In the ever-evolving landscape of human development, understanding the socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior is of paramount importance. These determinants—comprising factors such as income level, education, social status, and occupational environment—play a crucial role in shaping how individuals and communities respond to changing circumstances. Adaptive behavior, in this context, refers to the capacity of individuals to adjust their thoughts and actions in response to external demands and challenges. The interplay between one’s socio-economic environment and their adaptive capabilities is a subject of extensive study, as it sheds light on the broader dynamics of human resilience and growth.
Read Now : Contemporary Analysis In High-impact Journals
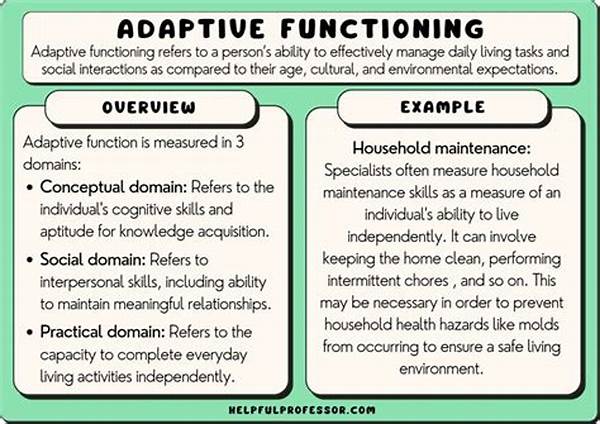
Factors Influencing Adaptive Behavior
Several critical factors constitute the socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior. Firstly, income level serves as a significant predictor, as financial resources often dictate access to education and healthcare, which consequently influence one’s adaptability. Secondly, educational attainment is recognized as a powerful driver of adaptive behavior, as it equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate complex situations. Thirdly, social status and community support play pivotal roles in establishing environments conducive to adaptive behavior. Finally, the occupational environment, including job security and workplace culture, also contributes significantly to how individuals adapt to changing circumstances. These factors collectively underscore the intricate relationship between socio-economic conditions and adaptive behavior.
Key Socio-Economic Determinants
1. Income Level: A critical socio-economic determinant of adaptive behavior, income influences access to essential resources that foster adaptability.
2. Education: Education imparts the skills crucial for adaptive behavior, representing a fundamental socio-economic determinant.
3. Social Status: As a socio-economic determinant of adaptive behavior, social status often dictates the level of community support individuals receive.
4. Occupational Environment: The nature of one’s employment significantly impacts adaptive behavior, making it an important socio-economic determinant.
5. Community Networks: Strong community networks reinforce adaptive behavior, highlighting their role among socio-economic determinants.
The Interconnection Between Socio-Economic Factors and Adaptation
Understanding the socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior requires a multifaceted approach. Various studies have shown that individuals with higher educational levels tend to exhibit more adaptive behaviors due to their access to critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Furthermore, income security can alleviate stress and promote a mindset conducive to adaptation, allowing individuals to focus on long-term goals rather than immediate survival. This correlation underpins efforts by policymakers to elevate the socio-economic standards in regions where adaptive behavior is markedly low.
Additionally, social networks and community ties enhance adaptive capacities by providing support systems that individuals can rely upon in times of crisis. The socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior are not only personal attributes but are also embedded within the larger social fabric. Through collaboration and collective action, communities can bolster individual adaptive behaviors, promoting resilience on a broader scale. Consequently, the recognition of these determinants is critical for designing interventions that can effectively improve adaptive behaviors across varied socio-economic contexts.
Read Now : Technologies Advancing Recycling Sustainability
Implications of Socio-Economic Factors on Behavior
The implications of socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior are profound, influencing policy-making and strategic development across various sectors. Socio-economic factors serve as the foundation for understanding human capacities to cope with adversity. Tenets such as social support networks, income stability, education accessibility, and occupational settings collectively construct the framework within which adaptive behavior thrives. Addressing these determinants involves comprehensive strategies that encompass both individual and collective approaches to enhance adaptability.
Sustainable development initiatives often emphasize improving educational access and reducing economic disparities as vital measures to enhance adaptive capacities. Socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior shape responses to environmental changes, urging leaders to prioritize policy shifts that address these variables. Furthermore, the establishment of robust social safety nets and community support systems can mitigate adverse impacts and cultivate an environment where adaptive behavior can flourish, thereby contributing to sustainable societal growth.
Enhancing Adaptability Through Socio-Economic Interventions
Understanding the socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior is crucial for crafting targeted interventions. These determinants, by their very nature, demand comprehensive policies that bridge gaps in education and economic disparity. Governments and organizations can enhance adaptive behavior by implementing educational programs aimed at skill development and offering financial aid to improve income levels. This creates an environment where individuals are not restrained by socio-economic barriers in their pursuit of growth and adaptability.
The role of occupational environments cannot be understated. By promoting job security and fostering positive workplace cultures, organizations can support the development of adaptive behaviors. Community engagement also serves as a powerful tool, reinforcing the socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior by harnessing collective strengths. In summary, a multi-pronged approach, addressing each determinant through collaborative means, promises to unlock greater adaptive potential within societies, fostering resilience and sustainable development.
Conclusion and Policy Directions
The socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior underscore the complex interplay between the environment and individual adaptability. By understanding these determinants, policymakers can tailor interventions to foster resilience in communities. Emphasizing education, economic stability, and social support systems is paramount in nurturing environments that support adaptive behavior. Continuous evaluation of socio-economic strategies will ensure effectiveness in enhancing the adaptability of populations. Consideration of these determinants will pave the way for informed policy decisions, ultimately promoting holistic growth and development.
Summary of Key Findings
The socio-economic determinants of adaptive behavior are instrumental in shaping individual and community resilience. An analysis of these determinants reveals the critical role of education, income level, social networks, and occupational environment in influencing adaptability. By addressing these socio-economic factors, stakeholders can foster enhanced adaptive behaviors, leading to strengthened resilience. Such insights guide strategic policy formulation aimed at promoting initiatives that mitigate socio-economic disparities. A sustained focus on these determinants will not only bolster individual capabilities but also contribute to the overarching goal of sustainable development.