elements interact in complex ways, determining how individuals and communities experience and respond to climate-induced hazards. In many cases, marginalized groups are disproportionately affected due to limited resources and access to adaptive measures. Enhancing community resilience requires a multifaceted approach that comprehensively addresses these vulnerabilities while bolstering local capacity through economic support and social programs.
Furthermore, governmental and non-governmental entities play a pivotal role in identifying high-risk populations and implementing policies that target these vulnerabilities. By assessing the intricate web of factors that contribute to social vulnerability to climate disruptions, stakeholders can tailor interventions to mitigate risk and promote sustainable adaptation strategies.
Key Factors Influencing Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
1. Economic Disparities: Economic factors significantly influence social vulnerability to climate disruptions, as lower-income populations often lack the resources to effectively prepare for, respond to, and recover from climatic events.
2. Geographic Location: Communities located in high-risk areas, such as coastal regions or flood plains, experience heightened social vulnerability to climate disruptions due to their increased exposure to natural disasters.
3. Demographic Profiles: Demographics, including age, health, and disability, contribute to social vulnerability to climate disruptions. Vulnerable groups, such as the elderly or those with chronic illnesses, face greater challenges during climatic events.
4. Social Networks and Cohesion: Strong community networks can reduce social vulnerability to climate disruptions by fostering collective action and mutual support during and after adverse events.
5. Governance and Policy: Effective governance and robust policy frameworks are essential in addressing social vulnerability to climate disruptions by ensuring resources are allocated to support vulnerable populations and enhance resilience.
Understanding the Scope of Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
The scope of social vulnerability to climate disruptions is vast, encompassing various dimensions that require careful examination and targeted intervention. First, it is paramount to recognize how social and economic disparities can exacerbate vulnerability, leading to inequitable impacts on marginalized communities. These impacts not only perturb the immediate well-being of affected populations but also compound over time, influencing overall social stability and economic development.
Addressing social vulnerability to climate disruptions demands a commitment to equity and justice, which can be actualized through inclusive policies that prioritize the most at-risk populations. Engaging communities in participatory resilience-building processes is key to empowering them to take ownership of adaptive strategies. This approach fosters an environment wherein vulnerabilities are systematically mitigated, maximizing the collective capacity to withstand and recover from climate-induced adversities.
Challenges in Addressing Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
1. Resource Allocation: Efficient allocation of resources is crucial to reduce social vulnerability to climate disruptions, yet it remains a challenging endeavor given competing priorities and limited budgets.
2. Identification of Vulnerable Populations: Accurately identifying populations at high risk of social vulnerability to climate disruptions is complex, necessitating comprehensive data collection and analysis.
3. Community Engagement: Engaging communities in resilience efforts is vital, yet obstacles such as language barriers and mistrust of authorities can hinder this process.
4. Policy Implementation: Translating policies into actionable plans to combat social vulnerability to climate disruptions requires coordination across various sectors and levels of government.
Read Now : **collaborative Educational Experiences**
5. Long-term Planning: Establishing long-term strategies to address social vulnerability to climate disruptions is essential, yet often hampered by short-term political agendas and funding cycles.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation: Developing robust systems to monitor and evaluate efforts to reduce social vulnerability to climate disruptions is necessary for ensuring accountability and progress.
7. Collaborative Efforts: Building collaborations among stakeholders, including government, private sector, and civil society, is crucial for effective action against social vulnerability to climate disruptions.
8. Technological Integration: Leveraging technology to better predict, prepare for, and respond to climate disruptions can aid in reducing social vulnerability.
9. Education and Awareness: Raising awareness and educating populations about social vulnerability to climate disruptions can empower communities to take proactive measures.
10. Adapting to Climate Change: Ensuring adaptation strategies are inclusive and equitable is vital to addressing social vulnerability to climate disruptions comprehensively.
Strategies for Mitigating Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
Effective strategies to mitigate social vulnerability to climate disruptions involve an intersectional approach incorporating social, economic, and environmental dimensions. Firstly, empowering local communities through capacity-building initiatives and participatory governance can enhance resilience by enabling communities to develop and implement their own adaptive measures. Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to education and resources equips individuals and communities to better understand and prepare for climate disruptions.
National and international policy frameworks must prioritize social equity, directing resources toward underserved populations. By incorporating climate adaptation planning into broader socio-economic development strategies, nations can foster systemic changes that address root causes of vulnerability. Strategic investments, especially in sustainable infrastructure, can significantly bolster the resilience of vulnerable communities, thereby diminishing social vulnerability to climate disruptions.
The Role of Technology in Addressing Social Vulnerability to Climate Disruptions
Technological advances play an integral role in combating social vulnerability to climate disruptions. Early warning systems, data analytics, and information dissemination platforms can drastically improve preparedness and response, offering timely support to at-risk populations. Technologies that facilitate real-time communication and resource allocation are essential for enhancing both immediate and long-term resilience strategies. Moreover, innovative solutions such as climate-resistant building materials and renewable energy sources contribute to sustainable adaptation and mitigation efforts, ultimately reducing the social and economic burdens posed by climate disruptions.
In conclusion, addressing social vulnerability to climate disruptions requires a concerted effort involving all sectors of society. Through coordinated action, increased awareness, and the strategic use of technology, communities can enhance their resilience and secure a sustainable future in the face of climate change.