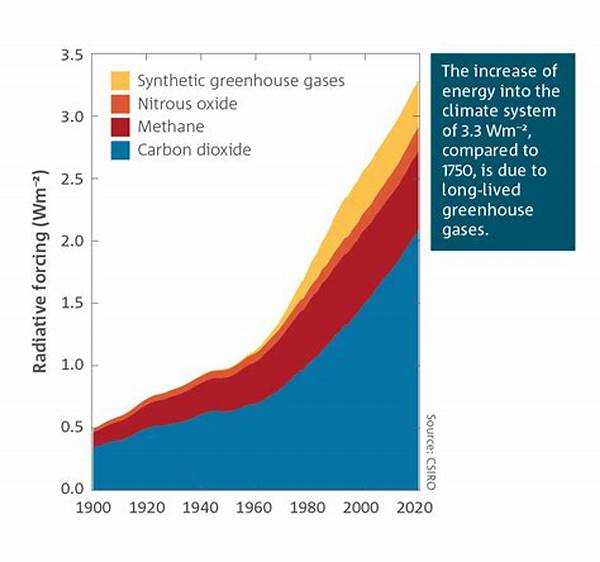
The topic of greenhouse gas emissions has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its pivotal role in influencing climate change. Various sectors, from industrial to agricultural, contribute to the emission of greenhouse gases, necessitating an in-depth analysis of the prevailing trends. Understanding the patterns and fluctuations in these emissions is crucial for formulating effective policy measures and strategies aimed at mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
Read Now : Emerging Topics In Scientific Research
Current Global Trends in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The current global trends in greenhouse gas emissions are characterized by a complex interplay of multiple factors including economic growth, technological advancements, and policy interventions. Over the past few decades, emissions have seen a general increase, primarily driven by rising industrial activity and energy consumption. However, recent years have witnessed a shift, with some regions experiencing stabilization or even decline in emissions.
In developing regions, rapid industrialization has led to increased emissions, substantially impacting the global trends in greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, some developed countries have made strides in reducing their footprints through technological innovation and stringent regulatory frameworks. The transition to renewable energy sources and enhanced energy efficiency are pivotal in shaping these trends. Despite these advancements, the overarching trajectory remains concerning, necessitating further global cooperation and commitment to achieve meaningful reductions in emissions.
Policies and international agreements such as the Paris Agreement play an essential role in influencing trends in greenhouse gas emissions. With countries pledging to meet specific targets, it is imperative to continually monitor and evaluate the efficacy of these commitments. Overall, while progress has been made, greater efforts are required to reverse the adverse trends and foster a sustainable future.
Factors Influencing Trends in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
1. Industrialization and Economic Growth: Increased industrial activity, especially in emerging economies, contributes significantly to the upward trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Energy Consumption Patterns: Reliance on fossil fuels boosts emissions, whereas shifts to renewable sources have the potential to alter these trends.
3. Technological Innovations: Advancements in clean technology play a crucial role in reducing emissions and changing trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Policy Frameworks and Regulations: Stringent environmental policies are instrumental in shaping trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
5. International Agreements: Pacts like the Paris Agreement are central to collaborative efforts in addressing and modifying these trends globally.
The Role of Policy in Shaping Emission Trends
The influence of policy on trends in greenhouse gas emissions is profound and multifaceted. Government policies, both on national and international levels, serve as critical instruments in regulating and curbing emissions. Over the years, countries have implemented a variety of policies aimed at addressing the escalating challenges posed by climate change, including carbon pricing, emissions trading systems, and emissions reduction targets.
In addition to domestic policies, international agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement have played a significant role in impacting trends in greenhouse gas emissions. These agreements facilitate a coordinated global approach, providing a framework for countries to collaboratively address emissions through legally binding commitments and voluntary pledges. Despite the challenges in enforcement and compliance, the existence of these agreements highlights the importance of unified global efforts in addressing environmental concerns.
Ultimately, the trends in greenhouse gas emissions are largely contingent upon the effectiveness and implementation of these policies. As policies evolve and adapt to the changing environmental landscape, they hold the potential to alter emission patterns, underscoring the need for continuous assessment and adjustment to achieve sustainable outcomes.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on Emission Trends
1. Renewable Energy Technologies: The adoption of solar, wind, and other renewable energies is pivotal in reversing trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Energy Storage Innovations: Enhanced battery and storage solutions facilitate the reliable use of renewable energy sources, impacting emission trends positively.
3. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS technologies aim to remove and sequester carbon dioxide, substantially influencing emission trends.
4. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: The transportation sector benefits from innovations in electric vehicles, reducing its emissions footprint.
5. Energy Efficiency Improvements: Technological advances in energy efficiency reduce energy consumption, thereby affecting trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
Read Now : “low-carbon Economic Development Plans”
6. Smart Grids and IoT: Modern smart grids and IoT technology optimize electricity usage, aiding in emission reductions.
7. Biotechnology in Agriculture: Innovations in agricultural practices can mitigate methane and other emissions, impacting trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
8. Cleaner Industrial Processes: Advancements in reducing emissions from industrial activities are vital in shaping emission trends.
9. Waste Management Technologies: Innovations in waste management can limit methane emissions and contribute to altering trends.
10. Green Building Technologies: Sustainable building practices reduce energy consumption and emissions, crucially affecting trends.
Challenges in Addressing Trends in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Addressing the prevailing trends in greenhouse gas emissions presents a multitude of challenges that require concerted efforts and innovative solutions. One primary challenge lies in balancing economic development with environmental sustainability. Developing countries, in particular, face the dilemma of fostering economic growth while mitigating environmental impacts. Bridging this gap necessitates substantial investments in clean technologies and providing adequate support for transitioning towards sustainable energy sources.
Moreover, the geopolitical landscape plays a significant role in influencing trends in greenhouse gas emissions. International cooperation is often hindered by differing national interests and priorities, complicating efforts to achieve consensus on global emissions targets. Ensuring effective monitoring, reporting, and verification mechanisms remains a persistent challenge in enforcing compliance with international agreements. Additionally, funding and investment in climate-related initiatives are often insufficient, impeding the progress needed to reverse detrimental trends.
Consumer behavior and public awareness also play a critical role in addressing these trends. While there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability, achieving widespread behavioral changes remains challenging. Encouraging shifts towards sustainable consumption patterns and raising awareness about the impact of emissions are essential components of a comprehensive strategy to combat climate change. Ultimately, overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative and multipronged approach, engaging governments, industries, and individuals alike.
Future Outlook on Trends in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The future trends in greenhouse gas emissions will undoubtedly be shaped by a combination of technological, political, and economic factors. Technological advancements promise significant possibilities in addressing emissions, particularly through the development of new energy sources and carbon capture technologies. The pace of innovation will be crucial in determining the extent to which emissions trends can be altered positively.
Politically, continued international collaboration will be essential in formulating and implementing effective climate policies. The commitment and resolve of the global community to adhere to established agreements and set ambitious yet achievable targets will play a decisive role in shaping future trends in greenhouse gas emissions.
Economically, the transition to a low-carbon future will require significant investments in sustainable infrastructure and clean technology. Incentivizing private sector participation and ensuring equitable access to technological advances will be essential in driving meaningful change. The integration of circular economy principles and the promotion of sustainable business practices will further contribute to achieving long-term emissions reductions.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding trends in greenhouse gas emissions is pivotal to addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change. The interplay of economic, technological, and policy-related factors has shaped current emission patterns, requiring coordinated efforts at various levels to induce impactful change. Key international agreements and national policies continue to play vital roles in influencing these trends, showing a path toward potential reductions when effectively implemented.
Technological innovations offer promising avenues for altering trends in greenhouse gas emissions, yet their success is contingent upon widespread adoption and investment. Furthermore, addressing existing barriers and fostering global cooperation remain essential for advancing international climate goals. As we look toward the future, understanding and addressing these trends is crucial in ensuring a sustainable and resilient global environment for generations to come.